Abstract
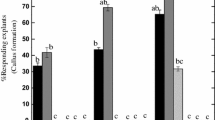
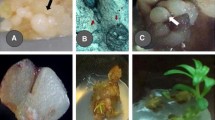
A number of media constituents including sucrose, ammonium nitrate and plant growth regulators were evaluated in an attempt to improve somatic embryo production in zonal geranium (Pelargonium ×hortorum) cv. Scarlet Orbit Improved. Somatic embryo production was characterized by the quantity and type of somatic embryo induced by the treatments. Sucrose at 4% supported the highest number of total somatic embryos while improving the proportion of the morphologically normal cotyledon-stage somatic embryos. Addition of ammonium nitrate also improved embryo production. With 1.89 mM ammonium nitrate, normal cotyledon-stage embryo development was increased by 53%; the proportion of normal cotyledon-stage embryos decreased and abnormal embryos with leaves or serrated margins in cotyledons (fringed-shoot type) increased with higher ammonium nitrate concentrations. The effect of plant growth regulators on somatic embryogenesis indicated that exogenous supply of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) at a range of 0.25 to 4 µM failed to promote somatic embryogenesis. In contrast, benzyladenine (BA) up to 2.0 µM increased the total embryo number and the proportion of desirable cotyledon-stage embryos. There was no interaction between IAA and BA. Our research has demonstrated that improvement in both quantity and quality of somatic embryos can be achieved in zonal geranium.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
benzyladenine
- IAA:
-
indole-3-acetic acid
References
Armstrong C L & Green C E (1985) Establishment of and maintenance of friable embryogenic maize callus and the involvement of L-proline. Planta 164: 207–214
Attree S M, Moore D, Sawhney V K & Fowke L C (1991) Enhanced maturation and desiccation tolerance of white spruce [Pecea glauca (Moench) Voss] somatic embryos. Effect of a non-plasmolysing water stress and abscisic acid. Ann. Bot. 68: 519–525
George E F & Sherrington (1984) Plant propagation by tissue culture. Eastern Press, Reading, Berks. UK
Gill R, Gerrath J M, Saxena P K (1993) High-frequency direct somatic embryogenesis in thin layer cultures or hybrid seed geranium (Pelargonium × hortorum). Can. J. Bot. 71: 408–413
Lai F M, Senaratna T & McKersie B D (1992) Glutamine enhances storage protein synthesis inMedicago sativa L. somatic embryos. Plant Sci. 87: 69–77
Maheshwaran G & Williams E G (1986) Direct secondary somatic embryogenesis from immature embryos ofTrifolium repens culturedin vitro. Amer. J. Bot. 57: 109–117
Marsolais A A, Wilson D P M, Tsujita M J & Senaratna T (1991) Somatic embryogenesis and artificial seed production in zonal and regal geranium. Can. J. Bot. 69: 1188–1193
Mamet H & Jonard J (1983) Differences des responses varietales vis-a-vis des besoins nutritifs en phytohormones et en azote, d'apex isolesin vitro a partir de trois varietes dePelargonium. Physiol. Vegetale 296: 381–388
May R A & Trigiano R N (1991) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from leaves ofDendranthema grandiflora. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 116: 366–371
Meijer E G M & Brown D C W (1987) Role of exogenous reduced nitrogen and sucrose in rapid high frequency somatic embryogenesis inMedicago sativa L. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 10: 11–19
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Pence V C, Hasegawa P M & Janick J (1981) Sucrose-mediated regulation of fatty acid composition in asexual embryos ofTheobroma cacao. Physiol. Plant 53: 378–384
Ronchi V N, Caligo M, Nozzolini M & Luccarini G (1984) Stimulation of carrot embryogenesis by proline and serine. Plant Cell Rep. 3:210–214
Schneider E F & Wightman F (1975) Auxins. In: Letham P S et al., (eds) Phytohormones and Related Compounds — a Comprehensive Treatise (pp 64–65). Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Senaratna T (1992) Artificial seeds. Biotech. Adv. 10: 377–392
Sharp W R, Sondahl M R, Caldas L S & Maraffa S B (1980) The physiology ofin vitro asexual embryogenesis. Hortic. Rev. 2: 268–310
Skokut T A, Manchester J & Scheafer J (1985) Regeneration in alfalfa tissue culture. Stimulation of somatic embryo production by amino acids and N 15 NMR determination of nitrogen utilization. Plant Physiol. 79: 579–583
Stuart D A, Nelsen J & Strickland S G (1985) Factors affecting developmental processes in alfalfa cell cultures. In: Henke R R et al. (eds) Tissue Culture in Forestry and Agriculture: 59–73. Plenum Press, New York, USA
Stuart D A & Strickland S G (1984a) Somatic embryogenesis from cell cultures ofMedicago sativa L. I. The role of amino acid addition to the regeneration medium. Plant Sci. Lett. 34: 165–174
Stuart D A & Strickland S G (1984b) Somatic embryogenesis from cell cultures ofMedicago sativa L. II. The interaction of amino acids with ammonium. Plant Sci. Lett. 34: 175–181
Trigiano R N, May R A & Conger B V (1992) Reduced nitrogen influences somatic embryo quality and plant regeneration from suspension cultures of orchardgrass.In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. 28P:187–191
Visser C, Qureshi J A, Gill R & Saxena P K (1992) Morphoregulatory role of thidiazuron: substitution of auxin and cytokinin requirement for the induction of somatic embryogenesis in geranium hypocotyl cultures. Plant Physiol. 99: 1704–1707
Wetherell D F & Dougall D K (1976) Sources of nitrogen supporting growth and embryogenesis in cultured wild carrot tissue. Physiol. Plant. 37: 97–103
Williams G E & Maheshwaran G (1986) Somatic embryogenesis: factors influencing coordinated behaviour of cells as an embryogenic group. Ann. Bot. 57: 443–462
Wilson D P M (1990) Somatic embryogenesis inPelargonium × domesticum Bailey andP. × hortorum Bailey. M.Sc. ThesisUniversity of Guelph (129p)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilson, D.P.M., Sullivan, J.A., Marsolais, A.A. et al. Improvement of somatic embryogenesis in zonal geranium. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 47, 27–32 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02318962
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02318962