Summary
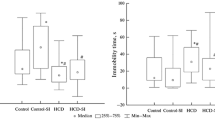
Experiments were carried out with male and female wild-born tree-shrews from Thailand. Both sexes arrived in a very bad shape. The males are meager, their adrenals enlarged and their testicles withdrawn into the abdomen. Tyrosine hydroxylase activity (THY) in the adrenal is high. These changes were induced by a longer period of stress caused by the housing conditions at the trader's. Animals housed singly after arrival recover. They reach normal body weights after 28 days (35% weight gain compared with newcomers). The THY activity in the adrenal decreases and reaches normal levels within 28 days. Adrenal weights reach control values after 70 days of adaptation (Fig. 1).
The THY activities in many parts of the brain are reduced in newcomers, compared with adapted controls. These changes are most prominent in the hypothalamus, in the basal ganglia and in the septum (Figs. 2, 3). These values remain unchanged until 70 days of recovery; after 119 days of recovery they are increased.
During recovery, the stress-induced THY activity changes in the brain fairly outlast the stress-induced variations of the peripheral parameters (body weight, adrenal weight, adrenal THY activity).
After more than 5 months of recovery and adaptation, the stress experiments started. To separate the more physical from mere psychic stress, which derive from certain social interactions, the male tree-shrews were exposed once a day to the attack of an experienced fighter for 2–5 min. The animals were defeated during these attacks. One group of the defeated animals rested in optical contact with the winner throughout the day (sociopsychic stress). The other group of defeated animals was optically separated from the victor after the combat (fighting-stress). The animals were killed after 3 days. Unfought animals served as controls.
During sociopsychic stress, the body weight decreases and the adrenal weight and the adrenal THY activity increase. Fighting-stress induces similar changes but to a smaller extent (Fig. 1).
The THY activity in the hypothalamus, in the basal ganglia and in the septum decrease during sociopsychic stress. Fighting-stress reduces the THY activity in the hypothalamus and — statistically not significant — in the basal ganglia. In the septum fighting-stress is not sufficient to decrease THY activity (Figs. 2, 3).
There is a correlation between the percentage of daily weight-loss of the individual and its THY activity in the basal ganglia in adapted animals serving as controls or stressed. A further correlation exists between adrenal and basal ganglia THY activities (Figs. 5, 6).
In females, group-housed for 10 days, the THY activity is reduced in the hypothalamus and in the septum, compared with singly housed controls. The peripheral parameters of females show no differences between both groups.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnett, S.A., Eaton, J.C., McCallum, H.M.: Physiological effects of “social stress” in wild rats. II. Liver glycogen and blood glucose. J. psychosom. Res.4, 251–260 (1960)
Breese, G.R., Smith, R.D., Mueller, R.A., Howard, J.L., Prange, A.J., Jr., Lipton, M.A.: Induction of adrenal catecholamine synthesizing enzymes following mother — infant seperation. Nature (Lond.) New Biol.226, 94–96 (1973)
Buening, M.K., Gibb, J.W.: Influence of methamphetamine and neuroleptic drugs on tyrosine hydroxylase activity. Europ. J. Pharmacol.26, 30–34 (1974)
Cicero, T.J., Sharpe, L.G., Robins, E., Grote, S.S.: Regional distribution of tyrosine hydroxylase in rat brain. J. Neurochem.19, 131–137 (1972)
Coyle, J.T.: Tyrosine hydroxylase in rat brain — cofactor requirements, regional, and subcellular distribution. Biochem. Pharmacol.21, 1935–1944 (1972)
Fibiger, H.C., McGeer, E.G.: Effect of acute and chronic methamphetamine treatment and tyrosine hydroxylase activity in brain and adrenal medulla. Europ. J. Pharmacol.16, 176–180 (1971)
Frank, K., Raab, A.: Male and female mice living in differently-sized groups. I. Noradrenaline metabolism in discrete brain areas, open-field activity and corticoid release. J. comp. Physiol.99, 153–164 (1975)
Gutman, Y., Segal, J.: Effect of calcium, potassium and sodium on tyrosine hydroxylase activity in different regions of the rat brain. Biochem. Pharmacol.22, 865–868 (1973)
Henry, J.P., Ely, D.L., Watson, F.M.C., Stephens, P.M.: Ethological methods as applied to the measurement of emotion. In: Emotions — Their parameters and measurement (L. Levi, ed.), pp. 469–497. New York: Raven Press 1975
Henry, J.P., Stephens, P.M., Axelrod, J., Mueller, R.A.: Effect of psychosocial stimulation on the enzymes involved in the biosynthesis and metabolism of noradrenaline and adrenaline. Psychosom. Med.33, 227–237 (1971)
