Summary
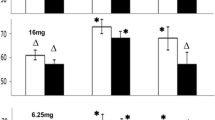
An anticholinergic, propantheline bromide, was given in a dosage of 5 mg./ kg. body weight twice daily to rats. Gastric function was studied after 3, 6, 9, and 12 months of this treatment. Gastric content was collected after (1) pyloric and cardia ligation; (2) pyloric ligation only; and (3) during a 24-hr, intravenous infusion of histamine. Under the experimental conditions described, a significant reduction of gastric secretion was found in rats after long-term administration of propantheline bromide. This is considered due to the impairment of gastric secretory function induced by repeated inhibition of gastric secretion over a prolonged period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bollman, J. L. A cage which limits the activity of rats.J Lab Clin Med 33:1348, 1948.
Brodie, D. A.The mechanism of gastric hyperacidity produced by pylorus ligation in the rat.Amer J Dig Dis 11:231, 1966.
Brodie, D. A., andKnapp, P. G. The mechanism of the inhibition of gastric secretion produced by esophageal ligation in the pylorus-ligated rat.Gastroenterology 50:787, 1966.
Glass, G. B. J. Gastric atrophy; its clinical significance and methods of detection.Amer J Dig Dis 2:709, 1957.
Komarov, S. A., Bralow, S. P., andBoyd, E. A permanent rat gastric fistula.Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 112:451, 1963.
Kowalewski, K. Effect of prolonged administration of an anticholinergic drug on gastric secretion of rats, mice and hamsters.Arch Int Pharmacodyn 152:404, 1964.
Kowalewski, K., andKasper, T. Achlorhydria, gastric mucosal atrophy and gastric neo-plastic lesions in rats, mice, and hamsters treated with an anticholinergic drug, propantheline bromide, and a carcinogen, 20-methylcholanthrene.Canad J Surg 10:99, 1967.
Kowalewski, K., Mackenzie, W. C, Shnitka, T. K., andBain, G. O. Protective action of pro-banthine (SC-3171) on experimental gastric ulcers of rats.Canad Med Ass J 71:417, 1954.
Kowalewski, K., van Geertruyden, J., Henrotin, E., and Gepts, W. Etude de l'ulcére expèrimental provoquè par la ligature de pylore chez le rat. Action protectrice du chiorhydrate de diéthylaminoéthyl-N-dibcuzoparathiazine(2987 RP, Diparcol).Ada Gastroent Belg 14:596, 1951.
Posey, E. L., Jr., Elliott, R., Aldridce, J., Turner, C, andFranklin, H. Long-term anticholinergic administration and gastric secretory function in dogs.Amer J Dig Dis 11:421, 1966.
Shay, H., Komarov, S. A., Fels, S. S., Meranze, D., Gruenstein, M., andSiplet, H. A. A simple method for the uniform production of gastric ulceration in the rat.Gastroenterology 5:53, 1945.
Skoryna, S. C, andWebster, D. E. A method of collection of pure gastric secretion in rats.Surg Forum 10:193, 1960.
Wilcoxon, F. Individual comparisons by ranking methods.Biometrics 1:80, 1945.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Propantheline bromide (Pro-Banthine) was donated by G. D. Searle & Co., Chicago, Ill.
The technical assistance of Mr. G. Chmm'a, Mrs. E. Dimition and Mrs. M. McCubbin is gratefully acknowledged.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kowalewski, K. Effect of long-term treatment with an anticholinergic drug on gastric secretion in rats. Digest Dis Sci 12, 988–993 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02233257
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02233257