Summary
A greenhouse experiment on a silt loam surface soil (Typic Hapludult) was done to investigate effects of P and S on yield, quality aspects and sugar reserves in the tropical forage legumeClitoria ternatea L. Four levels of P and two N treatments (NH4NO3 vs symbiotic) were arranged in a factorial design with four replications. After the first cutting two levels of S were imposed on this design.
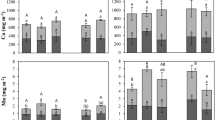
Phosphorus enhanced dry matter yield in the first cutting. Its effect was smaller in the second cutting. Amount of P required to produce maximum plant yield dropped from 200 mg/kg soil (or more) at the first cutting to 50–100 mg/kg at the second. Added S improved growth at suboptimal levels of P. At optimal P and S, symbiotic and +N plants yielded alike.
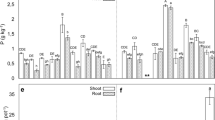
Phosphorus and S fertilization caused several changes in plant composition. Nitrogen concentration was raised by S treatment and lowered by P. Combined addition of P and S lowered plant nitrate content. In symbiotic plants, soluble sugar concentrations were higher than in N-treated plants, and were increased by P and S treatment. In N-treated plants, neither P nor S increased reducing sugar concentration, but they increased total sugar.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Anderson, A. J. and Spencer, D. 1950 Sulfur in nitrogen metabolism of legumes and nonlegumes. Aust. J. Sci. Res.3, 431–449.
Andrew, C. S. and Robins, M. F. 1969 The effect of phosphorus on the growth and chemical composition of some tropical legumes. I. Growth and critical percentages of phosphorus. Aust. J. Agric. Res.20, 665–674.
Andrew, C. S. 1977 The effect of sulfur on the growth, sulfur and nitrogen concentration of some tropical and temperate legumes. Aust. J. Agric. Res.28, 807–820.
Association of Official Analytical Chemists. 1970 Methods of Analysis, 11th Ed. Washington, D.C.
Bergersen, F. J. 1976 Physiological chemistry of dinitrogen fixation by legumes.In A Treatise on Dinitrogen Fixation III. R. W. F. Hardy and W. S. Siler John Wiley and Sons, New York.
Chen, C. L. H. 1967 Assimilation of14CO2 byMedicago sativa leaves in relation to sulfur nutrition. Ph.D. Thesis, University of California, Davis.
Fox, R. L., Nishimoto, R. K., Thompson, J. R., and de la Pěnã, R. S. 1976 Comparative external phosphorus requirements of plants growing in tropical soils. Trans. 10th Int. Congr. Soil. Sci. Moscow, U.S.S.R.4, 232–239.
Gates, C. T., Wilson, J. R. and Shaw, N. H. 1966 Growth and chemical composition of Townsville lucerne (Stylosanthes humilis) Aust. J. Exp. Agric. Anim. Husb.6, 266–276.
Gates, C. T. 1974 Nodule and plant development inStylosanthes humilis H.B.K.: Symbiotic response to phosphorus and sulfur. Aust. J. Bot.22, 45–55.
Hardy, R. W. F. and Havelka, V. D. 1975 Nitrogen fixation research: a key to world food. Science188, 633–643.
Johnson, C. M. and Ulrich, A. 1959 Analytical methods for use in plant analysis. Calif. Agric. Exp. Stn. Bull.766.
Mckenzie, H. A. and Wallace, H. S. 1954 Kjeldahl determination of nitrogen: a critical study of digestion conditions. Aust. J. Chem.7, 55–70.
Pasricha, N. S. and Randhawa, N. S. 1975 Effect of sulfur fertilization on the nitrogen metabolism in Berseem. Indian J. Agric. Sci.45, 213–218.
Plucknett, D. L. and Fox, R. L. 1965 Effect of phosphorus fertilization on yield and composition of pangola grass andDesmodium intortum. Proc. 9th Int. Grassl. Congr. 1525–1529.
Rendig, V. V. and McComb, E. A. 1959 Effect of nutritional stress on plant composition. I. The interaction of added nitrogen with varying sulfur supply. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc.23, 377–380.
Rendig, V. V. and McComb, E. A. 1961 Effect of nutritional stress on plant composition. Plant and Soil14, 176–186.
Robinson, P. J. and Jones, R. K. 1972 The effect of phosphorus and sulfur fertilization on the growth and distribution of dry matter, nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur in Townsville Stylo Aust. J. Agric. Res.23, 633–640.
Robson, A. D. 1978 Mineral nutrients limiting nitrogen fixation in legumes.In Mineral Nutrition of Legumes in Tropical and Subtropical Soils. Eds. C. S. Andrew and E. J. Kamprath CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia.
Small, J. G. C. and Leonard, O. A. 1969 Translocation of14C-labelled photosynthate in nodulated legumes as influenced by nitrate nitrogen. Am. J. Bot.56, 187–194.
Steinbergs, Iismaa, A. O., Freney, J. R. and Barrow, N. J. 1962 Determination of total sulfur in soil and plant material. Anal. Chim. Acta27, 158–164.
Wright, M. J. and Davidson, K. L. 1964 Nitrate accumulation in crops and nitrate poisoning in animals. Adv. Agron.16, 197–247.
Zaroug, M. G. and Munns, D. N. 1980 Effects of phosphorus and sulfur nutrition on soluble sugar and growth ofClitoria ternatea L. Plant and Soil55, 243–250.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaroug, M.G., Munns, D.N. Influence of phosphorus and sulfur nutrition on composition ofClitoria ternatea L.. Plant Soil 55, 251–259 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181805
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02181805