Hess, J.L., Denenberg, V.H., Zarrow, M.X., Pfeifer, W.D.: Modification of the plasma corticosterone response as a function of stimulation in infancy. Physiol. Behav.4, 109–111 (1969)
Hinde, R.A.: Animal behaviour. A synthesis of ethology and comparative psychology. New York-London: McGraw-Hill Book Company 1966
Holst, D. v.: Sozialer Streß bei Tupaias (Tupaia belangeri). Die Aktivierung des sympathischen Nervensystems und ihre Beziehung zu hormonal ausgelösten ethologischen Veränderungen. Z. vergl. Physiol.63, 1–58 (1969)
Holst, D. v.: Renal failure as the cause of death inTupaia belangeri exposed to persistent social stress. J. comp. Physiol.78, 236–273 (1972)
Kuczenski, R.T., Mandell, A.J.: Allosteric activation of hypothalamic tyrosine hydroxylase by ions and sulphated mucopolysaccharides. J. Neurochem.19, 131–137 (1972)
Kvetnansky, R., Gerwitz, G.P., Weise, V.K., Kopin, I.J.: Catecholamine synthesizing enzymes in the rat adrenal gland during exposure to cold. Amer. J. Physiol.220, 928–931 (1971)
Kvetnansky, R., Weise, V.K., Kopin, I.J.: Elevation of adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase and phenylethanolamine-N-methyl transferase by repeated immobilisation of rats. Endocrinology87, 744–749 (1970)
Lamprecht, F., Eichelmann, B., Thoa, N.B., Williams, R.B., Kopin, I.J.: Rat fighting behaviour: Serum dopamine-β-hydroxylase and hypothalamic tyrosine hydroxylase. Science177, 1214–1215 (1972)
Maengwyn-Davis, G.D., Johnson, D.G., Thoa, N.B., Weise, V.K., Kopin, I.J.: Influence of isolation and of fighting on adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase and phenylethanolamine-N-methyltransferase activities in three strains of mice. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.)28, 339–350 (1973)
Martin, R.D.: Reproduction and ontogeny in tree-shrews (Tupaia belangeri), with reference to their general behaviour and taxonomic relationships. Z. Tierpsychol.25, 409–495 and 505–532 (1968)
Musacchio, J.M., Julou, L., Kety, S.S., Glowinski, J.: Increase in rat brain tyrosine hydroxylase activity produced by electroconvulsive shock. Proc. N.A.S. 1117–1119 (1969)
Nagatsu, T., Levitt, M., Udenfriend, S.: A rapid and simple radioassay for tyrosine hydroxylase activity. Analyt. Biochem.9, 122–126 (1964)
Ng, L.K.J., Marsden, H.M., Colburn, R.W., Thoa, N.B.: Population density and social pathology in mice. Differences in catecholamine metabolism associated with differences in behavior. Brain Res.59, 323–330 (1973)
Pfeifer, W.D., Davies, L.C.: Effect of handling in infancy on responsiveness of adrenal tyrosine hydroxylase in maturity. Behav. Biol.10, 239–245 (1974)
Raab, A.: Der Serotoninstoffwechsel in einzelnen Hirnteilen vom Tupaia bei soziopsychischem Streß. Z. vergl. Physiol.75, 54–66 (1971)
Raab, A., Deisz, R.: Male and female mice living in differently-sized groups. II. Serotonin metabolism in discrete brain areas, open-field activity and corticoid release. J. comp. Physiol.99, 165–175 (1975)
Reis, D.J., Joh, D.H., Ross, R.A., Pickel, V.M.: Reserpine selectively increases tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine-β-hydroxylase enzyme protein in central noradrenergic neurons. Brain Res.81, 380–386 (1974)
Rose, R.M., Gordon, T.P., Bernstein, I.S.: Plasma testosterone levels in the male rhesus; influences of sexual and social stimuli. Science178, 643–645 (1972)
Rose, R.M., Holaday, J.W., Bernstein, I.S.: Plasma testosterone, dominance rank and aggressive behavior in male rhesus monkeys. Nature (Lond.)231, 366–368 (1971)
Sassenrath, E.N.: Increased adrenal responsiveness related to social stress in rhesus monkeys. Hormones Behav.1, 283–298 (1970)
Segal, D.S., Knapp, S., Kuczenski, R.T., Mandell, A.J.: The effects of environmental isolation on behavior and regional rat brain tyrosine hydroxylase and tryptophane hydroxylase activities. Behav. Biol.8, 57–63 (1973)
Thoenen, H.: Induction of tyrosine hydroxylase in peripheral and central adrenergic neurons by cold exposure of rats. Nature (Lond.)228, 861–862 (1970)
Thoenen, H., Oesch, F.: New enzyme synthesis as a long-term adaptation to increased transmitter utilisation. In: New concepts in neurotransmitter regulation (Mandell, A.J. ed.), pp. 33–52. New York: Plenum Press 1973
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work is supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Ra 210/1–4)
We wish to thank Prof. Dr. H. Autrum for permanent support and helpful critique
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raab, A., Storz, H. A long term study on the impact of sociopsychic stress in tree-shrews (Tupaia belangeri) on central and peripheral tyrosine hydroxylase activity. J. Comp. Physiol. 108, 115–131 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02169044
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02169044