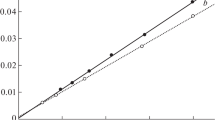
Summary
New electric interaction indices are proposed which can universally be used in GLC, HPLC and TLC. These indices can easily be calculated from a variety of the commonly used retention parameters, such as Kováts' retention indices, relative retention times, capacity factors, or RF values, and the average molecular polarizabilities of the reference compounds. Calculation examples for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and n-alkanes are given. Application of the electric interaction indices for studying the retention mechanism is demonstrated.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- a, b:
-
regression constants (a=slope, b=intercept)
- A, B, C, D:
-
constants depending on the system used
- Eint :
-
interaction energy between two molecules
- l1 :
-
electric interaction index
- IP:
-
first ionization potential
- k:
-
Boltzmann constant (in eq. (1)); also the capacity factor of a solute
- r:
-
distance of interaction
- r12 :
-
relative retention
- R:
-
correlation coefficient
- RF :
-
retardation factor (in TLC)
- Rl:
-
Kováts retention index
- T:
-
(absolute) temperature
- X:
-
retention parameter
- α:
-
average molecular polarizability
- λ:
-
other parameters characterizing the specific interactions of the solute
- η:
-
shape parameter
- μ:
-
dipole moment
- a, b:
-
two molecules
- ph:
-
phase
- s:
-
standard compound
- x:
-
solute
References
E. sz. Kováts, Helv. Chim. Acta41 1915 (1958).
M. Popl, V. Dolansky, J. Mostecky, J. Chromatogr.117, 117 (1976).
D. L. Vassilaros, R. C. Kong, D. W. Later, M. L. Lee, J. Chromatogr.252, 1 (1982).
U. Heldt, H. J. K. Köser, J. Chromatogr.192, 107 (1980).
L. Mathiasson, J. A. Jönsson, A. M. Olsson, L. Haraldson, J. Chromatogr.152, 11 (1978).
H. Lamparczyk, A. Radecki, Chromatographia18, 615 (1984).
A. Radecki, H. Lamparczyk, R. Kaliszan, Chromatographia12, 595 (1979).
S. A. Wise, W. J. Bonnett, F. R. Guenther, W. E. May, J. Chromatogr. Sci.19, 457 (1981).
L. Rohrschneider, J. Chromatogr.22, 6 (1966).
P. J. Schoenmakers, H. A. H. Billiet, L. de Galan, Chromatographia15, 205 (1982).
G. Grimmer, H. Böhnke, J. Ass. Offic. Anal. Chem.58, 725 (1975).
W. Schmidt, J. Chem. Phys.66, 828 (1977).
K. J. Miller, J. A. Savchik, J. Amer. Chem. Soc.101, 7206 (1979).
H. Colin, G. Guiochon, P. Jandera, Anal. Chem.55, 442 (1983).
K. Jinno, K. Kawasaki, Chromatographia17, 445 (1983).
E. Clar, W. Schmidt, Tetrahedron35, 1027 (1979).
R. H. White, J. W. Howard, J. Chromatogr.29, 108 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lamparczyk, H. The role of electric interaction in the retention index cencept. Universal interaction indices for GLC, HPLC and TLC. Chromatographia 20, 283–288 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02310384
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02310384