Abstract
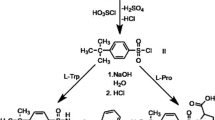
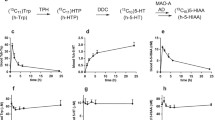
Peak E substance, 1,1′-ethylidenebis[tryptophan], a contaminant found inl-tryptophan tablets, has been suggested as a causative agent for eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome (EMS). Peak E substance (50 mg/kg) was administered perorally to Wistar rats to determine its metabolism and distribution. A purification procedure using Bond Elut C8 cartridges followed by HPLC was developed for the determination of peak E substance. The plasma concentration of peak E substance was 136 ng/ml at 1 h, and urinary excretion was 717 ng at 5 h and 10342 ng for 5–24 h, showing slow excretion of peak E substance into urine. The amount of peak E substance in the contents of the large intestine at 5 h, however, was 3136 Μg, much greater than urinary excretion for 24 h, indicating considerable transfer of peak E substance to large intestine without decomposition by gastric fluid in the stomach. We have detected for the first time not only the occurrence of peak E substance in plasma and urine, but also 1-methyl-tetrahydro-Β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid (MTCA) in blood and organs of rats treated with peak E substance, thereby suggesting MTCA as one of the the metabolites of peak E substance. The amount of MTCA in the contents of the large intestine as well as in urine of rats treated with peak E substance was significantly greater than inl-tryptophantreated rats (50 mg/kg p.o.), demonstrating that MTCA was more readily produced from peak E substance than froml-tryptophan. Finally, we propose acetaldehydeinduced production of MTCA from peak E substance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi J, Mizoi Y, Naito T, Ogawa Y, Uetani Y, Ninomiya I (1991a) Identification of tetrahydro-Β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid in foodstuffs, human urine and human milk. J Nutr 121: 646–652
Adachi J, Yamamoto K, Ogawa Y, Ueno Y, Mizoi Y, Tatsuno Y (1991b) Endogenous formation of 1-methyl-tetrahydro-Β-carboline-3-carboxylic acid in man as the possible causative substance of eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome associated with ingestion ofl-tryptophan. Arch Toxicol 65: 505–509
Belongia EA, Hedberg CW, Gleich GJ, White KE, Mayeno AN, Loegering DA, Dunnette SL, Pirie PL, MacDonald KL, Osterholm MT (1990) An investigation of the cause of the eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome associated with tryptophan use. N Engl J Med 323: 357–365
Brossi A, Focella A, Teitel S (1973) Alkaloids in mammalian tissues. 3. Condensation ofl-tryptophan andl-5-hydroxytryptophan with formaldehyde and acetaldehyde. J Med Chem 16: 418–420
Calabrese E (1983) Principles of animal extrapolation. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Centers for Disease Control (1990) Analysis ofl-tryptophan for the etiology of eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome. New Mexico MMWR 39: 589–591
Goda Y, Suzuki J, Maitani T, Yoshihira K, Takeda M, Uchiyama M (1992) 3-Anilino-l-alanine, structural determination of UV-5, a contaminant in EMS-associatedl-tryptophan samples. Chem Pharm Bull 40: 2236–2238
Hayashida M, Nihira M, Watanabe T (1990) Application of a computer-assisted high-performance liquid Chromatographic multi-wavelength ultraviolet detection system to simultaneous toxicological drug analysis. J Chromatogr 506: 133–143
Horie M, Saito K, Hoshino Y, Nose N, Hamada N, Nakazawa H (1990) Identification and determination of sulphamethazine and N-acetalsulphamethazine in meat by high-performance liquid chromatography with photodiode-array detection. J Chromatogr 502: 371–378
Ito J, Hosaki Y, Torigoe Y, Sakimoto K (1992) Identification of substances formed by decomposition of peak E substance in tryptophan. Food Chem Toxicol 30: 71–81
Mayeno AN, Lin F, Foote CS, Loegering DA, Ames MM, Hedberg CW, Gleich GJ (1990) Characterization of “peak E”, a novel amino acid associated with eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome. Science 250: 1707–1708
Sakimoto K (1990) The cause of the eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome associated with tryptophan use. N Engl J Med 323: 992
Smith MJ, Mazzola EP, Farrell TJ, Sphon JA, Page SW, Ashley D, Sirimanne SR, Hill RH, Needham LL (1991) 1,1′-Ethylidenebis(l-tryptophan), structure determination of contaminant “97”-Implicated in the eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome (EMS). Tetrahedron Lett 32: 991–994
Toyo'oka T, Yamazaki T, Tanimoto T, Sato K, Sato M, Toyoda M, Ishibashi M, Yoshihira K, Uchiyama M (1991) Characterization of contaminants in EMS-associatedl-tryptophan samples by high-performance liquid chromatography. Chem Pharm Bull 39: 820–822
Yamada S, Akimoto H (1969) Reductive decyanization of α-amino nitriles with NaBH4. A new synthetic approach to isoquinoline- and indole-alkaloids. Tetrahedron Lett 3105–3108
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adachi, J., Naito, T., Ueno, Y. et al. Metabolism and distribution in the rat of peak E substance, a constituent inl-tryptophan product implicated in eosinophilia-myalgia syndrome. Arch Toxicol 67, 284–289 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01974348
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01974348