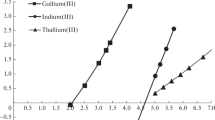
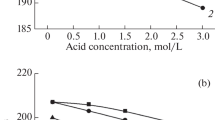
Summary
For the determination of heavy metals in biological material, especially lead and thallium, atomic absorption spectrophotometry with a heatable graphite atomizer (HGA) is recommended. Because of matrix effects caused by the iron content of blood the calibration curves are rather flat and correspondingly imprecise. Such matrix effects can be avoided by adding lanthanium salts. For precise determinations of heavy metals, e.g. normal content of lead in human blood, a preliminary dry ashing procedure with activated oxygen in a HF-induction furnace is suggested. Linear extinction versus concentration is given from 5–150 μg/100 g (0.05–1.5 ppm).
Zusammenfassung
Zur Bestimmung von Schwermetallen in biologischem Material, insbesondere von Blei und Thallium, empfiehlt sich die Atomabsorptionsspektrophotometrie mit heizbarer Graphitrohrküvette (HGA). Die Matrixeinflüsse, bedingt durch den Eisengehalt im Blut, ergeben relativ flache Eichgerade und damit stark streuende Werte. Dieser störende Einfluß kann durch Zusatz von Salzen, vorzugsweise Lanthansalze, behoben werden. Für genaueste Bestimmungen, z. B. der Normalgehalte von Blei im menschlichen Blut, wird eine vorhergehende Veraschung in einer Hochfrequenzanlage mit aktiviertem Sauerstoff empfohlen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Amos, M. D., Benett, P. A., Brodie, K. G., Lung, P. W. Y., Matousek, J. P.: Carbon rod atomizer in atomic absorption and fluorescence spectrometry and its clinical application. Analyt. Chem.43, 211 (1971).
Ediger, R. D., Coleman, R. L.: A modified delves cup atomic absorption procedure for the determination of lead in blood. Atomic Absorption Newsletter11, 33 (1972).
Hauck, G.: Blutbleibestimmung mittels Röntgenfluorescenz. Dtsch. Z. ges. gerichtl. Med.55, 140 (1964).
Hessel, D. W.: A simple and rapid quantitative determination of lead in blood. Atomic Absorption Newsletter7, 55 (1968).
Heyrovsky, J.: Polarographie. Wien: Springer 1941.
Hwang, J. Y., Ullucci, P. A., Smith, St. B., Jr., Malenfant, A. L.: Microdetermination of lead in blood by flameless atomic absorption spectrometry. Analyt. Chem.43, 1319 (1971).
Iwantscheff, G.: Das Dithizon und seine Anwendung in der Mikro- und Spurenanalyse. Weinheim: Verlag Chemie 1958.
Kahn, H. L., Peterson, G. E., Schallis, J. E.: Atomic absorption microsampling with the “sampling boat” technique. Atomic Absorption Newsletter7, 35 (1968).
L'Vov, B. V.: The analytical use of atomic absorption spectra. Spectrochim. Acta17, 761 (1961).
L'Vov, B. V.: Potentialities of the graphite crucible method in atomic absorption spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta24 B, 53 (1969).
Manning, D. C., Fernandez, F.: Atomization for atomic absorption using a heated graphite tube. Atomic Absorption Newsletter9, 65 (1970).
Massmann, H.: Vergleich von Atomabsorption und Atomfluorescenz in der Graphitküvette. Spectrochim. Acta23 B, 215 (1968).
Matousek, J. P., Stevens, B. J.: Biological application of the carbon rod atomizer in atomic absorption spectroacopy. Clin. Chem.17, 363 (1971).
Morrison, G. H.: Microanalysis of solids by atomic absorption and emission spectroscopy using an R. F. Furnace. Analyt. Chem.42, 809 (1970).
Neeb, R.: Inverse Polarographie und Voltametrie. Weinheim: Verlag Chemie 1969.
Neuninger, H., Machata, G.: Der Nachweis von Metallgiften. Beitr. gerichtl. Med.26, 235 (1969).
Pfeilsticker, K.: Eine spektrochemische Mikrobestimmung des Bleis in biologischem Material. Mikrochim. Acta1956, 320.
Slavin, W.: Atomic absorption spectroscopy. New York: Wiley-Interscience Inc. 1968.
Weinig, E., Neugebauer, G., Neugebauer, I.: Polarographische Bleibestimmung in Blut und Harn. Arch. Hyg.(Berl.)139, 551 (1955).
Welz, B., Wiedeking, E.: Bestimmung von Spurenelementen in Serum und Urin mit flammen-loser Atomisierung. Z. analyt. Chem.252, 111 (1970).
Willis, J. B.: The analysis of biological material by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Clin. Chem.11, 251 (1965).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Prof. Dr. G. Dotzauer zum 60. Geburtstag herzlichst gewidmet.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Machata, G., Binder, R. Bestimmung von Blei-, Thallium-, Zink- und Cadmiumspuren in biologischem Material mittels flammenloser Atomabsorption. Z Rechtsmed 73, 29–34 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02114771
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02114771