Abstract
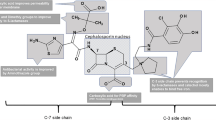
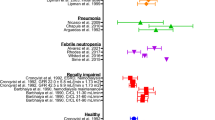
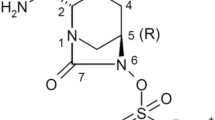
The dependence of the antibacterial activity of the two oral cephalosporins cefixime and cefaclor on pharmacokinetic properties was investigated in an in vitro model using strains of enterobacteria and a streptococcal strain. In the cultures the course of serum concentrations of the respective antibiotic was simulated. The more rapidly attained (1 h) high peak levels (17.5 µg/ml) of cefaclor (500 mg dose) in no case showed an advantage over the more slowly reached (3 h) low peak levels (2.5 µg/ml) of cefixime (200 mg dose). Cefixime was comparable to cefaclor with respect to its initial killing velocity, whereas it was generally superior with respect to maximum values for reduction of bacterial counts. Due to its long elimination half-life (2.5 h) cefixime prevented regrowth for at least twice as long as cefaclor, which has a short half-life (0.7 h). As a result of its antibacterial activity and pharmacokinetic properties cefixime can be administered less frequently than cefaclor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neu, H. C., Chin, N.-X., Labthavikul, P.: Comparative in vitro activity andβ-lactamase stability of FR 17027, a new orally active cephalosporin. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1984, 25, 174–180.
Brittain, D. C., Scully, B. E., Hirose, T., Neu, H. C.: The pharmacokinetic and bactericidal characteristics of oral cefixime. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1985, 38: 590–594.
Faulkner, R. D., Yacobi, A., Barone, J. S., Kaplan, S. A., Silber, B. M.: Pharmacokinetic profile of cefixime in man. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal 1987, 6: 963–970.
Brogard, J. M., Comte, F.: Pharmacokinetics of the new cephalosporins. In: Schönfeld, H. (ed.): Antibiotics and chemotherapy, Volume 31, Pharmacokinetics II. S. Karger, Basel, 1982, p. 145–210.
Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V.: Methoden zur Empfindlichkeitsprüfung von bakteriellen Krankheits-erregern (außer Mykobakterien) gegen Chemotherapeutika. DIN 58 940 Teil 5. Beuth Verlag, Berlin, 1979.
Grasso, S., Meinardi, G., De Carneri, I., Tamassia, V.: New in vitro model to study the effect of antibiotic concentration and rate of climination on antibacterial activity. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1978, 13: 570–576.
White, C. A., Toothaker, R. D., Smith, A. L., Slattery, J. T.: Correction for bacterial loss in in vitro dilution models. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1987, 31: 1859–1860.
Drusano, G. L.: Role of pharmacokinetics in the outcome of infections. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1988, 32: 289–297.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nies, B.A. Comparative activity of cefixime and cefaclor in an in vitro model simulating human pharmacokinetics. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 8, 558–561 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01967481
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01967481