Abstract
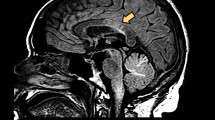
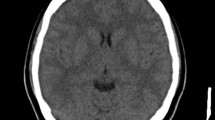
Altered cardiovascular and respiratory function is uncommonly encountered in multiple sclerosis, though it may appear late in the course of the disease [4]. Episodes of acute ventilatory failure due to autonomic and/or voluntary respiratory function paralysis have already been described. These episodes are often accompanied by a focal neurological deficit which expresses lesion at the level of the medulla [6]. A demyelinating bulbar lesion leading to altered cardiovascular function is likewise infrequent but when it happens, bradycardia, postural hypotension [2], or acute pulmonary edema without heart failure may occur [1].
We present a case of non cardiogenic acute pulmonary edema which had neither a toxic insult nor an infective agent as etiology, but appeared as the initial manifestation of a multifocal demyelinating syndrome.
Sommario
I disturbi cardio-vascolari e respiratori sono piuttosto rari nella sclerosi multipla, anche se possono comparire nella fase terminale della malattia. Sono stati descritti episodi di deficit acuto nella ventilazione polmonare; questi episodi sono spesso accompagnati da deficit neurologici focali, che sono espressione di localizzazioni della malattia a livello del bulbo. Lesioni bulbari demielinizzanti in grado di alterare la funzione cardiovascolare sono rare, ma quando si verificano esse possono indurre bradicardia, ipotensione ortostatica o edema polmonare acuto senza deficit della funzione cardiaca. Noi presentiamo un caso di edema polmonare acuto non cardiogeno, non tossico e non infettivo, ma che appare come la manifestazione iniziale di una sindrome demielinizzante multifocale.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Giroud M., Guard O., Dumas R.:Anomalies cardio-respiratoires dans la sclérose en plaques. Rev. Neurol. (Paris) 144, 4, 284–88, 1988.
Noronha M.J., Vas C.J., Aziz H.:Autonomic dysfunction in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry, 31:19–22, 1968.
Ochiai Y., Yokojama M., Kosokabe Y., Abe S., Taniguchi M., Tada K.:Intensive care of multiple sclerosis with bulbar palsy. J. Intensive Care Med. (Tokyo) 5:579–86, 1981.
Stefoski D., Davis F.A.:Central disturbances of respiration in multiple sclerosis. In: W.J. Weiner (Ed.), Respiratory dysfunction in neurologic disease. Futura Mount Kisco NY pag. 187–196, 1980.
Theodore J., Robin E.D.:Speculations on neurogenic pulmonary edema. Ann. Rev. Respir. Dis., 113:405–11, 1976.
Torn Yamamoto, Terukuni Imai, Masahiro Yamasaki:Acute ventilatory failure in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. Sci., 89:313–24, 1989.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gentiloni, N., Schiavino, D., Della, C.F. et al. Neurogenic pulmonary edema: a presenting symptom in multiple sclerosis. Ital J Neuro Sci 13, 435–438 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02312151
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02312151