Abstract
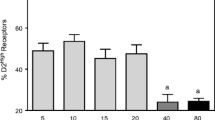
Previous studies used either racemic 3-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-N-n-propylpiperidine [(±)-3-PPP] or lower doses of the mixed dopamine (DA) D1/D2 agonist apomorphine (APO) to conclude that brain DA D2 autoreceptors are not behaviorally functional until 28 days of age. The purpose of this study was to provide behavioral evidence for functional D2 autoreceptors before 28 days of age using DA agonists with greater selectivity for D2 autoreceptors. The locomotor activity of 10-, 21-, 35-day-old and adult rats was monitored after injection of a D2 autoreceptor agonist. There were significant decreases in the locomotor activity of 21-, 35-day-old, and adult rats injected with (-)-3-PPP, SND 919, or PD 128483. Lower doses of APO significantly decreased the activity of adult and 35-day-old rats but not younger rats. The only significant effect on the locomotor activity of 10-day-old rats was an increase in activity after injection of APO, 0.01 mg/kg or higher, or B-HT 920, 0.01 mg/kg. The results suggest that brain DA D2 autoreceptors are behaviorally functional at 21, but not 10, days of age.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andén, N-E, Grabowska-Andén M (1990) B-HT 920 is a full agonist at both pre- and postsynaptic D-2 dopamine receptors. J Neural Transm 79:209–214
Andén N-E, Golembiowska-Nikitin, K., Thornström U (1982) Selective stimulation of dopamine and noradrenaline autoreceptors by B-HT 920 and B-HT 933, respectively. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 321:100–104
Arnt J (1983) Differential behavioural effects of dopamine agonists in developing rats: a study of 3-PPP enantiomers. Eur J Pharmacol 91:273–278
Arnt J, Bøgesø KP, Christensen AV, Hyttel J, Larsen J-J, Svendsen O (1983) Dopamine receptor agonistic and antagonistic effects of 3-PPP enantiomers. Psychopharmacology 81:199–207
Carlson JH, Bergstrom DA, Walters JR (1987) Stimulation of both D1 and D2 dopamine receptors appears necessary for full expression of postsynaptic effects of dopamine agonists: a neurophysiological study. Brain Res 400:205–218
Carlsson A (1975) Receptor-mediated control of dopamine metabolism. In: Usdin E, Bunney WE Jr (eds) Pre- and postsynaptic receptors. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 49–65
Carter AJ, Müller RE (1991) Pramipexole, a dopamine D2 autoreceptor agonist, decreases the extracellular concentration of dopamine in vivo. Eur J Pharmacol 200:65–72
Chandler CJ, Wohab W, Starr BS, Starr MS (1990) Motor depression: a new role for D1 receptors? Neuroscience 38:437–445
Coyle JT, Campochiaro P (1976) Ontogenesis of dopaminergic-cholinergic interactions in the rat striatum: a neurochemical study. J Neurochem 27:673–678
De Fonseca FR, Cebeira M, Fernández-Ruiz JJ, Navarro M, Ramos JA (1991) Effects of pre- and perinatal exposure to hashish extracts on the ontogeny of brain dopaminergic neurons. Neuroscience 43:713–723
DeVries TJ, Mulder AH, Schoffelmeer ANM (1992) Differential ontogeny of functional dopamine and muscarinic receptors mediating presynaptic inhibition of neurotransmitter release and postsynaptic regulation of adenylate cyclase activity in rat striatum. Dev Brain Res 66:91–96
Drukarch B, Schepens E, Dolleman-Van der Weel MJ, DeBoer P, Van Vliet BJ, Stoof JC (1990) Lack of a dopamine autoreceptor selective profile of B-HT 920 in functional in vitro model systems of D2 receptors in rat striatum. Eur J Pharmacol 187:257–269
Drukarch B, Stoof JC (1990) D-2 dopamine autoreceptor selective drugs: do they really exist? Life Sci 47:361–376
Eilam D, Talangbayan H, Canaran G, Szechtman H (1992) Dopaminergic control of locomotion, mouthing, snout contact, and grooming: opposing roles of D1 and D2 receptors. Psychopharmacology 106:447–454
Eriksson E, Svensson K, Clark D (1985) The putative dopamine autoreceptor agonist B-HT 920 decreases nigral dopamine cell firing rate and prolactin release in rat. Life Sci 36:1819–1827
Flügge G, Wuttke W, Fuchs E (1986) Postnatal development and sexual differentiation of central nervous catecholaminergic systems. Biogenic Amines 3:249–255
Goodlett CR, Valentino ML (1987) Differential effects of clonidine, B-HT 933 and B-HT 920 in immature rat pups. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 27:283–290
Groves PM, Wilson CJ, Young SJ, Rebec GV (1975) Self-inhibition by dopaminergic neurons. An alternative to the “neuronal feedback loop” hypothesis for the mode of action of certain psychotropic drugs. Science 190:522–529
Hedner T, Lundborg P (1985) Development of dopamine autoreceptors in the postnatal rat brain. J Neural Transm 62:53–63
Heffner TG, Caprathe B, Davis M, Jaen J, Meltzer L, Pugsley T, Wise L (1992) Effects of PD 128483, a novel dopamine autoreceptor agonist, in preclinical antipsychotic tests. In: Meltzer HY (ed) Novel antipsychotic drugs. Raven Press, New York, pp 79–90
Hjorth S, Carlsson A, Wikström H, Lindberg P, Sanchez D, Hacksell U, Arvidsson L-E, Svensson U, Nilsson JLG (1981) 3-PPP, a new centrally acting DA-receptor agonist with selectivity for autoreceptors. Life Sci 28:1225–1238
