Abstract
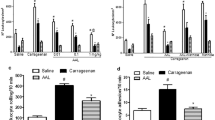
Pleurisy was induced in rats after intrapleural injection of 2% λ-carrageenin. The volume of the pleural exudate increased rapidly between 1 and 3 h, continuing to increase until 7 h. The dye amounts exuded into the pleural cavity for 20 min after 5% pontamine sky blue (60 mg/kg, i.v.) increased markedly at 1 to 3 h, then they kept constant until 6 h, decreasing thereafter. The PGE level in the pleural fluid increased rapidly during the period from 1 to 3 h, when the exudate commenced to accumulate, and then decreased slightly until 7 h. The main PG in the pleural fluid was recognized as PGE2 on thin-layer chromatography. The pretreatment of rats with a PG synthetase inhibitor, indomethacin (5 mg/kg, i.p.), 30 min before carrageenin administration resulted in the significant reduction of dye leakage at 1 h and of the pleural fluid exudation at 1 to 3 h. The intravenous injection into rats of stem bromelain (10 mg/kg, i.v.), a SH-protease from pineapples, caused the depletion of high molecular weight kininogen in plasma without effect on the content of low molecular weight kininogen. The pretreatment of rats with bromelain 30 min before carrageenin caused a marked reduction in the dye exudation during the periods from 1 to 3 h and 5 to 6 h. The accumulation of the exudate was strongly suppressed at the same periods. Although each treatment by itself did not completely abolish the dye and fluid exudation, the treatment of rats simultaneously with indomethacin and bromelain resulted in suppression of dye leakage from 1 to 6 h and practically no fluid accumulation was observed until 4 h. These results strongly indicate that prostaglandin is released in combination with bradykinin at the period when the pleural exudate commences to accumulate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.J. Williams andJ. Moreley,Prostaglandins as Potentiators of Increased Vascular Permeability in Inflammation, Nature246, 215–217 (1973).
K. Ikeda, K. Tanaka andM. Katori,Potentiation of Bradykinin-Induced Vascular Permeability Increase by Prostaglandin E 2 and Arachidonic Acid in Rabbit Skin, Prostaglandins10, 747–768 (1975).
S. Moncada, S.H. Ferreira andJ.R. Vane,Prostaglandins, Aspirin-like Drugs and Oedema of Inflammation, Nature246, 217–219 (1973).
G. Thomas andG.B. West,Prostaglandins, Kinin and Inflammation in the Rat, Br. J. Pharmacol.50, 231–235 (1974).
A.J. Lewis, D.J. Nelson andM.F. Sugrue,On the Ability of Prostaglandin E 1 and Arachidonic Acid to Modulate Experimentally Induced Oedema in the Rat Paw, Br. J. Pharmacol.55, 51–66 (1975).
B.M. Jaffe, H.R. Behrman andC.W. Parker,Radioimmunoassay Measurement of Prostaglandin E, A, and F in Human Plasma, J. Clin. Invest.52, 398–405 (1973).
Y. Harada, S. Oh-ishi andM. Katori,Differential Bioassay Method of Prostaglandin E 2 and F 2α by Superfusion Technique, Jap. J. Pharmacol.25, Suppl. 38p (1975).
K. Gréen andB. Samuelsson,Prostaglandins and Related Factor: XIX. Thin Layer Chromatography of Prostaglandins, J. Lipid Res.5, 117–120 (1964).
A.L. Willis,Simplified Thin-Layer Chromatography of Prostaglandins in Biological Extracts, Br. J. Pharmacol.40, 583p (1970).
W.E. Brocklehurst andI.J. Zeitlin,Determination of Plasma Kinin and Kininogen Levels in Man. J. Physiol.191, 417–426 (1967).
M. Katori andY. Uchida,An Improved Method for Determination of Total Kininogen in Plasma, Agents and Actions (in press).
G.W. Snedecor andW.G. Cochran,Statistical Methods, 6th edition (The Iowa State University Press, 1967), p. 114.
GP. Velo, C.J. Dunn, J.P. Giroud, J. Timsit andD.A. Willoughby,Distribution of Prostaglandins in Inflammatory Exudate, J. Path.111, 149–158 (1973).
M. Di Rosa, J.P. Giroud andD.A. Willoughby,Studies of Mediators of Acute Inflammatory Response Induced in Rats in Different Sites by Carrageenan and Turpentine. J. Path.104, 15–29 (1971).
P. Crunkhorn andS.C.R. Meacock,Mediators of Inflammation Induced in the Rat Paw by Carrageenin, Br. J. Pharmacol.42, 392–402 (1971).
J. Garcia Leme, L. Hammamura, M.P. Leite andM. Rocha e Silva,Pharmacological Analysis of the Acute Inflammatory Process Induced in the Rat's Paw by Local Injection of Carrageenin and by Heating, Br. J. Pharmacol.48, 88–96 (1973).
A.L. Willis,Release of Histamine, Kinin and Prostaglandins during Carrageenin-Induced Inflammation in the Rat, in:Prostaglandins, Peptides and Amines (Eds. Mantegazza and E.W. Horton: Academic Press, London and New York, 1969), p. 31.
W.C. Chang, S. Murota andS. Tsurufuji,Contents of Prostaglandin E in the Exudate of Rat Carrageenin Granuloma, Jap. J. Pharmacol.25, 219–221 (1975).
K. Ohuchi, H. Saito andS. Tsurufuji,The Content of Prostaglandin E and Prostaglandin F 2α in the Exudate of Carrageenin Granuloma of Rats, Biochim. biophys. Acta424, 439–448 (1976).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katori, M., Ikeda, K., Harada, Y. et al. A possible role of prostaglandins and bradykinin as a trigger of exudation in carrageenin-induced rat pleurisy. Agents and Actions 8, 108–112 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972411
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01972411