Abstract
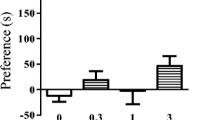
The effect of the non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist dizocilpine (MK-801) on conditioned place preference induced by morphine was studied in mice. As expected, morphine (1–8 mg/kg, IP) elicited a significant preference for the drug-paired compartment. Pretreatment of mice with (+)-dizocilpine (0.1 and 0.2 mg/kg, IP), the more active dizocilpine enantiomer, dose-dependently reversed the conditioned place preference produced by morphine (4 mg/kg, IP), whereas (−)-dizocilpine (0.2 mg/kg, IP) did not modify morphine-induced effects. In contrast, both enantiomers of dizocilpine (at a dose of 0.2 mg/kg, IP) elicited a conditioned place preference. These data suggest that (1) NMDA receptors play a role in morphine-induced place preference, and (2) dizocilpine-reinforcing properties in the place preference paradigm do not seem to be dependent on NMDA receptor blockade.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bardo MT, Miller JS, Neisewander JL (1984) Conditioned place preference with morphine: the effect of extinction training on the reinforcing CR. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 21:545–549
Bardo MT, Neisewander JL, Miller JS (1986) Repeated testing attenuates conditioned place preference with cocaine. Psychopharmacology 89:239–243
Barr GA, Paredes W, Bridger WH (1985) Place conditioning with morphine and phencyclidine: dose dependent effects. Life Sci 36:363–368
Beardsley PM, Hayes BA, Balster RL (1990) The self-administration of MK-801 can depend upon drug-reinforcement history, and its discriminative stimulus properties are phencyclidine-like in rhesus monkeys. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 252:953–959
Ben-Eliyahu S, Marek P, Vaccarino AL, Mogil JS, Sternberg WF, Liebeskind JC (1992) The NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 prevents long-lasting non-associative morphine tolerance in the rat. Brain Res 575:304–308
Bespalov A, Dumpis M, Piotrovsky L, Zvartau E (1994) Excitatory amino acid receptor antagonist kynurenic acid attenuates rewarding potential of morphine. Eur J Pharmacol 264:233–239
Carr GD, White NM (1983) Conditioned place preference from intra-accumbens but not intra-caudate amphetamine injections. Life Sci 33:2551–2557
Chen L, Huang LY (1991) Sustained potentiation of NMDA receptor-mediated glutamate responses through activation of protein kinase C by a mu opioid. Neuron 7:319–326
Fundytus ME, Coderre TJ (1994) Effect of activity at metabotropic, as well as ionotropic (NMDA), glutamate receptors on morphine dependence. Br J Pharmacol 113:1215–1220
Galbicka G, Kautz MA, Jagers T (1994) Behavioral effect of enantiomers of dizocilpine under two “counting” procedures in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 49:943–948
Garcia MM, Harlan RE (1993) Chronic morphine increases calbindin D28k in rat striatum: possible NMDA receptor involvement. Neuroreport 5:65–68
Gudehithlu KM, Reddy PL, Barghava HN (1994) Effect of morphine tolerance and abstinence on the binding of [3H]MK-801 to brain regions and spinal cord of the rat. Brain Res 639:269–274
Heale V, Harley C (1990) MK-801 and AP5 impair acquisition, but not retention, of the Morris milk maze. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 36:145–149
Herberg LJ, Rose IC (1989) The effect of MK-801 and other antagonists of NMDA-type glutamate receptors on brain-stimulation reward. Psychopharmacology 99:87–90
Hoffman DC (1994) The noncompetitive NMDA antagonist MK-801 fails to block amphetamine-induced place conditioning in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 47:907–912
Jeziorski M, White FJ, Wolf ME (1994) MK-801 prevents the development of behavioural sensitization during repeated morphine administration. Synapse 16:137–147
Layer RT, Kaddis FG, Wallace LJ (1993) The NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801 elicits conditioned place preference in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 44:245–247
Lodge D, Johnson KM (1990) Noncompetitive excitatory amino acid receptor antagonists. Trends Pharmacol Sci 11:81–86
Löscher W, Annies R, Hönack D (1993) Comparison of competitive and uncompetitive NMDA receptor antagonists with regard to monoaminergic neuronal activity and behavioural effects in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 242:263–274
Lutfy K, Hurlburt DE, Weber E (1993) Blockade of morphine-induced analgesia and tolerance in mice by MK-801. Brain Res 616:83–88
Marek P, Ben-Eliyahu S, Gold M, Liebeskind JC (1991a) Excitatory amino acid antagonists (kynurenic acid and MK-801) attenuate the development of morphine tolerance in the rat. Brain Res 547:77–81
Marek P, Ben-Eliyahu S, Vaccarino AL, Liebeskind JC (1991b) Delayed application of MK-801 attenuates development of morphine tolerance in rats. Brain Res 558:163–165
Mucha RF, Iversen SD (1984) Reinforcing properties of morphine and naloxone revealed by conditioned place preferences: a procedural examination. Psychopharmacology 82:241–247
Price GW, Ahier RG, Middlemiss DN, Singh L, Tricklebank MD, Wong EH (1988) In vivo labelling of the NMDA receptor channel complex by [3H]MK-801. Eur J Pharmacol 158:279–282
Ransom RW, Stec NL (1988) Inhibition ofN-methyl-d-aspartate evoked sodium flux by MK-801. Brain Res 444:25–32
Self DW, Stein L (1992) Receptor subtypes in opioid and stimulant reward. Pharmacol Toxicol 70:87–94
Spyraki C (1988) Drug reward studies by the use of place conditioning in rats. In: Lader M (ed) The psychopharmacology of addiction. Oxford University Press, Oxford New York Tokyo, pp 97–114
Stolerman I (1992) Drugs of abuse: behavioural principles, methods and terms. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13:170–176
Stone TW (1993) Neuropharmacology of quinolinic and kynurenic acids. Pharmacol Rev 45:309–379
Suzuki T, Funada M, Narita M, Misawa M, Nagase H (1991) Pertussis toxin abolishesμ- andδ-opioid agonist-induced place preference. Eur J Pharmacol 205:85–88
Suzuki T, Funada M, Narita M, Misawa M, Nagase H (1993) Morphine-induced place preference in the CXBK mouse: characteristics ofμ opioid receptor subtypes. Brain Res 602:45–52
Tang AH, Ho PM (1988) Both competitive and non-competitive antagonists ofN-methyl-d-aspartic acid disrupt brightness discrimination in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 151:143–146
Trujillo KA, Akil H (1991) Inhibition of morphine tolerance and dependence by the NMDA receptor antagonist MK-801. Science 251:85–87
Trujillo KA, Akil H (1994) Inhibition of morphine tolerance by non-competitiveN-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists. Brain Res 633:178–188
White NM, Carr GD (1985) The conditioned place preference is affected by two independent reinforcement processes. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 23:37–42
Wolf ME, Jeziorski M (1993) Coadministration of MK-801 with amphetamine, cocaine or morphine prevents rather than transiently masks the development of behavioral sensitization. Brain Res 613:291–294
Xie CW, Lewis DV (1991) Opioid mediated facilitation of long-term potentiation at the lateral perforant path-dentate granule cell synapse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 256:289–296
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Del Pozo, E., Barrios, M. & Baeyens, J.M. The NMDA receptor antagonist dizocilpine (MK-801) stereoselectively inhibits morphine-induced place preference conditioning in mice. Psychopharmacology 125, 209–213 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247330
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02247330