Abstract
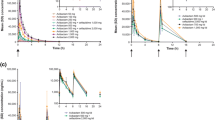
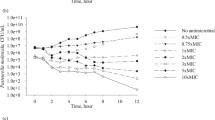
Experimental examples of different beta-lactam-organism combinations in vitro and in vivo are presented to demonstrate that a rationale for dosage regimens of antibiotics should not be based solely on pharmacokinetic parameters. The time course of the pharmacological response (onset and speed of bacterial killing) and the presence or absence of a postantibiotic effect must also be considered. Such pertinent information can be derived from in vitro studies such as time-kill curves and regrowth curves of bacteria obtained at and after short exposure of the target organisms to various concentrations of the drug.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gerber, A. U., Craig, W. A., Brugger, H. P., Feller, C., Vastola, A. P., Brandel, J.: Impact of dosing intervals on the activity of gentamicin and ticarcillin againstPseudomonas aeruginosa in leukopenic mice. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1983, 147: 910–917.
Bundtzen, R. W., Gerber, A. U., Cohn, D., Craig, W. A.: Postantibiotic suppression of bacterial growth. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1981, 3: 28–37.
Gerber, A. U., Craig, W. A.: Aminoglycoside selected subpopulations ofPseudomonas aeruginosa. Characterization and virulence in normal and leukopenic mice. Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine 1982, 100: 671–681.
Gerber, A. U., Craig, W. A.: Experimentelle Studien zur Frage des optimalen Dosisintervalls in der Antibiotikatherapie. Schweizerische Medizinische Wochenschrift 1982, 112: 42–45.
Hunter, P. A., Rolinson, G. N., Witting, D. A.: Effect of carbenicillin on pseudomonas infection. In: Williams, J. D., Geddes, A. M. (ed.): Chemotherapy. Volume 2 Plenum Press, New York, 1976, p. 289–293.
Ryan, D. M., Cars, O.: Antibiotic assays in muscle: Are conventional tissue levels misleading as indicator of the antibacterial activity? Scandinavian Journal of Infectious Diseases 1980, 12: 307–309.
Gerber, A. U., Vastola, A. P., Brandel, J., Craig, W. A.: Selection of aminoglycoside-resistant subpopulations ofPseudomonas aeruginosa in an in vivo model. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1982, 146: 691–697.
Barza, M., Brusch, J., Bergeron, M. G., Weinstein, L.: Penetration of antibiotics into fibrin loci in vivo. III. Intermittent versus continuous infusion and the effect of probenecid. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1973, 129: 73–78.
Bergeron, M. G., Beauchamp, D., Poisier, A., Bastille, A.: Continuous versus intermittent administration of anti-microbial agents: tissue penetration and efficacy in vivo. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1981, 3: 84–97.
Pennington, J. E.: Penetration of antibiotics into respiratory secretions. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1981, 3: 67–73.
Brugger, H. P., Gerber, A. U., Feller, C.: The impact of half-life on the activity of netilmicin againstPseudomonas aeruginosa in vivo. In: Spitzy, K. H., Karrer, K.: Proceedings of the 13th International Congress of Chemotherapy. Volume 117, Egermann, Vienna 1983, p. 22–25.
Powell, S. H., Thompson, W. L., Luthe, M. A., Stern, R. C., Grossniklaus, D. A., Bloxham, D. D., Groden, D. L., Jacobs, M. R., DiScenna, A. O., Cash, H. A., Klinger, J. D.: Once-daily versus continuous aminoglycoside dosing: efficacy and toxicity in animal and clinical studies of gentamicin, netilmicin, and tobramycin. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1983, 147: 918–932.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerber, A.U., Feller, C. & Brugger, H.P. Time course of the pharmacological response to beta-lactam antibiotics in vitro and in vivo. Eur. J, Clin. Microbiol. 3, 592–597 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02013630
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02013630