Abstract
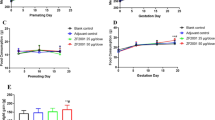
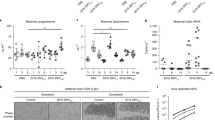
Aciclovir (synonym: acyclovir) causes abnormal thymus development in rats. After treatment on day 10 of gestation a weight reduction of the organ is obvious in 21-day-old fetuses which persists postnatally. Adult male rats exposed in utero to one or three injections of 100 mg aciclovir/kg body wt given to the dam on day 10 of pregnancy showed a reduction of the thymus weight to 333±158 mg and 276±61 mg (control: 428±92 mg;n=10). Corresponding alterations were detectable in female offspring. Liver weight was also decreased and spleen weight (in relation to body wt) was significantly increased in the offspring after the three exposures. In a host resistance model withTrichinella spiralis the function of the immune system of rats prenatally exposed to aciclovir was examined. Six weeks postnatally 10–12 randomly selected male rat offspring of one control and two treatment groups (1 or 3 injections of 100 mg aciclovir/kg body wt on day 10 of gestation) were infected orally with 500Trichinella spiralis muscle larvae. Before and several times after the infection blood was taken from a tail vein or obtained by decapitation for examination of the antibody titers (IgM, IgG, IgA, IgE) to antigens ofT. spiralis. Six weeks after the infection the weight of relevant organs was determined and tongue preparations were used forT. spiralis muscle larvae counting. Aciclovir exposed animals showed a different immune response than control rats. IgM titers in both treatment groups werehigher than in controls two weeks after the infection but not different by the end of the experiment. The IgG and IgE titers in the high dose group werelower than in the other groups at the end of the observation period. IgA antibody titers in the high dose group were alsolower than controls, but only 2 weeks after the infection. The number ofT. spiralis muscle larvae in tongue preparations was higher in the 3×100 mg aciclovir group than in the low dose group or in controls. Our results indicate that morphological thymus alterations and functional deficits of the immune system can be induced by prenatal exposure of rats to aciclovir on day 10 of gestation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnett JB, Soderberg LSF, Menna JH (1985) The effect of prenatal chlordane exposure on the delayed hypersensitivity response of BALB/c mice. Toxicol Lett 25: 173–183
Chahoud I, Kwasigroch TE (1977) Controlled breeding of laboratory animals. In: Neubert D, Merker H-J, Kwasigroch TE (eds) Methods in prenatal toxicology. Thieme, Stuttgart, pp 78–91
Chahoud I, Stahlmann R, Bochert G, Dillmann I, Neubert D (1988) Gross structural defects in rats after acyclovir application on day 10 of gestation. Arch Toxicol 62: 8–14
Cohen M, Rubinstein A, Li JK, Nathenson G (1987) Thymic hypoplasia associated with isotretinoin embryopathy. Am J Dis Child 141: 263–266
Faith RE, Moore JA (1977) Impairment of thymus-dependent immune functions by exposure of the developing immune system to 2, 3,7, 8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). J Toxicol Environ Health 3: 451–464
Furuhama K, Onodera T (1983) A simple technique for repeated blood collection from the tail vein of the rat. J Toxicol Sci 8: 161–163
Haake DA, Zakowski PC, Haake DL, Bryson YJ (1990) Early treatment with acyclovir for varicella pneumonia in otherwise healthy adults: retrospective controlled study and review. Rev Infect Dis 12: 788–798
Heinrich-Hirsch B, Jacob-Müller U (1987) Studies on the embryotoxic effect of acyclovir on the development of chick embryos. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 335 [Suppl]: R 29 (Abstr No 115)
Heinrich-Hirsch B, Neubert D (1991) Effect of aciclovir on the development of the chick embryo in ovo. Arch Toxicol 65: 402–408
Klug S, Lewandowski C, Blankenburg G, Merker H-J, Neubert D (1985) Effect of aciclovir on mammalian embryonic development in culture. Arch Toxicol 58: 89–96
Klug S, Lewandowsky C, Stahlmann R, Neubert D (1987) Teratogenic potential of two virustatic agents in the rat: comparison of in vitro and in vivo data Teratology 36: 27A
Klug S, Lewandowski C, Merker HJ, Stahlmann R, Wildi E, Neubert D (1991) In vitro and in vivo studies on the prenatal toxicity of five virustatic nucleoside analogues in comparison to aciclovir. Arch Toxicol 65: 283–291
Köhler G, Ruitenberg EJ (1974) Comparison of three methods for the detection ofTrichinella spiralis infections in pigs by five European laboratories. Bull WHO 50: 413
Körte M, Stahlmann R, Thiel R, Nagao T, Chahoud I, Van Loveren H, Vos JG, Neubert D (1990) Effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachloridibenzo-p-dioxin on hepatic monooxygenases and resistance toTrichinella spiralis infection in rat offspring after perinatal exposure. In: Hutzinger O, Fiedler E (eds) Organo Halogen Compounds, Vol. 1: Dioxin '90-EPRI-Seminar. Ecoinforma, Bayreuth, 89–94
