Abstract
Effect of photoperiod and temperature on the developmental stages of Acrotylus insubricus Scop. (Orth., Acrididae)
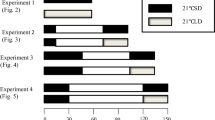
The effect of different temperatures and photoperiods on the developmental stages ofAcrotylus insubricus Scop. was studied. The species has no embryonic or nymphal diapause. The relatively low temperature of the winter months prolonges the incubation period as well as the nymphal development. By rising temperature both eggs and nymphs began to continue their development. The shortest nymphal duration at 27 °C (63.9 days) was obtained when rearing nymphs at long photoperiod (16L:8D), while the longest duration (92 days), was recorded at short photoperiod (8L:16D). In intermediate photoperiod (12L:12D), the nymphal duration was 82.8 days, between the long and the short photoperiods. At 37 °C, the nymphal durations were shorter than at 27 °C and still the shortest at a long day (4310 days) than the two other conditions. The total nymphal mortality was higher at short day-length than that at the other photoperiods tested. The incubation period as well as the percentage of hatching were not affected by the different photoperiodic regimes while the low temperature prolonges the incubation period and nymphal development. The higher temperature (37 °C) tended to mask or abolish the effect of the photoperiod while the moderate temperature (27 °C) clarified this effect when the two factors were combined together.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literaturverzeichnis
Abou-Elela, R. G., 1971 a: Observations expérimentales au cours de la diapause larvaire d'un Pyrgomorphe septentrional (Orth., Acrid). C. R. Sc. Paris, + 273, P. 760–763.
Abou-Elela, R. G., 1971 b: Conditionnement photopériodique de l'entrée et de la sortie de diapause larvaire chezPyrgomorpha conica. Colloque Diapausedormance, Gr. Et. Rythmes biol. France, Clermontferrand.
Danilevskii, A. S., 1961: Photoperiodism and seasonal development of insects Engt. transt. 1965. Edingburgh and London: Oliver Boyd.
Geyspitz, K. F., 1953: Reactions of monovoltine butterflies to prolongation of day length. Entomol. Obozrenie33, 17–31.
Geyspitz, K. F., 1965: Photoperiodic and temperature reactions affecting the seasonal development of the pine mothsDeadrolimus pini L. andD. sibiricus Tschetw. Entomol. Rev.44, 316–325 (transl. For Entomol. Soc. Am.).
Geyspitz, K. F.;Zarakina, A. I., 1963: Some features of the photoperiodic reactions ofDasychira pudibunda L. (Lepidoptera, Orgyidae). Entomol. Rev.42, 14–19.
Lees, A. D., 1955: The physiology of diapause in Arthropods. Cambridge Univ. Press, London and New York.
Shelford, V. E., 1929: Laboratory and field Ecology. Baltimore; Willims and Wilkins.
Verdier, M., 1964: Effect photoperiodique sur la maturation et la fertilité deLocusta gregaires du Sud de la France. Rev. De Path. Vég. et Ent. Agr. Fr.43 (4) 1964, 215–225.
Zohdy, N. Z.;Abou-Elela, R. G., 1975: Effect of photoperiod on the different developmental stages ofSpodoptera littoralis (Boisd.) (Lepidoptera; Noctuidae). Z. ang. Ent.79, 52–56.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abou-Elela, R., Hilmy, N. Wirkungen der Fotoperiode und Temperatur auf die Entwicklungsstadien von Acrotylus insubricus Scop. (Orthopt., Acrididae). Anz. Schadlingskde., Pflanzenschutz, Umweltschutz 50, 25–28 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01984685
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01984685