Summary
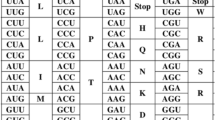
We have calculated the average effect of changing a codon by a single base for all possible single-base changes in the genetic code and for changes in the first, second, and third codon positions separately. Such values were calculated for an amino acid's polar requirement, hydropathy, molecular volume, and isoelectric point. For each attribute the average effect of single-base changes was also calculated for a large number of randomly generated codes that retained the same level of redundancy as the natural code. Amino acids whose codons differed by a single base in the first and third codon positions were very similar with respect to polar requirement and hydropathy. The major differences between amino acids were specified by the second codon position. Codons with U in the second position are hydrophobic, whereas most codons with A in the second position are hydrophilic. This accounts for the observation of complementary hydropathy. Single-base changes in the natural code had a smaller average effect on polar requirement than all but 0.02% of random codes. This result is most easily explained by selection to minimize deleterious effects of translation errors during the early evolution of the code.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alff-Steinberger C (1969) The genetic code and error transmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 64:584–591
Blalock JE, Smith EM (1984) Hydropathic anti-complementarity of amino acids based on the genetic code. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 121:203–207
Brentani RR (1988) Biological implications of complementary hydropathy of amino acids. J Theor Biol 135:495–499
Brentani RR (1990) Complementary hydropathy and the evolution of interacting peptides. J Mol Evol 31:239–243
Bulmer M (1988) Evolutionary aspects of protein synthesis. Oxf Surv Evol Biol 5:1–40
Crick FHC (1968) The origin of the genetic code. J Mol Biol 38:367–379
Di Giulio M (1989a) Some aspects of the organization and evolution of the genetic code. J Mol Evol 29:191–201
Di Giulio M (1989b) The extension reached by the minimization of the polarity distances during the evolution of the genetic code. J Mol Evol 29:288–293
Epstein CJ (1966) Role of the amino-acid ‘code’ and of selection for conformation in the evolution of proteins. Nature 210:25–28
Garel JP, Filliol D, Mandel P (1973) Coéfficients de partage d'aminoacides, nucléobases, nucléosides et nucléotides dans un système solvant salin. J Chromatography 78:381–391
Gibson TJ, Lamond AI (1990) Metabolic complexity in the RNA world and implications for the origin of protein synthesis. J Mol Evol 30:7–15
Goldberg AL, Wittes RE (1966) Genetic code: aspects of organization. Science 153:420–424
Grantham R (1974) Amino acid difference formula to help explain protein evolution. Science 185:862–864
Kurland CG (1987) Strategies for efficiency and accuracy in gene expression. 2. Growth optimized ribosomes. Trends Biochem Sci 12:169–171
Kyte J, Doolittle RF (1982) A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol 157:105–132
Lagerkvist U (1980) Codon misreading: a restriction operative in the evolution of the genetic code. Am Sci 68:192–198
Salemme FR, Miller MD, Jordan SR (1977) Structural convergence during protein evolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:2820–2824
Sjöström M, Wold S (1985) A multivariate study of the relationship between the genetic code and the physical-chemical properties of amino acids. J Mol Evol 22:272–277
Sonneborn TM (1965) Degeneracy of the genetic code: extent, nature, and genetic implications. In: Bryson V, Vogel HJ (eds) Evolving genes and proteins. Academic Press, New York, pp 377–397
Weber AL, Lacey JC (1978) Genetic code correlations: amino acids and their anticodon nucleotides. J Mol Evol 11:199–210
Woese CR (1965) On the evolution of the genetic code. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 54:1546–1552
Woese CR (1973) Evolution of the genetic code. Naturwissenschaften 60:447–459
Woese CR, Dugre DH, Dugre SA, Kondo M, Saxinger WC (1966) On the fundamental nature and evolution of the genetic code. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 31:723–736
Wong JT-F (1980) Role of minimization of chemical distances between amino acids in the evolution of the genetic code. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:1083–1086
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haig, D., Hurst, L.D. A quantitative measure of error minimization in the genetic code. J Mol Evol 33, 412–417 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02103132
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02103132