Abstract
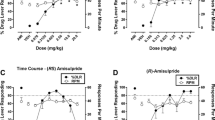
Alpidem in an imidazopyridine derivative which binds selectively to theθ 1(BZ1) receptor subtype. It is active in some, but not all, behavioural tests sensitive to benzodiazepine anxiolytics and has clinical anti-anxiety effects. However, in a previous study, it was shown that alpidem did not substitute for chlordiazepoxide in rats trained to discriminate this benzodiazepine. The present experiments were carried out to investigate the discriminative stimulus properties of alpidem in greater detail. In the first experiment rats learned to discriminate a dose of 10 mg/kg alpidem from saline. Acquisition of the discrimination was long and performance unstable. Chlordiazepoxide, clorazepate and zolpidem substituted only partially for alpidem but the effects of the training dose of alpidem were blocked by 10 mg/kg flumazenil. The second experiment established stimulus control more rapidly to a dose of 30 mg/kg alpidem. Alpidem induced dose-related stimulus control, and dose-related and complete substitution for alpidem was produced by zolpidem, abecarnil, CL 218,872, triazolam and suriclone. Partial substitution occurred with chlordiazepoxide, clorazepate and pentobarbital. In most cases, high levels of substitution were produced only by doses which greatly reduced response rates even though the training dose of alpidem produced only modest decreases in rates. Ethanol, buspirone and bretazenil produced very little substitution for alpidem and both flumazenil and bretazenil antagonised the effects of alpidem. In two further experiments alpidem was found to substitute for the stimulus produced by zolpidem (2 mg/kg) but not for that produced by ethanol (1.5 g/kg). In the latter case the benzodiazepines chlordiazepoxide and triazolam did substitute for the ethanol cue. These results confirm that the discriminative stimulus effects of alpidem differ from those produced by benzodiazepines. The effects of alpidem are most similar to those of the other imidazopyridine derivative, zolpidem, and may be related to the selectivity of these drugs of theθ 1(BZ1) receptor subtype.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews JS, Stephens DN (1991) Discriminative stimulus properties of the benzodiazepine partial agonist β-carbolines abecarnil and ZK 95962: a comparison with chlordiazepoxide. Behav Pharmacol 2:171–185
Ator NA (1990) Drug discrimination and drug stimulus generalization with anxiolytics. Drug Dev Res 20:189–204
Ator NA, Griffiths RR (1989) Differential generalisation to pentobarbital in rats trained to discriminate lorazepam, chlordiazepoxide, diazepam or triazolam. Psychopharmacology 98:20–30
Barrett JE, Gleeson S (1991) Anxiolytic effects of 5-HT1A agonists, 5-HT3 antagonists and benzodiazepines: conflict and drug discrimination studies. In: Rodgers AJ, Cooper SJ (eds), 5HT1A agnosists, 5HT3 antagonists and benzodiazepines. Their comparative behavioural pharmacology. Wiley, Chichester, pp 59–105.
