Abstract
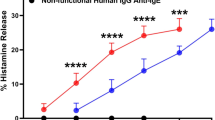
Histamine release caused by anti-IgE was examined in leukocyte suspensions from 10 healthy individuals. Influenza A virus was found to enhance the histamine release but did not release histamineper se. When monoclonal antibodies directed against the viral neuraminidase were included in the samples, the potentiating effect of the virus was completely abolished. The same occurred using a neuraminidase inhibitor. However, monoclonal antibodies directed against the viral haemagglutinin also abolished the potentiation. A binding of virus to the basophil cell surface by haemagglutinin therefore seems to be necessary for the viral neuraminidase to cause potentiation of mediator release.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Clementsen, C. Hannoun and S. Norn,Influenza A virus enhances allergic histamine release. Effect of neuraminidase. Allergy (in press).
P. Clementsen, C. B. Jensen, J. O. Jarløv, C. Hannoun, M. Søborg and S. Norn,Influenza A virus enhances Staphylococcus aureus-induced basophil histamine release in normal individuals and patients with intrinsic asthma. Allergy (in press).
P. Clementsen, C. B. Jensen, C. Hannoun, M. Søborg and S. Norn,Influenza A virus potentiates basophil histamine release caused by endotoxin-induced complement activation. Examination of normal individuals and patients with intrinsic asthma. Allergy43, 93–99 (1988).
P. Clementsen, H. Bisgaard, M. Pedersen, H. Permin, E. Struve-Christensen, N. Milman, B. Nüchel-Petersen and S. Norn,Staphylococcus aureus and influenza A virus stimulate human bronchoalveolar cells to release histamine and leukotrienes. Agents and Actions27, 107–109 (1989).
P. Stahl Skov and S. Norn,A simplified method for measuring basophil histamine release and blocking antibodies in hay fever patients. Basophil histamine content and cell preservation. Acta Allergol.32, 170–182 (1977).
S. Ida, J. Hooks, R. P. Siraganian and A. L. Notkins,Enhancement of IgE-mediated histamine release from human basophils by viruses: role of interferon. J. exp. Med.145, 892–906 (1977).
T. Chonmaitree, M. A. Lett-Brown, Y. Tsong, A. S. Goldman and S. Baron,Role of interferon in leukocyte histamine release caused by common respiratory viruses. J. infect. Dis.157, 127–132 (1988).
R. Schauer and A. P. Corfield,Sialidases and their inhibitors. In:Medicinal Chemistry Advances. (Ed. F. G. De Las Heras and S. Vega) pp. 423–434. Pergamon Press, Oxford 1981.
D. W. Kingsburgy.Orthomyxo- and Paramyxoviruses and Their Replication. InVirology. (Ed. B. N. Fields) pp. 1157–1178, Raven Press, New York 1985.
W. Weis, J. H. Brown, S. Cusack, J. C. Paulson, J. J. Skehel and D. C. Wiley,Structure of the influenza virus haemagglutinin complexed with its receptor, sialic acid. Nature333, 426–431 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clementsen, P., Douglas, A.R., Skehel, J.J. et al. Influenza A virus enhances IgE-mediated histamine release from human basophil leukocytes. Examination of the effect of viral neuraminidase and haemagglutinin. Agents and Actions 27, 58–61 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02222198
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02222198