Abstract
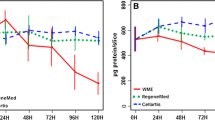
In order to obtain more information concerning the effects of culture and medium conditions on the glutathione dependent detoxication system in hepatocyte cultures, glutathione reductase (GR) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx) activities were studied in both pure cultures of adult rat hepatocytes and their co-cultures with rat epithelial cells. Cells were isolated either with an oxygen saturated Krebs Henseleit buffer (KHB) or with a non-gassed Hepes buffer. As medium conditions, additions of 10% fetal calf serum (FCS), 25 mM nicotinamide, 0.1 μM selenium and 2% dimethylsulphoxide, respectively, to the culture medium were examined. It was found that co-cultures of rat hepatocytes can cope better with oxidative stress than pure cultures do. This conclusion was reached from the following observations. When oxygenated KHB was used as isolating buffer, GR and GPx activities increased during the first days of pure culture and then slowly decreased. This was observed for all the medium conditions studied and no significant differences between the different media could be observed. For co-cultures, however, after some initial variations GR and GPx activities reached stabilized levels which were not only significantly lower than those observed for pure cultures, but were also maintained throughout the whole culture period. Supplementation of the medium had no effect on these findings with the exception of high GPx activities when Se was added to the co-culture medium. When Hepes buffer with a low oxygen content was used in cell isolation, pure cultures showed significantly lower GR and GPx activities than those first mentioned. Both approached the values measured for cocultures. The shape of the enzymatic activity curve as a function of culture time remained essentially unchanged. In co-cultures no significant differences could be observed in GPx activities when both perfusion techniques were involved, with the exception of the measurements done during the first 2 days of co-culture. Using the non-gassed Hepes buffer instead of the oxygenated KHB had no statistical effect on the GSH content of the hepatocytes in either of the two culture systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arthur JR, Morrice PhC, Nicol F, Beddows SE, Boyd R, Hayes JD, Beckett GJ (1987) The effects of selenium and copper deficiencies on glutathione S-transferase and glutathione peroxidase in rat liver. Biochem J 248: 539–544
Berry MN, Friend DS (1969) High yield preparation of isolated rat liver parenchymal cells: a biochemical and fine structural study. J Cell Biol 43: 506–520
Burk RF (1991) Molecular biology of selenium with implications for its metabolism. FASEB J 5: 2274–2279
Carlberg I, Mannervik B (1975) Purification and characterization of the Flavoenzyme Glutathione reductase from rat liver. J Biol Chem 250: 5475–5480
Deagen JT, Butler JA, Beilstein MA, Whanger PD (1987) Effects of dietary selenite, selenocystine and selenomethionine on selenocysteine lyase and glutathione peroxidase activities and on selenium levels in rat tissues. J Nutr 117: 91–98
Frazier JM, Goldberg AM (1990) Alternatives to and reduction of animal use in biomedical research, education and testing. ATLA 18: 65–74
Guillouzo A (1986) Use of isolated and cultured hepatocytes for xenobiotic metabolism and cytotoxicity studies. In: Guillouzo A, Guguen-Guillouzo C (eds) Isolated and cultured hepatocytes. John Libbey Ltd, London, pp 313–332
Lane HW, Strength R, Johnson J, White M (1991) Effect of chemical form of selenium on tissue glutathione peroxidase activity in developing rats. J Nutr 121: 80–86
Mannervik B, Widersten, M, Board PHG (1989) Glutathione-linked enzymes in detoxication reactions. In: Tanigushi N, Higashi T, Sakamoto Y, Meister A (eds) Glutathione centennial, molecular perspectives and clinical implications. Academic Press, San Diego, California, pp 23–34
Meister A (1989) On the biochemistry of glutathione. In: Tanigushi N, Higashi T, Sakamoto Y, Meister A (eds) Glutathione centennial, molecular perspectives and clinical implications. Academic Press, San Diego, California, pp 3–21
Mertens K, Rogiers V, Sonck W, Vercruysse A (1991 a) Measurement of reduced and oxidized glutathione in cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. J Chromatogr 565: 149–157
Mertens K, Rogiers V, Sonck W, Vercruysse A (1991 b) Reduced and oxidized glutathione contents in adult rat hepatocytes under various culture conditions. Cell Biol Toxicol 7: 101–110
Norusis MJ (1984) SPSS/PC+ for the IBM PC/XT. SPSS Inc., Chicago, Illinois, USA
Office of Technology Assessment, Congress of the United States (1988) Alternatives to animal use in research, testing, and education, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York, pp 113–1146 and pp 175–195
Rogiers V, Paeme G, Vercruysse A, Bouwens L (1983) Procyclidine metabolism in isolated rat liver cells. In: Van Bezooyen CFA (ed) Pharmacological, morphological and physiological aspects of liver ageing. Topics in ageing research in Europe, Vol. I. Eurage, The Netherlands, pp 121–126
Rogiers V, Vandenberghe Y, Callaerts A, Verleye G, Sonck W, Cornet M, Mertens K, Vercruysse A (1990) Phase I and phase II xenobiotic biotransformation in cultures and co-cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol 40: 1701–1706
Sies H (1985) Oxidative stress. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, London Orlando San Diego
Tanigushi N, Tsukada Y, Mukuo K, Hirai H (1974) Effect of hepatocarcinogenic azo dyes on glutathione and related enzymes in rat liver. GANN 65: 381–387
Terrada ML, Munoz ML (1990) Publications on glutathione, 1983 to 1987. A bibliometric study. In: Vina J (ed) Glutathione: metabolism and physiological functions. CRC Press, Inc., Florida, pp 1–10
Toyoda H, Himeno S-I, Imura N (1989) The regulation of glutathione peroxidase gene expression relevant to species difference and the effects of dietary selenium manipulation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1008: 301–308
Vandenberghe Y, Morel F, Pemble S, Taylor JB, Rogiers V, Ratanasavanh D, Vercruysse A, Ketterer B, Guillouzo A (1990) Changes in expression of mRNA coding for glutathione S-transferase subunits 1–2 and 7 in cultured rat hepatocytes. Mol Pharmacol 37: 372–376
Williams GM, Weisburger EK, Weisburger JH (1971) Isolation and long-term culture of epithelial-like cells from rat liver. Exp Cell Res 69: 106–112
Yuan C, Penttila KE, Alfthan G, Lindros O (1991) Role of selenium-dependent glutathione peroxidase in protecting against t-butyl hydroperoxide-induced damage in hepatocytes. Pharmacol Toxicol 68: 196–200
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mertens, K., Rogiers, V. & Vercruysse, A. Glutathione dependent detoxication in adult rat hepatocytes under various culture conditions. Arch Toxicol 67, 680–685 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01973691
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01973691