Hjorth S, Carlsson A, Clark D, Svensson K, Wirkström H, Sanchez D, Lindberg P, Hacksell U, Arvidsson L-E, Johansson A, Nilsson JLG (1983) Central dopamine receptor agonist and antagonist actions of the enantiomers of 3-PPP. Psychopharmacology 81:89–99
Hoffman DC, Beninger RJ (1985) The D1 dopamine receptor antagonist, SCH 23390, reduces locomotor activity and rearing in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 22:341–342
Imperato A, Tanda G, Frau R, DiChiara G (1988) Pharmacological profile of dopamine receptor agonists as studied by brain dialysis in behaving rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 245:257–264
Jaen JC, Wise LD, Caprathe BW, Tecle H, Bergmeier S, Humblet CC, Heffner TG, Meltzer LT, Pugsley TA (1990) 4-(1,2,5,6-tetrahydro-1-allyl-3-pyridinyl)-2-thiazolamines: a novel class of compounds with central dopamine agonist properties. J Med Chem 33:311–317
Johansen PA, Clark D, White FJ (1988) B-HT 920 stimulates post-synaptic D2 dopamine receptors in the normal rat: electrophysiological and behavioral evidence. Life Sci 43:515–524
Kellogg C, Lundborg P (1972) Ontogenic variations in responses to L-dopa and monoamine receptor-stimulating agents. Psychopharmacology 23:187–200
Kelly PH, Seviour PW, Iversen SD (1975) Amphetamine and apomorphine responses in the rat following 6-OHDA lesions of the nucleus accumbens septi and corpus striatum. Brain Res 94:507–522
Laduron PM (1985) Presynaptic heteroreceptors in regulation of neuronal transmission. Biochem Pharmacol 34:467–470
Lehmann J, Langer SZ (1982) Dopamine autoreceptors differ pharmacologically from postsynaptic dopamine receptors: effects of (-)-N-(2-chloroethyl)-norapomorphine. Eur J Pharmacol 77:85–86
Lynch MR (1991) Dissociation of autoreceptor activation and behavioral consequences of low-dose apomorphine treatment. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 15:689–698
Mailman RB, Schulz DW, Lewis MH, Staples L, Rollema H, Dehaven DL (1984) SCH-23390: a selective D1 dopamine antagonist with potent D2 behavioral actions. Eur J Pharmacol 101:159–160
McDougall SA, Arnold TF, Nonneman AJ (1990) Ontogeny of locomotor activity and grooming in the young rat: role of dopamine D1 and D2 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 186:223–230
Mierau J, Schingnitz G (1992) Biochemical and pharmacological studies on pramipexole, a potent and selective dopamine D2 receptor agonist. Eur J Pharmacol 215:161–170
Moody CA, Spear LP (1992) Ontogenetic differences in the psychopharmacological responses to separate and combined stimulation of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors during the neonatal to weanling age period. Psychopharmacology 106:161–168
Nomura Y, Naitoh F, Segawa T (1976) Regional changes in monoamine content and uptake of the rat brain during postnatal development. Brain Res 101:305–315
Rao PA, Molinoff PB, Joyce JN (1991) Ontogeny of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor subtypes in rat basal ganglia: a quantitative autoradiographic study. Dev Brain Res 60:161–177
Roberts DCS, Zis AP, Fibiger HC (1975) Ascending catecholamine pathways and amphetamine-induced locomotor activity: importance of dopamine and apparent non-involvement of norepinephrine. Brain Res 93:441–454
Shalaby IA, Spear LP (1980) Psychopharmacological effects of low and high doses of apomorphine during ontogeny. Eur J Pharmacol 67:451–459
Shaywitz BA, Gordon JW, Klopper JH, Zelterman DA, Irvine J (1979) Ontogenesis of spontaneous activity and habituation of activity in the rat pup. Dev Psychobiol 12:359–367
Stoof JC, Kebabian JW (1981) Opposing roles for D1 and D2 dopamine receptors in efflux of cyclic AMP from rat neostriatum. Nature 294:366–368
Strömbom U (1975) On the functional role of pre- and postsynaptic catecholamine receptors in brain. Acta Physiol Scand [Suppl] 431:1–43
Strömbom U (1976) Catecholamine receptor agonists. Effects on motor activity and rate of tyrosine hydroxylation in mouse brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 292:167–176
Symes AL, Lal S, Sourkes TL (1976) Time-course of apomorphine in the brain of the immature rat after apomorphine injection. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 223:260–264
Walters DE, Carr LA (1986) Changes in brain catecholamine mechanisms following perinatal exposure to marihuana. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 25:763–768
Walters DE, Howard SG (1990) The D1 agonist SKF 38393 increases dopamine release in the developing rat striatum. Eur J Pharmacol 184:257–264
Zetterström T, Sharp T, Ungerstedt U (1986) Effect of dopamine D1 and D2 receptor selective drugs on dopamine release and metabolism in rat striatum in vivo. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 334:117–124
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, MY., Walters, D.E. Dopamine D2 autoreceptors in rats are behaviorally functional at 21 but not 10 days of age. Psychopharmacology 114, 262–268 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244847
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02244847