Lammer EJ, Chen DT, Hoar RM, Agnish ND, Benke PJ, Braun JT, Curry CJ, Fernhoff PM, Grix AW Jr, Lott IT, Richard JM, Sun SC (1985) Retinoic acid embryopathy. N Engl J Med 313: 837–841
Luster MI, Boorman GA, Dean JH, Harris MW, Luebke RW, Padarathsingh ML, Moore JA (1980) Examination of bone marrow, immunologic parameters and host susceptibility following pre- and postnatal exposure to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin (TCDD). Int J Immunopharmacol 2: 311–320
Moore Jr HL, Szczech GM, Rodwell DE, Kapp Jr RW, de Miranda P, Tucker Jr WE (1983) Preclinical toxicology studies with aciclovir. teratologic, reproductive and neonatal tests. Fund Appl Toxicol 3: 560–568
Neubert D, Neubert R, Stahlmann R, Helge H (1989) Immuno-toxicology and -pharmacology. Brazil J Med Biol Res 22: 1457–1473
Neubert D, Klug S, Chahoud I, Stahlmann R (1990) Assessment of teratogenic potency using a modified dosing schedule. Teratology 41: 582
NN (1989) Acyclovir in pregnancy registry. International interim report: June 1, 1984 through June 30, 1989. Research Triangle Park, NC, Burroughs Wellcome Division of Epidemiology, Information and surveillance, Burroughs Wellcome Co., 3030 Cornwallis Road, Research Triangle Park, NC 27709
Ruitenberg EJ, Elgersma A, Kruizinga W, Leenstra F (1977)Trichinella spiralis infection in congenitally athymic (nude) mice. Parasitological, serological and haematological studies with observations on intestinal pathology. Immunology 33: 581
Schmidt RR (1984) Altered development of immunocompetence following prenatal or combined prenatal-postnatal insult: a timely review. J Am Coll Toxicol 3: 57–72
Shenefelt RE (1972) Morphogenesis of malformations in hamsters caused by retinoic acid: relation to dose and stage of treatment. Teratology 5: 103–118
Stahlmann R, Chahoud I, Schimmel A, Neubert D (1985) Pharmacokinetics and nephrotoxicity of gentamicin in pregnant rats. Maternal, fetal, and postnatal data. Teratology 32: 34 A (Abstract)
Stahlmann R, Chahoud I, Bochert G, Neubert D (1987) Teratogenic and postnatal defects in rats after aciclovir application on day 10 of gestation. Teratology 36: 31A-32A (Abstract)
Stahlmann R, Franz R, Merker H-J (1988a) Embryotoxicity of aciclovir in rats after single application. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337: R35 (Abstract 138)
Stahlmann R, Chahoud I, Meister R, Düerkop C, Neubert D (1988b) Gentamicin and urea concentrations in plasma of non-pregnant and pregnant rats and fetuses after single and multiple injections. Arch Toxicol 62: 232–235
Stahlmann R, Klug S, Lewandowski C, Bochert G, Chahoud I, Rahm U, Merker H-J, Neubert D (1988c) Prenatal toxicity of aciclovir in rats. Arch Toxicol 61: 468–479
Stahlmann R, Chahoud I, Korte M, Thiel R, Van Loveren H, Vos JG, Foerster M, Merker H-J, Neubert D (1991) Structural anomalies of thymus and other organs and impaired resistance toTrichinella spiralis infection in rats after prenatal exposure to aciclovir. In: Kendall MD, Ritter MA (eds) Thymus Update Vol. 4, Harwood, Chur, London, Paris, New York, Melbourne, pp 129–155
Stray-Pedersen B (1990) Acyclovir in late pregnancy to prevent neonatal herpes simplex. Lancet ii: 756 (letter)
Streiberg B, Roehmel J (1984) Exact nonparametrics in APL. APL Quote Quad 14: 313–325
Van Loveren H, Osterhaus ADME, Nagel J, Schuurman HJ, Vos JG (1988) Detection of IgA-antibodies and enumeration of IgA-antibody producing cells specific for Ovalbumin orTrichinella spiralis in the rat. Scand J Immunol 28: 377–381
Vos JG, Moore JA (1974) Suppression of cellular immunity in rats and mice by maternal treatment with 2,3,7,8-tetrachloro-dibenzo-p-dioxin. Int Arch Allergy 47: 777–794
Vos JG, Boerkamp J, Buys J, Steerenberg PA (1980) Ovalbumin immunity in the rat: simultaneous testing of IgM, IgG and IgE response measured by ELISA and delayed-type hypersensitivity. Scand J Immunol 12: 289–295
Vos JG, De Klerk A, Kranjc EJ, Kruizinga W, Van Immen B, Rozing J (1984) Toxicity of bis (tri-n-butyltin) oxide in the rat. II. Suppression of thymus dependent immune responses and of parameters of non-specific resistance after short-term exposure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 75: 387–408
Vos JG, DeKlerk A, Kranjc EJ, Van Loveren H, Rozing I (1990) Immunotoxicity of bis (tri-n-butyltin) oxide in the rat: effects of thymus dependent immunity and on non-specific resistance following long-term exposure in young versus aged rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 105: 144–155
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stahlmann, R., Korte, M., Van Loveren, H. et al. Abnormal thymus development and impaired function of the immune system in rats after prenatal exposure to aciclovir. Arch Toxicol 66, 551–559 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01973385
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01973385