Abstract
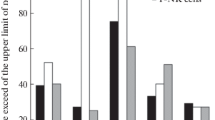
The occurrence of atypical lymphocytes has been observed in the course of experimental acute infection withCandida albicans in mice. In animals injected intravenously with 2.5 × 106 ofCandida albicans cells, an increased number of monocytes was seen in 24 hours. Monocytes showed toxic vacuolisation in most instances in protoplasm and sometimes in the nuclei. Only a few atypical lymphocytes could be seen at that time. In the following days the number of monocytes diminished and the number of atypical lymphocytes increased. After four days atypical lymphocytes constituted frequently over 20 % of white cells. The autopsy of sacrificed or dead animals with the presence of such elevated percentages of atypical lymphocytes showed enlargement of cervical lymphnodes in all animals. In mice infected with 1.4 × 103 ofCandida albicans cells, no level higher than 12% of atypical lymphocytes was seen. Pictures were returning to normal with only a few atypical lymphocytes present among the animals which survived for two months after infection withCandida albicans.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bender, C. E. (1957) Interpretation of Hematologic and Serologic findings in the diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis.Annals of Internal Medicine, 49:852–865.
Benyesh-Melnick, M., Smith, K. O. &Fernback, D. L. (1964) Electron microscopic findings in children with acute leukemia and in children with infectious mononucleosis.J. Nat. Cancer Inst. 33:571–579.
Downey, H. &McKinley, C. A. (1923) Acute lymphadenosis compared with acute lymphatic leukemia.Arch. Intern. Med. 32:82–112.
Finch, S. C. (1969) In monograph “Infectious Mononucleosis” ed. byCarter, R. L. &Penman, H. G. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford and Edinburgh. pp 47.
Gowans, J. L. &McGregor, D. D. (1965) The immunological activities of lymphocytes.Progr. allergy 9:1–78.
Henle, G., Henle, W. &Diehl, V. (1968) Relation ofBurkitt tumor associated herpes-type virus to infectious mononucleosis.Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 59:94.
Hoagland, R. J. (1967) Infectious Mononucleosis. Grune & Stratton, Inc., New York.
Klemola, E., Kääriäinen, L. (1965) Cytomegalovirus as a possible cause of a disease resembling infectious mononucleosis.Brit. Med. J. 2:1099–1102.
Klemola, E., von Essen, R., Henle, G. &Henle, W. (1970) Infectious-mononucleosis-like disease with negative heterophile agglutination test. Clinical features in relation toEpstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus antibodies.J. Infect. Diseasls 121:608–613.
Kääriäinen, L., Klemola, E. &Paloheimo, J. (1966) Rise of cytomegalovirus antibodies in an infectious-mononucleosis-like syndrome after transfusion.Brit. Med. J. 1:1270–1272.
Litwins, J., Leibowitz, S. (1951) Abnormal lymphocytes (“virocytes”) in virus diseases other than infectious mononucleosis.Acta haemat. 5:223–231.
Mankowski, Z. T. (1963) Occurrence of malignancy, collagen diseases and myasthenia gravis in the course of experimental infections withCandida albicans.Mycopath. et Mycol. appl. 19:1–18.
Mankowski, Z. T. (1966) Blood changes and fertility derangements following the injection ofCandida albicans into the spleen of the experimental animals (occurence of hypersplenism).Mycopathologia et Mycologia Applicata 30:59–71.
Mankowski, Z. T. (1968) Production of glycoprotein byCandida albicans in a synthetic medium and its influence on the growth of newborn mice.Mycopath. et Mycol. appl. 34:123–118.
Mankowski, Z. T. (1970) Influence ofCandida albicans glycoprotein on 3-methylcholanthrene induced malignancy in newborn rodents.Mycopath. et Mycol. appl. 41:167–176.
Osgood, E. E. (1935) Fenestration of nuclei of lymphocytes; A new diagnostic sign in infectious mononucleosis.Proc. Soc. Exper. Biol. and Med. 33:218.
Paul, J. R. &Bunnell, W. W. (1932) The presence of heterophile antibodies in infectious mononucleosis.Am. J. Med. Sci. 183:90–104.
Penman, H. G. (1969) In monograph “Infectious Mononucleosis” ed, byCarter, R. L. &Penman, H. G. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford and Edinburgh. pp 201.
Sprunt, T. &Evans, F. A. (1920) Mononuclear leucocytosis in reaction to acute infections.Bul. John Hopkins Hosp. 31:410.
Wood, A. T. &Frenkel, E. P. (1967) The atypical lymphocytes.Amer. J. of Med. 42:923–936.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported partially byDora Kaplan, Joan Sloan, Cathy Cooper. Memorial Funds and the Roon Foundation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mankowski, Z.T. Occurrence of atypical lymphocytes following intravenous injection of Candida albicans in mice. Mycopathologia et Mycologia Applicata 45, 243–251 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02051971
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02051971