Benavides J, Peny B, Durand A. Arbilla S, Scatton B (1992) Comparative in vivo and in vitro regional selectivity of centralθ(BZ) modulatory site ligands as displacers of [3H] flumazenil binding in the rat central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 263:884–896
Colpaert FC, Desmedt LKC, Janssen PAJ (1976) Discriminative stimulus properties of benzodiazepines, barbiturates and pharmacologically related drugs: relation to some intrinsic and anti-convulsant effects. Eur J Pharmacol 37:113–123
De Vry J, Slangen JL (1986) Effects of training dose on discrimination and cross-generalization of chlordiazepoxide, pentobarbital and ethanol in the rat. Psychopharmacology 88:341–345
Facklam M. Schoch P, Haefely WE (1992a) Relationship between benzodiazepine receptor occupancy and potentiation ofγ-aminobutryic acid-stimulated chloride flux in vitro in four ligands of differing efficacies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 261:1106–1112
Facklam M. Schoch P, Bonetti EP, Jenck F, Martin JR, Moreau JL, Haefely WE (1992b) Relationship between benzodiazepine receptor occupancy and functional effects in vivo of four ligands of different intrinsic efficacies. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 261:1113–1121
Frattola L, Piolti R, Bassi S, Albizzati MG, Cesana BM, Bottani MS, Priorie P, Borghi C, Morselli PL (1992) Effects of alpidem in anxious elderly outpatients: a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Clinical Neuropharmacol 15:477–487
Garcha HS, Rose IC, Stolerman IP (1985) Midazolam cue in rats: generalisation tests with anxiolytic and other drugs. Psychopharmacology 87:233–237
Gardner CR (1989) Discriminative stimulus properties of CL 218872 and chlordiazepoxide in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 34:711–715
Gardner CR, Tully WR, Hedgecock CJR (1993) The rapidly expanding range of neuronal benzodiazepine receptor ligands. Prog Neurobiol 40:1–61
Giusti P, Guidetti G, Costa E, Guidotti A (1991) The preferential antagonism of pentylenetetrazole proconfilct responses differentiates a class of anxiolytic benzodiazepines with potential antipanic action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 257:1062–1068
Giusti P, Romeo E, Auta J, Guidotti A (1992) Structural variety of GABAA receptors and specificity of benzodiazepines pharmacological profiles. In: Biggio G, Concas A, Costa E (eds), GABAergic synaptic transmission. Raven, New York, pp 163–177
Goudie AJ, Leathley MJ (1992) Assessment of the dependence potential of the imidazopyridine anxiolytic, alpidem, in rats. Br J Pharmacol 1075:353P
Hendry JS, Balster RL, Rosecrans JA (1983) Discriminative stimulus properties of buspirone compared to central nervous system depressants in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 19:97–101
Joly D, Sanger DJ (1991) Social competition in rats: a test sensitive to acutely administered anxiolytics. Behav Pharmacol 2:205–213
Langer SF, Feighner JP, Pambakian R, Manouwitz NR, Venable TC (1988) Pilot study of alpidem, a novel imidazopyridine compound, in anxiety. Psychopharmacol Bull 24:161–163
Langer SZ, Arbilla S, Tan S, Lloyd KG, George P, Allen J, Wick AE (1990) Selectivity for omega-receptor subtypes as a strategy for the development of anxiolytic drugs. Pharmacopsychiatry 23 [suppl.]:103–107
Martin JR, Pieri L, Bonetti EP, Schaffner R, Burkard WP, Cumin R, Haefely WE (1988) Ro 16-6028: a novel anxiolytic acting as a partial agonist at the benzodiazepine receptor. Pharmacopsychiatry 21:360–362
Morton S, Lader M (1992a) Alpidem and lorazepam in the treatment of patients with anxiety disorders: comparison of efficacy and rebound. Human Psychopharmacol 7:239–248
Morton S, Lader M (1992b) Alpidem and lorazepam in the treatment of patients with anxiety disorders: comparison of physiological and psychological effects. Pharmacopsychiat 25:177–181
Perrault G, Morel E, Sanger DJ, Zivkovic B (1992) Lack of tolerance and physical dependence after treatment with alpidem, a new imidazopyridine anxiolytic, in mice. Behav Pharmacol 3 [suppl 1]:58
Pritchett DB, Seeburg PH (1990)γ-Aminobutyric acidA receptorα 5-subunit creates novel type II benzodiazepine receptor pharmacology. J Neurochem 54:1802–1804
