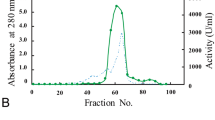
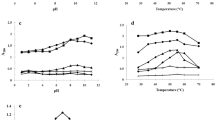
Abstract
Several physical and chemical parameters of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) were determined using a spectrophotometric assay of gill tissue homogenates from rainbow trout. This assay is based on the evolution of free hippuric acid via enzymatic cleavage of histidyl-leucine from the synthetic substrate hippuryl-l-histidyl-l-leucine (HHL). Piscine ACE exhibited enzymatic and kinetic properties similar to those reported for the partially purified mammalian enzyme. Proteolytic activity was both temperature and pH dependent and demonstrated hyperbolic kinetics with an apparent Km of 2.5 mM. Hydrolysis of HHL was activated by Cl− at concentrations between 20 mM and 100 mM. Captopril (1 × 10−6 M) and MK-422 (1 × 10−6 M) blocked trout gill ACE activity, however, EDTA was inhibitory only at high concentrations (1 × 10−3 M). These results demonstrate that trout ACE is functionally similar to mammalian ACE and that the spectro-photometric assay for ACE developed by Cushman and Cheung can be applied to analysis of converting enzyme activity in fish tissue homogenates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
Bunning, P. and Riordan, J.F. 1983. Activation of angiotensin converting enzyme by monovalent anions. Biochemistry. 22: 110–116.
Cushman, D.W. and Cheung, H.S. 1971. Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochem. Pharmacol. 20: 1637–1648.
Das, M. and Soffer, R.L. 1975. Pulmonary angiotensin-converting enzyme. J. Biol. Chem. 250: 6762–6768.
Fishman, A.P. and Pietra, G.G. 1974. Handling of bioactive materials by the lung. New England J. Med. 291: 884–890.
Galardy, R., Podhasky, P., Olson, K.R. 1984. Angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in tissues of the rainbow trout. J. Exp. Zool. 230: 155–158.
Hayakari, M., Kondo, Y., Izumi, H. 1978. A rapid and simple spectrophotometric assay of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Anal. Biochem. 84: 361–369.
Hochachka, P.W. and Somero, G.N. 1984. Biochemical Adaptation. Princeton University Press, Princeton.
Iwata, K., Blacher, R., Soffer, R. and Lai, C.-Y. 1983. Rabbit pulmonary angiotensin-converting enzyme: The NH2-terminal fragment with enzymatic activity and its formation from the native enzyme by NH4OH treatment. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 227: 188–201.
Kiceniuk, J.W. and Jones, D.R. 1977. The oxygen transport system in trout (Salmo gairdneri) during sustained exercise. J. Exp. Biol. 69: 247–260.
Miyazaki, M., Okunishi, H., Nishimura, K. and Toda, N. 1984. Vascular angiotensin-converting enzyme activity in man and other species. Clin. Sci. 66: 39–45.
Nishimura, H., Ogawa, M. and Sawyer, W.H. 1973. Reninangiotensin system in primitive bony fishes and a holocephalin. Am. J. Physiol. 224: 950–956.
Nishimura, H., Norton, V.M. and Bumpus, F.M. 1978. Lack of specific inhibition of angiotensin II in eels by angiotensin antagonists. Am. J. Physiol. 235: H95–H103.
Olson, K.R., Kullman, D., Narkates, A.J. and Oparil, S. 1986. Angiotensin extraction by trout tissuesin vivo and metabolism by the perfused gill. Am. J. Physiol. 250: (Regulatory Integrative Comp. Physiol. 19): R532–538.
Opdyke, D.F. and Holcombe, R. 1976. Response to angiotensin I and II and to the AI converting enzyme inhibitor in a shark. Am. J. Physiol. 231: 1750–1753.
Reeves, R.B. 1977. The interaction of body temperature and acid-base balance in ectothermic vertebrates. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 39: 559–586.
Said, S.I. 1982. Metabolic functions of the pulmonary circulation. Circ. Res. 50: 325–333.
Sander, G.E. and Huggins, C.G. 1972. Vasoactive peptides. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. 12: 227–263.
Skeggs, L.T., Marsh, W.H., Kahn, J.R. and Shumway, N.P. 1954. The existence of two forms of hypertensin. J. Exp. Med. 99: 275–282.
Takada, Y., Unno, M., Hiwada, K. and Kokubu, T. 1982. Biochemical and immunological studies of angiotensin converting enzymes from human, bovine, dog, hog, rabbit, rat and sheep kidneys. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 73B: 189–194.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lipke, D.W., Thomas, R.L. & Olson, K.R. Characterization of angiotensin-converting enzyme in the gills of rainbow trout,Salmo gairdneri (Richardson). Fish Physiol Biochem 3, 91–97 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02183003
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02183003