Summary
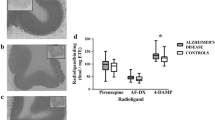
ATP-sensitive K+ channels were examined in sections of the hippocampus from patients with Alzheimer's disease and age-matched control subjects by means of quantitative autoradiography. ATP-sensitive K+ channels were labelled with the sulfonylurea, [3H]-glibenclamide, which is a potent blocker of these channels. The density of cells in the subiculum and the activity of choline acetyltransferase were determined in the same hippocampal tissue samples. In the hippocampal formation of control subjects, the density of high affinity [3H]-glibenclamide binding sites ranged from 17.6±0.9 pmoles/g in the presubiculum to 11.6±0.6 pmoles/g in the parvopyramidal layer of the presubiculum. There was no difference between Alzheimer patients and controls in the level of high affinity [3H]-glibenclamide binding in any hippocampal region although there was a marked loss of subicular cells (reduced by 29% compared to controls) and a reduction in choline acetyltransferase activity (reduced by 60% compared to controls). The results suggest that ATP-sensitive K+ channels are associated with elements in the hippocampus which are preserved in Alzheimer's disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abele AE, Miller J (1990) Potassium channel activators abolish excitotoxicity in cultured hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Neurosci Lett 115: 195–200
Amaral DG, Insausti R (1990) Hippocampal formation. In: Paxinos G (ed) The human nervous system. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 711–755
Amoroso S, Schmid-Antomarchi H, Fosset M, Lazdunski M (1990) Glucose, sulfonylureas, and neurotransmitter release: role of ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Science 247: 852–854
Ashford MLJ, Sturgess NC, Trout NJ, Gardner NJ, Hales CN (1988) Adenosine-5′-triphosphate-sensitive ion channels in neonatal rat cultured central neurones. Pflügers Arch 412:297–304
Ben-Ari Y (1990) Galanin and glibenclamide modulate the anoxic release of glutamate in rat CA3 hippocampal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 2: 62–68
Ben-Ari Y, Krnjevic K, Crépel V (1990) Activators of ATP-sensitive K+ channels reduce anoxic depolarization in CA3 hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience 37: 55–60
Bernardi H, Fosset M, Lazdunski M (1988) Characterization, purification, and affinity labeling of the brain [3H]glibenclamide-binding protein, a putative neuronal ATP-regulated K+ channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 9816–9820
Fonnum F (1975) A rapid radiochemical method for the determination of choline actyltransferase. J Neurochem 24: 407–409
Gehlert DR, Gackenheimer DL, Mais DE, Robertson DW (1991) Quantiative autoradiography of the binding sites for [125I]iodoglyburide, a novel high-affinity ligand for ATP-sensitive potassium channels in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Neurol 257: 901–907
Greenamyre JT, Young AB (1989) Excitatory amino acids and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging 10: 593–602
Hyman BT, van Hoesen GW, Damasio AR, Barnes CL (1984) Alzheimer's disease: cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science 225: 1168–1170
Ikeda M, Dewar D, McCulloch J (1991a) Selective reduction of [125I]-apamin binding sites in Alzheimer hippocampus: a quantitative autoradiographic study. Brain Res: 51–56
Ikeda M, Dewar D, McCulloch J (1991b) Preservation of [125I]-galanin binding sites despite loss of cholinergic neurones to the hippocampus in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 568: 303–306
Ikeda M, Dewar D, McCulloch J (1992) A correlative study of calcium channel antagonist binding and local neuropathological features in the hippocampus in Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res 589: 313–319
Khachaturian ZS (1985) Diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 42: 1097–1104
Krnjevic K (1990) Adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels in anoxia. Stroke 21 [Suppl III]: III-190–III-193
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193: 265–275
Mann DMA, Yates PO, Marcyniuk P (1985) Some morphometric observations on the cerebral cortex and hippocampus in presenile Alzheimer's disease, senile dementia of Alzheimer type and Down's syndrome in middle age. J Neurol Sci 69: 139–159
Miller RJ (1990) Glucose-regulated potassium channels are sweet news for neurobiologists. Trends Neurosci 13: 197–199
Mourre C, Ben-Ari Y, Bernardi H, Fosset M, Lazdunski M (1989) Antidiabetic sulfonylureas: localization of binding sites in the brain and effects on the hyperpolarization induced by anoxia in hippocampal slices. Brain Res 486: 159–164
Mourre C, Widmann C, Lazdunski M (1990) Sulfonylurea binding sites associated with ATP-regulated K+ channels in the central nervous system: autoradiographic analysis of their distribution and ontogenesis, and of their localization in mutant mice cerebellum. Brain Res 519: 29–43
Mourre C, Widmann C, Lazdunski M (1991) Specific hippocampal lesions indicate the presence of sulfonylurea binding sites associated to ATP-sensitive K+ channels both post-synaptically and on mossy fibres. Brain Res 540: 340–344
Quast U, Cook NS (1989) Moving together: K+ channel openers and ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Trends Pharmacol Sci 10: 431–435
Schmid-Antomarchi H, Amoroso S, Fosset M, Lazdunski M (1990) K+ channel openers activate brain sulfonylurea-sensitive K+ channels and block neurosecretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 3489–3492
Treherne JM, Ashford MLJ (1991) The regional distribution of sulphonylurea binding sites in rat brain. Neuroscience 40: 523–531
Tremblay E, Zini S, Ben-Ari Y (1991) Autoradiographic study of the cellular localization of [3H]glibenclamide binding sites in the rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 127: 21–24
Zini S, Tremblay E, Roisin MP, Ben-Ari Y (1991) Two binding sites for [3H]-glibenclamide in the rat brain. Brain Res 542: 151–154
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikeda, M., Dewar, D. & McCulloch, J. High affinity hippocampal [3H]-glibenclamide binding sites are preserved in Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm Gen Sect 5, 177–184 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02257672
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02257672