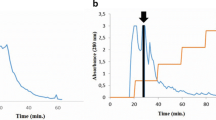
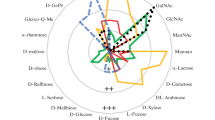
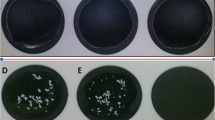
Abstract
Agglutinating antibodies toCoprococcus comes and three other obligately anaerobic coccoid rods from the intestinal flora are used in the diagnosis of Crohn's disease. Further studies on the pathogenetic role as well as the development of more sensitive and specific methods for detecting antibodies require extraction of the antigen fractions. Culturing methods to obtainC. comes with optimal antigen presentation and isolation of soluble antigen fractions were therefore developed. Hot water extraction of whole cells and subsequent removal of proteins with trichloroacetic acid provided a fraction that (1) absorbed serum agglutinins, (2) was useful for an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and (3) induced agglutinating antibodies in rats.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Boer WR, Kruyssen FJ, Wouters JTM (1976) The structure of teichoic acid fromBacillus subtilus var. niger WM as determined by 13C nuclear-resonance spectroscopy. Eur J Biochem 62:1–6
Ellwood DC (1970) The wall content and composition ofBacillus subtilus var. niger grown in a chemostat. Biochem J 118:367–373
Engvall E, Perlmann P (1972) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, ELISA. III. Quantitation of specific antibodies by enzyme-labeled anti-immunoglobulin in antigen-coated tubes. J Immunol 109:129–135
Ruseler-van Embden JGH, Both-Patoir HC (1983) Anaerobic gram-negative faecal flora in patients with Crohn's disease and healthy subjects. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 49:125–132
van de Merwe JP (1981) Agglutination ofEubacterium andPeptostreptococcus species as a diagnostic test for Crohn's disease. Hepatogastroenterology 28:155–156
van de Merwe JP, Schmitz PIM, Wensinck F (1981) Antibodies toEubacterium andPeptostreptococcus species and the estimated probability of Crohn's disease. J Hyg 87:25–33
Voller A, Bidwell DE, Huldt G, Engvall E (1974) A microplate method of ELISA and its application to malaria. Bulletin of the world health organization 51:209–211
Wensinck F, Ruseler-van Embden JGH (1971) The intestinal flora of colonization-resistant mice. J Hyg 69:413–421
Wensinck F, Custers-van Lieshout LMC, Poppelaars-Kustermans PAJ, Schröder AM (1981) The faecal flora of patients with Crohn's disease. J Hyg 87:1–12
Wensinck F, van de Merwe JP (1981) Serum agglutinins ofEubacterium andPeptostreptococcus species in Crohn's and other diseases. J Hyg 87:13–24
Wensinck F, van de Merwe JP, Mayberry JF (1983) An international study of agglutinins toEubacterium, Peptostreptococcus andCoprococcus species in Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis and control subjects. Digestion 27:63–69
Wicken AJ, Gibbens JW, Knox KW (1973) Comparative studies on the isolation of membrane lipoteichoic acid fromLactobacillus fermenti. J Bacteriol 113:365–372
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hazenberg, M.P., Pennock-Schröder, A.M. & van de Merwe, J.P. Culturing and extraction ofCoprococcus comes, absorption of serumagglutinins by soluble fractions and relation between agglutinins and antibodies in sera of patients with Crohn's disease. Med Microbiol Immunol 175, 299–306 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02126051
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02126051