Abstract
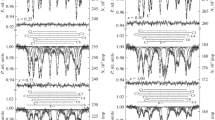
The strong, and heretofore unexplained, dependence of the magnetic properties of the R-type hexaferrites MX2Fe4O11 on heat treatment has been investigated by means of57Fe and119Sn Mössbauer spectroscopy at 297 K.57Fe Mössbauer spectra of samples of BaTi2Fe4O11, BaSn2Fe4O11, and SrSn2Fe4O11, annealed at several temperatures consist of three partially resolved quadrupole doublet patterns. The pattern with the very large quadrupole splitting, i.e. 1.3 mm s−1 ≤ δE Q ≤ 1.7 mm s−1, is readily assigned to the trigonal bipyramidal site, and exhibits no dependence of its parameters, including the relative intensity, on heat treatment. The remaining two patterns are assigned to Fe3+ ions on octahedral sites, and exhibit relative intensities that are strongly dependent on heat treatment. The119Sn spectrum of BaSn2Fe4O11 is a broad, apparently single line that, with the exception of verifying the presence of tin as Sn4+, provides little insight into the details of the structure. The distributions of the cations over all the lattice sites have been deduced from the Mössbauer spectra and compared with the magnetic susceptibility data. It is concluded that the cation distributions of the Sn-containing phase are not strongly dependent on heat treatment, and the magnetic properties exhibit a similar insensitivity to heat treatment. The Ti analogs exhibit a strong dependence of cation distribution on heat treatment, which is reflected in widely varying magnetic ordering temperatures, a variation that is confirmed by the incipient magnetic hyperfine splitting despite the strong magnetic frustration in the R-type hexaferrites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E. Kneller, M. Velicescu and F. Haberey, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 7(1978)49.
X. Obradors, A. Collomb, J. Pannetier, A. Isalgué, J. Tejada and J.C. Joubert, Mater. Res. Bull. 18(1983)1543.
T. Birchall and C. Hallett, Solid State Commun. 56(1985)77.
K. Iwauchi and Y. Ikeda, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 59(1986)73.
K. Iwauchi, Y. Ikeda, N. Koizumi and Y. Bando, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 31–34(1983)1384.
M.C. Cadée and D.J.W. Ijdo, J. Solid State Chem. 52(1984)302.
B.J. Evans, F. Grandjean, A.P. Lilot, R.H. Vogen and A. Gérard, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 67(1987)123.
L. Pauling,The Nature of the Chemical Bond (Cornell University Press, Ithaca, 1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thompson, G.K., Evans, B.J. Structure-property relationships in the R-type hexaferrites: Cation distributions and magnetic susceptibilities of MX2Fe4O11 . Hyperfine Interact 94, 2039–2044 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02063737
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02063737