Abstract
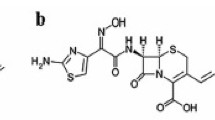
A rapid and reliable method for the quantitative determination of cefmenoxime in serum and urine by reversed phase high-performance liquid chromatography is described. Serum was deproteinized with acetonitrile. Urine was diluted with dilute acetic acid (17.5 mmol/l). Separations were performed in isocratic mode using a C18 type column and a precolumn packed with Perisorb RP/8. The eluant consisted of a mixture of acetonitrile and 25.0 mmol/l acetic acid in a ratio of 32/69 (vol/vol). In normal subjects cefmenoxime was well separated from endogenous compounds and various added drugs. Its complete separation was confirmed by selective degradation with beta-lactamase fromBacillus cereus and UV spectrophotometry. The detection limit was 0.3 mg/l at a detection wave-length of 254 nm. Peak areas gave linear results up to concentrations of 500 mg/l. Within-batch precision (coefficient of variation) ranged from 1.1 to 6.2 %. Recovery rates varied from 99.0 to 103.3%. Results of a standard microbiological assay correlated well with those obtained by the present HPLC method. Eight healthy volunteers who were given a single intravenous dose of 1 g cefmenoxime excreted 86.3 ± 5.8 % of the unchanged drug within 24 h in urine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsuchiya, K.: Cefsulodin (SCE-129), cefotiam (SCE-963), and cefmenoxime (SCE-1365). In: Mitsuhashi, S. (ed.): Beta-lactam antibiotics. Springer, Berlin, 1981, p. 107–119.
Tsuchiya, K., Kondo, M., Kida, M., Nakao, M., Iwahi, T., Nishi, T., Noji, Y., Takeuchi, M., Nozaki, Y.: Cefmenoxime (SCE-1365), a novel broadspectrum cephalosporin: in vitro and in vivo antibacterial activities. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1981, 19: 56–65.
Stamm, J. M., Girolami, P. L., Shipkowitz, N. L., Bower, R. R.: Antimicrobial activity of cefmenoxime (SCE-1365). Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1981, 19: 454–460.
Reeves, R. S., Bywater, M. J.: Assay of antimicrobial agents. In: De Louvois, J. (ed.): Selected topics in clinical bacteriology. Bailliere Tindall, London, 1976, p. 21–78.
Sachs, L.: Angewandte Statistik. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1974.
Averdunk, R., Borner, K.: Korrelation der Thromboplastinzeiten bei Dicumarol-behandelten Patienten unter Verwendung verschiedener Thrombokinase-Präparate. Zeitschrift für Klinische Chemie und Klinische Biochemie 1970, 8: 263–268.
Granneman, G. R., Senello, L. T., Steinberg, F. J., Sonders, R. C.: Intramuscular and intravenous pharmacokinetics of cefmenoxime, a new broadspectrum cephalosporin, in healthy subjects. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1982, 21: 141–145.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Borner, K., Borner, E., Lode, H. et al. Determination of cefmenoxime in human body fluids by high-performance liquid chromatography. Eur. J, Clin. Microbiol. 2, 17–21 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02019917
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02019917