Abstract
The present investigation deals with the stress distribution in the vicinity of rectangular inserts in finite rectangular plates. This problem is more complex due to the singularities at the corners of the inserts. In this paper, the finite-element technique is used to determine the deformations and, subsequently, the stresses. The paper treats the problem in a generalized form in the sense that the size and orientation of the insert are taken as variables. The finite rectangular plate is subjected to a uniform axial tensile load. The material of the plate and that of the insert are considered to be different.
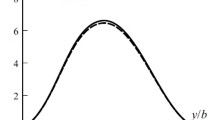
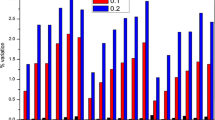
Element selections are made which are optimal with regard to accuracy and computational effort. The local element stresses which generate considerable discontinuity at the element nodes are plotted. Averaging process for the local stress calculations is discussed and these are compared with the results available1 which are obtained by experimental techniques.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a i ,b i :
-
arbitrary coefficients
- E :
-
modulus of elasticity
- {f}:
-
displacement vector
- [N]:
-
shape functions
- u, v :
-
displacements in the x and y direction
- x, y :
-
nondimensionalized coordinates
- {ε}:
-
strain matrix
- {σ}:
-
stress matrix
- ν:
-
Poisson’s ratio
References
Mirza, S. andAnsari, K., “On Stress Concentration in Rectangular Plates,”Experimental Mechanics,14 (10),412–416 (Oct. 1974).
Chang, C. S. and Conway, H. D., “A Parametric Study of the Complex Variable Method for Analyzing the Stresses in an Infinite Plate Containing Rigid Rectangular Inclusion,” Intnl. J. Solid Struct., 1057–1066 (April 4, 1968).
Laura, P. A. A., Reyes, J. A. and Rossi, R. E., “Stress Concentration Factors: A Comparison of Experimental and Numerical Results,” Strains, 58–64 (April, 1974).
Durelli, A. J., “Strains and Stresses in Matrices with Inserts,” Proc. of the Fifth Symp. on Naval Struct. (1970).
Yamamoto, Y. andTokauda, N., “Determination of Stress Intensity Factors in Cracked Plates by the Finite Element Method,”Intnl. J. of Num. Method Engrg.,6,427–430 (1973).
Byskov, E., “The Calculation of Stress Intensity Factors Using the Finite Element Method with Cracked Elements,”Intnl. J. Fract. Mech.,6,159–167 (1970).
Rao, A. K., Krishnamurthy, A. V., Raju, I. S., “Special Finite Elements for the Analysis of Stress Concentrations and Singularities,” M,Proc. of 1st Int. Conf. on Struct. Mech. in Reactor Tech., Berlin (1971).
Zienkiewicz, O. C., “The Finite Element Method in Engineering Science,” Sec. Edition, McGraw-Hill (London).
Williams, M. L., “Stress Singularities Resulting from Various Boundary Conditions in Angular Corners of Plates in Extension,” J. of Ap. Mech. (ASME), 526–528 (Dec. 1952).
Oden, J. T., “A General Theory of Finite Elements: I, II, Topological Considerations and Applications,” Intnl. J. Num. Method Engrg., 1 (1969).
Szabo, B. A. and Lee, G. C., “Derivation of Stiffness Matrices for Problems in Plane Elasticity by Gaberkin Method,” Intnl. J. Num. Method Engrg., 1 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirza, S. Finite-element analysis of rectangular plates with rectangular inserts. Experimental Mechanics 16, 392–396 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02320697
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02320697