Abstract
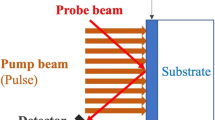
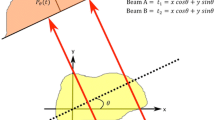
Photothermal deflection is among the most sensitive techniques available for the measurement of small, localized heating, such as that from the absorption of a focused laser beam in the bulk or surface of a material. A thin optical probe beam is deflected by the refractive-index gradients arising from the heating, and the size of the deflection provides the measure of the heating. We describe the use of a critical fluid to enhance the sensitivity of the technique by at least 103. The diverging coefficient of thermal expansion of a pure fluid near the gas-liquid critical point gives this dramatic enhancement when used as a sensing fluid. With sensitivity calculations and measurements in supercritical xenon,T c≈16.7‡C, we show that the noise floor of our apparatus when used for surface absorption measurements corresponds to a fractional power absorbed ofP absorbed/P incident=10−10, while the noise floor for bulk measurements corresponds to an absorption coefficientα=10−13 cm−1. We report the first measurements of the surface absorption of superpolished surfaces of sapphire and fused quartz,P a/P i≈2×10−5, and the first measurements of the bulk absorption in xenon,α≈2×10−6 cm−1. We also show how the present work fits into the current status of absorption measurement techniques and describe the effects of the peculiar properties of critical fluids on the execution of photothermal deflection measurements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
For a comprehensive list of photothermal applications, seePhotoacoustic and Photothermal Phenomena II, J. C. Murphy, J. W. Maclachlan Spicer, L. C. Aamodt, and B. S. H. Royce, eds. (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1991).
M. E. Briggs and R. W. Gammon, submitted for publication.
A. C. Boccara, D. Fournier, W. Jackson, and N. M. Amer,Opt. Lett. 5:377 (1980).
United Detector Technologies (UDT) Corporation 1223 Detector head and 431 analog processing electronics, with a 4-kHz bandwidth.
W. B. Jackson, N. M. Amer, A. C. Boccara, and D. Fournier,Appl. Opt. 20:1333 (1981).
M. V. Klein,Optics (Wiley, New York, 1970).
A. Onuki, H. Hao, and R. A. Ferrell,Phys. Rev. A 41:2256 (1990).
H. Boukari, J. N. Shaumeyer, M. E. Briggs, and R. W. Gammon,Phys. Rev. A 41:2260 (1990).
D. Fournier and A. C. Boccara, inPhotothermal Investigations of Solids and Fluids, J. A. Sell, ed. (Academic Press, San Diego, CA, 1989).
M. Commandré and E. Pelletier,Appl. Opt. 29:4276 (1990).
M. R. Moldover, J. V. Sengers, R. W. Gammon, and R. J. Hocken,Rev. Mod. Phys. 51:79 (1979).
H. E. Stanley,Introduction to Phase Transitions and Critical Phenomena (Oxford, New York, 1971).
R. Gupta, inPrinciples and Perspectives of Photothermal and Photoacoustic Penomena, A. Mandelis, ed. (Elsevier, New York, 1992).
PMS Corporation, Boulder, CO, U.S.A.
J. V. Sengers and J. M. H. Levelt Sengers,Amu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 37:189 (1986).
A. C. Boccara and D. Fournier, inPrinciples and Perspectives of Photothermal and Photoacoustic Phenomena, A. Mandelis, ed. (Elsevier, New York, 1992).
D. E. Gray (ed.),AIP Handbook of Physics, 3rd ed. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1972).
R. C. Weast (ed.),CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics, 60th ed. (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1980).
W. L. Wolf, inHandbook of Optics, W. G. Driscoll and W. Vaugham, eds. (McGraw-Hill, New York, 1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Briggs, M.E., Gammon, R.W. Photothermal deflection in a supercritical fluid. Int J Thermophys 16, 1439–1453 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02083552
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02083552