Abstract
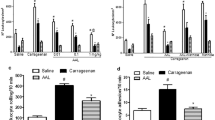
The anti-inflammatory effect of glucocorticoids has been investigated in two standard models of experimental inflammation, i.e. rat paw oedema induced by carrageenin or dextran.
Both types of oedema are suppressed by dexamethasone while indomethacin and BW755C only suppress carrageenin oedema.
Dexamethasone inhibits dextran oedema according to the accepted mode of action of steriod hormones since the inhibition occurs after a 2–3 h time lag and is abolished by pretreating animals with actinomycin D. Dextran oedema and carrageenin oedema are also controlled by endogenous corticoids since adrenalectomy potentiates the paw oedema formation induced by low concentrations of phlogogenic agents.
It has been shown that glucocorticoids induce bothin vitro andin vivo the formation and release of antiphospholipase proteins which are anti-inflammatory in that they greatly suppress carrageenin oedema. However, these proteins have no effect on dextran oedema.
We conclude that the inhibition of dextran oedema by glucocorticoids depends on the formation of another type of anti-inflammatory protein.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Carnuccio, M. Di Rosa andP. Persico,Hydrocortisone induced inhibitor of prostaglandin biosynthesis in rat leucocytes, Br. J. Pharmac.68, 14–16 (1980).
G.J. Blackwell, R. Carnuccio, M. Di Rosa, R.J. Flower, L. Parente andR. Persico,Macrocortin: a polypeptide causing the anti-phospholipase effect of glucocorticoids,Nature, Lond. 287, 147–149 (1980).
F. Hirata, E. Schiffman, K. Venkatasubramanian, D. Salomon andJ. Axelrod,A phospholipase A 2 inhibitory protein in rabbit neutrophils induced by glucocorticoids. Proc. Natn. Acad. Sci. USA77, 2533–2536 (1980).
J.F. Cloix, O. Colard, B. Rothhut andF. Russo-Marie,Characterization and partial purification of ‘renocortins’: two polypeptides formed in renal cells causing the anti-phospholipase-like action of glucocorticoids, Br. J. Pharmac.79, 313–321 (1983).
F. Hirata, Y. Notsu, M. Iwata, L. Parente, M. Di Rosa andR.J. Flower,Identification of several species of phospholipase inhibitory protein(s) by radioimmunoassay for lipomodulin, Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun.109, 223–230 (1983).
G.J. Blackwell, R. Carnuccio, M. Di Rosa, R.J. Flower, C.S.J. Langham, L. Parente, P. Persico, C. Russell-Smith andD. Stone,Glucocorticoids induce the formation and release of anti-inflammatory and anti-phospholipase proteins into the peritoneal cavity of the rat. Br. J. Pharmac.76, 185–194 (1982).
G.J. Blackwell, R. Carnuccio M. Di Rosa, R.J. Flower, J. Ivanyi, C.S.J. Langham, L. Parente, P. Persico andJ. Wood, Suppression of archidonate oxidation by glucocorticoid-induced anti-phospholipase peptides. InProstaglandins, Thromboxane and Leukotriene Res., Vol. 11, pp. 65–71 (EdsB. Samuelsson, R. Paoletti andP. Ramwell). Raven Press, New York 1983.
M. Di Rosa andD.A. Willoughby,Screens for anti-inflammatory drugs, J. Pharm. Pharmac.23, 297–298 (1971).
G.A. Higgs, R.J. Flower andJ.R. Vane,A new approach to anti-inflammatory drugs, Biochem. Pharmac.28, 1959–1961 (1979).
R.E. Buller andB.W. O'Malley,The biology and mechanism of steroid hormone receptor interaction with the eukaryotic nucleus, Biochem. Pharmac.25, 1–12 (1976).
S. Tsurufuji, K. Sugio andF. Takemasa,The role of glucocorticoid receptor and gene expression in the anti-inflammatory action of dexamethasone, Nature, Lond.280, 408–410 (1979).
Y. Oyanagui,Steroid-like anti-inflammatory effect of superoxide dismutase in serotonin, histamine, and kinin-induced edemata of mice: existence of vascular permeability regulating proteins(s), Biochem. Pharmac.30, 1791–1798 (1981).
Y. Oyanagui,Anti-inflammatory effects of polyamines in serotonin and carrageenan paw edemata—possible mechanism to increase vascular permeability inhibitory protein level which is reulated by glucocorticoids and superoxide radical, Agents and Actions14, 81–89 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calignano, A., Carnuccio, R., Di Rosa, M. et al. The anti-inflammatory effect of glucocorticoid-induced phospholipase inhibitory proteins. Agents and Actions 16, 60–62 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01999650
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01999650