Summary
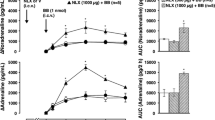
Studies performed in conscious female rats confirmed that iv injection of cholecystokinin octapeptide (CCK; 20µ/kg) increased the circulating concentration of oxytocin but not that of vasopressin, and confirmed that the stimulation of oxytocin release was markedly facilitated after iv administration of naloxone (1mg/kg), indicating attenuation of oxytocin release by endogenous opioids. To investigate the site of action of the endogenous opioids, the electrical activity of putative oxytocin neurones in the supraoptic nucleus was recorded in urethaneanaesthetised female rats. Oxytocin neurones responded to CCK injection with an increase in firing rate lasting 5–15 min, but this response was not facilitated by prior injection of naloxone. The results suggest that the opioid influence upon CCK-induced oxytocin release operates at the level of the neurosecretory terminals in the neurohypophysis rather than centrally. Since CCK does not elevate vasopressin release, it appears unlikely that dynorphin, the opioid peptide co-existing with vasopressin, is responsible in these circumstances for the cross-inhibition of oxytocin release. It is suggested that products of proenkephalin A, the met-enkephalin precursor present in the supraoptic nucleus and in the neurohypophysis itself, may be active in the regulation of oxytocin release.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bicknell RJ, Leng G (1982) Endogenous opiates regulate oxytocin but not vasopressin secretion from the neurohypophysis. Nature 298:161–162
Bicknell RJ, Brown D, Chapman C, Hancock PD, Leng G (1984) Reversible fatigue of stimulus-secretion coupling in the rat neurophypophysis. J Physiol (Lond) 348:601–613
Blackburn RE, Leng G (1990) Abalation of the region anterior and ventral to the third ventricle (AV3V region) in the rat does not abolish the release of oxytocin in response to systemic cholecystokinin. Brain Res 508:156–160
Bondy AB, Gainer H, Russell JT (1988) Dynorphin A inhibits and naloxone increases the electrically stimulated release of oxytocin but not vasopressin from the terminal of the neural lobe. Endocrinology 122:1321–1327
Bondy CA, Jensen RT, Brady LS, Gainer H (1989) Cholecystokinin evokes secretion of oxytocin and vasopressin from rat neural lobe independent of external calcium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 886:5198–5201
Castanas E, Bourhim N, Giraud P, Boudouresque F, Cantau P, Oliver C (1985) Interaction of opiates with opioid binding sites in the bovine adrenal medulla. II Interaction with k sites. J Neurochem 45:688–699
Clarke G, Wood P, Merrick L, Lincoln DW (1979) Opiate inhibition of peptide release from the neurohumoral terminals of hypothalamic neurones. Nature 282:746–748
Clarke G, Wright DM (1984) A comparison of analgesia and suppression of oxytocin release by opiates. Br J Pharmacol 83:799–806
Coombes J, Russell JA (1988) Inhibition by a Kappa-opioid receptor agonist (U50 488H) of electrically-stimulated oxytocin secretion from the neurohypophysis and anaesthetised lactating rats. J Physiol (Lond) 410:34P
Cutting R, Fitzsimons N, Gosden RS, Humphrey EM, Russell JA, Scott S, Stirland JA (1986) Evidence that morphine interrupts parturition in rats by inhibiting oxytocin secretion. J Physiol (Lond) 371:182P
Dyball REJ, Koizmui K (1969) Electrical activity in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei associated with neurohypophysial hormone release. J Physiol (Lond) 201:711–722
Dyer RG, Weick RC, Mansfield S, Corbett H (1981) Secretion of luteinising hormone in ovariectomised adult rats treated neonatally with monosodium glutamate. J Endocrinol 91:341–346
Flanagan LM, Verbalis JG, Stricker EM (1988) Naloxone potentiation of effects of cholecystokinin and lithium chloride on oxytocin secretion, gastric motility and feeding. Neuroendocrinology 48:668–673
Gerstberger R, Baden N (1986) Dynorphin 1–8 binds to opiate kappa receptors in the neurohypophysis. Neuroendocrinology 42:376–382
