Abstract
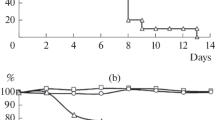
The ability of inactivated influenza A vaccines to induce serum HI antibody and immunity to challenge infection was studied in hamsters and in volunteers. Groups of hamsters were immunized with 200 IU of influenza virus A/Scotland/74, A/Port Chalmers/73, A/England/72, or A/Hong Kong/68. The serum HI antibody response of animals to, and immunity to challenge infection was directly related to the known relationship between the vaccine and test viruses. Thus, hamsters given A/Hong Kong/68 or A/England/72 vaccine produced serum HI antibody and immunity to A/Hong Kong virus infection, and animals given A/Scotland/74, A/Port Chalmers/73, and A/England/72 produced antibody and immunity to A/Scotland infection.
In a volunteer study, groups of students were immunized with 400 IU of the same vaccines as used above. The ability to infect these volunteers with WRL 105 virus given 4 weeks later was directly related to the vaccine-induced serum HI antibody to the challenge virus. The highest titers of serum HI antibody to A/Scotland virus were found in volunteers inoculated with homologous vaccine, lower titers were found in volunteers given A/Port Chalmers or A/England/ 72 vaccine and the lowest levels were seen in volunteers given A/Hong Kong/68 vaccine: the largest number of infections by the challenge virus was seen in volunteers given A/Hong Kong/68 vaccine, less were observed in volunteers given A/England/72 vaccine, and least were found in groups given A/Port Chalmers or A/Scotland/74 vaccine. Compared with the incidence of infection in volunteers given B/Hong Kong/73 vaccine, all groups given heterologous influenza A vaccines showed some immunity to challenge infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aymard-Henry, M., Coleman, M.T., Dowdle, W.R., Laver, W.G., Webster, R.G.: Influenza virus neuraminidase and neuraminidase-inhibition test procedures. Bull. WHO48, 199–202 (1973)
Bevan, A., Furminger, I.G.S., Smith, C.H.: Neuraminidase assay of influenza vaccines. Dev. Biol. Stand.28, 173–179 (1975)
Bradstreet, C.M.P., Taylor, C.E.D.: Technique of complement-fixation applicable to the diagnosis of virus diseases. Month. Bull. Min. Hlth. Lab. Serv.21, 96–104 (1962)
Foy, H.M., Cooney, M.K., McMahan, R., Bor, E., Grayston, J.T.: Single-dose monovalent A2/Hong Kong influenza vaccine. J.A.M.A.217, 1067–1071 (1971)
Freestone, D.S., Bowker, C.H., Letley, E., Ferris, R.D., White, W.G., Barnes, G.M.: A clinical trial of WRL 105 strain live attenuated influenza vaccine comparing four methods of intranasal vaccination. J. Hyg. (Camb.)76, 459–466 (1976)
Hobson, D.: Assessment of the efficacy of influenza vaccines against natural challenge. Dev. Biol. Stand.28, 285–294 (1975)
Hobson, D., Beare, A.S., Ward-Gardner, A.: Haemagglutination-inhibiting serum antibody titres as an index of response of volunteers to intranasal infection with live, attenuated strains of influenza virus. Proceedings of the Symposium on Live Influenza Vaccines, Zagreb, 1971. pp. 73–84 Yugoslav Acad. of Sci. Art. (1972)
Hoskins, T.W., Davies, J.R., Allchin, A., Miller, C.L., Pollock, T.M.: Controlled trial of inactivated influenza vaccine containing A/Hong Kong strain during an outbreak of influenza due to the A/England/42/72 strain. Lancet1973 II, 116–120
Jennings, R., Denton, M.D., Potter, C.W.: The hamster as an experimental animal for the study of influenza. 1. The role of antibody in protection. Med. Microbiol. Immunol.162, 217–226 (1976)
Jennings, R., Potter, C.W., McLaren, C.: Effect of preinfection and preimmunization on the serum antibody response to subsequent immunization with heterotypic influenza vaccines. J. Immunol.113, 1834–1843 (1974)
Meiklejohn, G., Kempe, C.H., Tahalman, W.G., Lennette, E.H.: Evaluation of monovalent influenza vaccines. Observations during an influenza A-prime epidemic. Am. J. Hyg.55, 12–21 (1952)
Moffatt, M.A.J., Stealey, V.M., Freestone, D.S., MacDonald, A.: Assessment of elicited antibody responses, clinical reactions and transmissibility of WRL 105 live influenza vaccine. J. Biol. Stand.4, 92–95 (1976)
Morris, C.A., Freestone, D.S., Stealey, V.M., Oliver, P.R.: Recombinant WRL 105 strain live attenuated influenza vaccine. Lancet1975 II, 196–199
Pereira, M.S., Chakraverty, P., Schild, G.C., Coleman, M.T., Dowdle W.R.: Prevalence of antibody to current influenza viruses and effect of vaccination on antibody response. Brit. Med. J.1972 IV, 701–703
Potter, C.W., Jennings, R., McLaren, C., Edey, D., Stuart-Harris, C.H., Brady, M.: A new surface-antigen-adsorbed influenza virus vaccine. II. Studies in a volunteer group. J. Hyg. (Camb.)75, 353–362 (1975)
Potter, C.W., Rees, R.C., Shore, S.L., McLaren, C.: Immunity to influenza in ferrets IX Delayed hypersensitivity following infection or immunization with A2/Hong Kong virus. Microbios.10, 7–21 (1974)
Ruben, F.L., Johnston, F., Streiff, E.J.: Immunity in a partially immunized aged population. Effectiveness of killed Hong Kong vaccine against infection with the England strain. J.A.M.A.230, 863–866 (1974)
Schild, G.C., Oxford, J.S., Dowdle, W.R., Coleman, M.T., Pereira, M.S., Chakraverty, P.: Antigenic variation in current influenza A viruses. Evidence of a high frequency of antigenic drift in the Hong Kong virus. Bull. WHO51, 1–11 (1974)
Sever, J.L.: Application of a microtechnique to viral serological investigations. J. Immunol.88, 320–329 (1962)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Potter, C.W., Jennings, R. & Nicholson, K. Immunity to influenza virus infection induced by heterologous, inactivated vaccines. Med Microbiol Immunol 166, 99–108 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02121139
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02121139