Summary
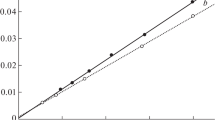
This paper describes the resolution of multimodal GPC chromatograms into their individual components through the use of two optimization techniques, applied sequentially. The principle of the method can be applied to any form of curve but only the mathematics for Gaussian curves is given. The method has been successfully tested against both model and real chromatograms. The model chromatograms consisted of overlapping, perfectly Gaussian, curves whilst the real chromatograms were obtained from oligomeric polyesters submitted for routine GPC analysis and contained from three to five components. These chromatograms, which would have been too complex to resolve by “pencil and ruler” techniques, were resolved by this method to a precision within experimental error.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. W. Yau andS. W. Fleming, J.A.P.S.12, 2111–6 (1968).
L. H. Tung, Sep. Sci.5 (3), 339–47 (1970).
J. M. Evans, Poly. Eng. Sci.13, 401–8 (1973).
A. C. Ouano, J. Macromol. Sci. C9 (1), 123–48 (1973).
M. Shrager andA. L. Ward, J.A.P.S.14, 1235–42 (1970).
D. J. Wilde, “Optimum Seeking Methods”, Prentice Hall, 1964.
F. Horsfall, private communication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hawley, S.W. Multiple peak analysis in gel permeation chromatography. Chromatographia 11, 499–507 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02311071
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02311071