Abstract
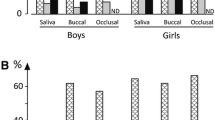
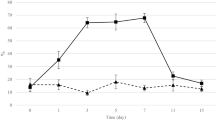
Erythromycin and clindamycin were given orally to ten subjects in recommended doses for seven days in order to study the effects of these antibiotics on human flora. Saliva and faecal specimens were collected for up to 29 days after administration of the antibiotics. Erythromycin caused only minor changes in the saliva flora while the aerobic and anaerobic colon flora were considerably disturbed. Clindamycin depressed both the anaerobic saliva and colon flora. Both erythromycin and clindamycin induced new colonization of the oral cavity and colon. The levels of free volatile fatty acids sank in saliva and faeces when erythromycin and clindamycin were given. The ecological disturbances caused by antibiotics require further investigation and should be taken into consideration in therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bonhoff, M., Miller, C. P., Martin, W. R.: Resistances of the mouse's intestinal tract to experimentalSalmonella infections. Journal of Experimental Medicine 1964, 120: 805–816.
Van der Waaij, D., Vossen, J. M., Korthals Altes, C., Hartgrink, C.: Reconventionalization following antibiotic decontamination in man and animals. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1977, 30: 1887–1895.
Simon, C., Harhausen, S.: Erythromycin in upper respiratory tract infections. Current Medical Research Opinion 1980, 6, Suppl. 8: 48–53.
Fraser, D. W., Tsai, T. R., Orenstein, W., Parkin, W. E., Beecham, H. J., Sharrar, R. G., Harris, J., Mattison, G. F., Martin, S. M., McDade, J. E., Shepard, C. C., Brachman, P. S. and the field investigation team: Legionnaire's disease. New England Journal of Medicine 1977, 297: 1189–1197.
Miguéres, J., Jover, A.: Respiratory infections due toMycoplasma pneumoniae in the adult patient. Current Medical Research Opinion 1980, 6, Suppl. 8: 73–76.
Watt, B.: Erythromycin and anaerobes: in vitro aspects. Scottish Medical Journal 1977, 22: 389–391.
Bartlett, J. G., Sutter, V. L., Finegold, S. M.: Treatment of anaerobic infections with lincomycin and clindamycin. New England Journal of Medicine 1972, 16: 1006–1010.
Rodriguez, W., Ross, S., Kalm, W., McKay, D., Moskowitz, P.: Clindamycin in the treatment of osteomyelitis in children. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1977, 131: 1088–1093.
Heimdahl, A., von Konow, L., Nord, C. E.: Isolation of beta-lactamase producingBacteroides strains associated with clinical failures with penicillin treatment of human orofacial infections. Archives of Oral Biology 1980, 25: 689–692.
Hartley, C. L., Clements, H. M., Linton, K. B.: Effect of cephalexin, erythromycin and clindamycin on the aerobic gram-negative faecal flora in man. Journal of Medical Microbiology 1977, 11: 125–135.
Bystedt, H., Dahlbäck, A., Dornbusch, K., Nord, C. E.: Concentrations of azidocillin, erythromycin, doxycline and clindamycin in human mandibular bone. International Journal of Oral Surgery 1978, 7: 442–449.
Simon, C., Clasen, I.: Sputum levels of erythromycin after single and repeated oral administration in adult patients with bronchitis. Current Medical Research Opinion 1978, 5, Suppl. 2: 19–22.
Jalling, B., Malmborg, A. S., Lindman, A., Boréus, L. O.: Evaluation of a micromethod for determination of antibiotic concentrations in plasma. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1972, 4: 150–157.
Heimdahl, A., Nord, C. E., Weilander, K.: Effect of bacampicillin on human mouth, throat and colon flora. Infection 1979, 7, Suppl. 5: 446–451.
Holdeman, L. V., Cato, E. C., Moore, W. E. C.: Anaerobe laboratory manual. Virginia Polytechnic Institute, Blacksburg, 1977.
Dornbusch, K., Nord, C. E., Wadström, T.: Biochemical characterization and in vitro determination of antibiotic susceptibility of clinical isolates ofBacteroides fragilis. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1974, 6: 253–257.
Eriksson, H. M., Sherris, J. C.: Antibiotic sensitivity testing. Report of an international collaborative study. Acta Pathologica Microbiologica Scandinavica 1971, Suppl. 217: 35–37.
Bartlett, J. G., Chang, T. W., Gurwith, M., Gorbach, S. L., Onderdonk, A, B.: Antibiotic-associated pseudomembranous colitis due to toxinproducing clostridia. New England Journal of Medicine 1978, 298: 531–534.
Heimdahl, A., Nord, C. E., Okuda, K.: Effect of tinidazole on the oral, throat and colon microflora of man. Medical Microbiology and Immunology 1980, 168: 1–10.
Drasar, B. S., Hill, M. J.: Human intestinal flora. Academic Press, London, 1974.
Kagan, B. M.: Antimicrobial therapy. Saunders, Philadelphia, 1980.
Kwok, Y. Y., Sutter, V. L., Oberhammer, I., Finegold, S. M.: The susceptibility of anaerobic bacteria to rosamycin, erythromycin and clindamycin and factors affecting the activity of rosamycin. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy 1979, 5: 61–66.
Leigh, D. A., Simmons, K.: Effect of clindamycin and lincomycin therapy on faecal flora. Journal of Clinical Pathology 1978, 31: 439–443.
Nichols, R. L., Condon, R. E., Di Santo, A. R.: Preoperative bowel preparation. Archives of Surgery 1977, 112: 1493–1496.
Möllby, R., Nord, C. E., Aronsson, B.: Diagnosis ofClostridium difficile associated enterocolitis in Sweden. Laboratory and epidemiological aspects. Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1980, 22: 30–36.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heimdahl, A., Nord, C.E. Effect of erythromycin and clindamycin on the indigenous human anaerobic flora and new colonization of the gastrointestinal tract. Eur. J, Clin. Microbiol. 1, 38–48 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02014139
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02014139