Hatton GI (1990) Emerging concepts of structure-function dynamics in adult brain: the hypothalamo-neurohypophysial system. Prog Neurobiol 34:437–504
Herkenham M, Rice KC, Jacobson AE, Rothman RB (1986) Opiate receptors in rat pituitary are confined to the neural lobe and are exclusively kappa. Brain Res 382:365–371
Higuchi T, Honda K, Fukuoka T, Negoro H, Wakabayashi K (1985) Release of oxytocin during suckling and parturition in the rat. J Endocrinol 105:339–346
Leng G (1980) Rat supraoptic neurones: the effects of locally applied hypertonic saline. J Physiol (Lond) 304:405–414
Leng G, Russell JA (1989) Opioids, oxytocin and parturition. In: Dyer RG and Bicknell RJ (ed) Brain Opioid Systems in Reproduction. Oxford University Press, pp 231–256
Leng G, Mansfield S, Bicknell RJ, Blackburn RE, Brown D, Chapman C, Dyer RG, Hollingsworth S, Shibuki K, Yates JO, Way S (1988) Endogenous opioid actions and effects of environmental disturbance on parturition and oxytocin secretion in rats. J Reprod Fertil 84:345–356
Leng G, Pumford K, Russell JA (1990) Actions of the K-type opioid receptor agonist U50 488H on oxytocin neurones in the supraoptic nucleus (SON) in normal and morphine-tolerant urethane anaesthetised rates. J Physiol (Lond) 420:71P
Leng G, Way SA, Dyball REJ (1991) Identification of oxytocin cells in the rat supraoptic nucleus by their response to CCK injection. Neurosci Lett 122:159–162
Lightman SL, Young W Scott III (1987) Vasopressin, oxytocin, dynorphin, enkephalin and corticotrophin-releasing factor mRNA stimulation in the rat. J Physiol (Lond) 394:23–29
Lorenz RG, Evans CJ, Barchas JD (1985) Effect of dehydration on prodynophin derived peptides in the neurointermediate lobe of the rat pituitary. Life Sci 37:1523–1528
Martin R, Voigt KH (1981) Enkephalins co-exist with oxytocin and vasopressin in nerve terminals of rat neurohypophysis. Nature 289:502–504
Martin R, Geis R, Holl R, Schafer M, Voigt KH (1983) Co-existence of unrelated peptides in oxytocin and vasopressin terminals of rat neurohypophysis: immunoreactive methionine-enkephalin-, leucine-enkephalin- and cholecystokinin-like substances. Neuroscience 8:213–227
Moore G, Lutterodt A, Burford G, Lederis K (1977) A highly specific antiserum for arginine vasopressin. Endocrinology 101:1421–1435
Schafer MK-H, Day R, Ortega MR, Akil H, Watson SJ (1990) Proenkephalin messenger RNA is expressed both in the rat anterior and posterior pituitary. Neuroendocrinology 51:444–448
Shibuki K, Leng G, Way SA (1988) Effects of naloxone and of intraperitoneal hypertonic saline upon oxytocin release and upon supraoptic neuronal activity. Neurosci Lett 88:75–80
Summy-Long JY (1989) Cross-inhibition of oxytocin neurones during activation of the vasopressin system. In: Dyer RG, Bicknell RJ (eds) Brain opioid systems in reproduction. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 271–287
Summy-Long JL, Miller DS, Rosella-Dampan LM, Hartman RD, Emmert SE (1984) A functional role for opioid peptides in the differential secretion of vasopressin and oxytocin. Brain Res 309:362–366
Watson SJ, Akil A, Fischli W, Goldstein A, Zimmermann E, Nilaver G, Wimersma Greidanus TB van (1982) Dynorphin and vasopressin; common localization in magnocellular neurones. Science 216:85–87
Whitnall MH, Gainer H, Cox BM, Molineaux CJ (1983) Dynorphin-A-(1–8) is contained within vasopressin neurosecretory vesicles in rat pituitary. Science 222:1137–1138
Zhao B-G, Chapman C, Bicknell RJ (1988a) Opioid-noradrenergic interactions in the neurohypophysis. Neuroendocrinology 48:16–24
Zhao B-G, Chapman C, Bicknell RJ (1988b) Functional K-opioid receptors on oxytocin and vasopressin nerve terminals isolated from the rat neurohypophysis. Brain Res 462:62–66
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leng, G., Dyball, R.E.J. & Way, S.A. Naloxone potentiates the release of oxytocin induced by systemic administration of cholecystokinin without enhancing the electrical activity of supraoptic oxytocin neurones. Exp Brain Res 88, 321–325 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02259107
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02259107