Puia G, Ducic I, Vicini S, Costa E (1992) Molecular mechanisms of the partial allosteric modulatory effects of bretazenil atγ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci 89:3620–3624
Rijnders HJ, Jarbe TUC, Slangen JL (1991) The pentylenetetrazolecue antagonist actions of bretazenil (Ro 16-6028) as compared to midazolam. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39:129–132
Romeo E, Auta J, Kozikowksi AP, Ma D, Papadopoulos V, Puia G, Costa E, Guidotti A (1992) 2-aryl-3-indoleacetamides (FGIN-1) a new class of potent and specific ligands for the mitochondrial DBI receptor (MDR). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 262:971–978
Sanger DJ (1987) Further investigation of the stimulus properties of chlordiazepoxide and zolpidem. Agonism and antagonism by two novel benzodiazepines. Psychopharmacology 93:365–368
Sanger DJ (1988) Discriminative stimulus properties of anxiolytic and sedative drugs: pharmacological specificity. In: Colpaert FC, Balster RL (eds) Transduction mechanisms of drug stimuli. Springer, Berlin, pp 73–84
Sanger DJ (1993) Substitution by NMDA antagonists and other drugs in rats trained to discriminate ethanol. Behav Pharmacol (in press)
Sanger DJ, Benavides J (1993) Discriminative stimulus effects ofθ(BZ) receptor ligands: correlation with in vivo inhibition of [3H]-flumazenil binding in different regions of the rat central nervous system. Psychopharmacology (in press)
Sanger DJ, Zivkovic B (1986) The discriminative stimulus properties of zolpidem, a novel imidazopyridine hypnotic. Psychopharmacology 89:317–322
Sanger DJ, Perrault G, Morel E, Joly D, Zivkovic B (1987) The behavioural profile of zolpidem, a novel hypnotic drug of imidazopyridine structure. Physiol Behav 41:235–240
Sanger DJ, Perrault G, Morel E, Joly D, Zivkovic B (1991) Animal models of anxiety and the development of novel anxiolytic drugs. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 15:205–212
Sanger DJ, Perrault G, Morel E, Joly D, Zivkovic B (1993) The psychopharmacological profile of alpidem. In: Bartholini G, Garreau M, Morselli PL, Zivkovic B (eds), Imidazopyridines in anxiety disorders. Raven, New York, (in press)
Schechter MD, Lovano DM (1985) Ethanol-chlordiazepoxide interactions in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 23:927–930
Shannon HE, Herling S (1983) Discriminative stimulus effects of diazepam in rats: evidence for a maximal effect. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227:160–166
Tang AH, Franklin SR (1991) The discriminative stimulus effects of diazepam in rats at two training doses. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 258:926–931
Wettstein JG, Gauthier B (1992) Discriminative stimulus effects of alprazolam and diazepam: generalization to benzodiazepines, antidepressants and buspirone. Behav Pharmacol 3:229–237
Young R, Glennon RA (1987) Stimulus properties of benzodiazepines: correlations with binding affinities, therapeutic potency, and structure activity relationships (SAR). Psychopharmacology 93:529–533
Zivkovic B., Morel E, Joly D, Perrault G, Sanger DJ, Lloyd KG (1990) Pharmacological and behavioral profile of alpidem as an anxiolytic. Pharmacopsychiatry 23 [suppl]:108–113
Zivkovic B, Arbilla S, Perrault G, Sanger DJ, Langer SZ (1991) Alpidem, an omega-1 receptor-selective partial agonist: a new approach to anxiety treatment. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 1:202–205
Zivkovic B, Perrault G., Sanger DJ (1992) Receptor subtype-selective drugs: a new generation of anxiolytics and hypnotics. In: Mendlewicz J, Racagni G (eds), Target receptors for anxiolytics and hypnotics: from molecular pharmacology to therapeutics. Karger, Basel, pp 55–73
Zivkovic B, Perrault G, Morel E, Garrigou-Gadenne D, Thenot JP, Sanger DJ (1993) Tolerance and dependence studies with alpidem. In: Bartholini G, Garreau M, Morselli PL, Zivkovic B (eds), Imidazopyridines in anxiety disorders. Raven, New York, (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sanger, D.J., Zivkovic, B. Discriminative stimulus effects of alpidem, a new imidazopyridine anxiolytic. Psychopharmacology 113, 395–403 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245215
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02245215