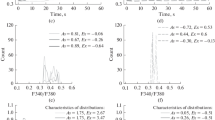
Summary
The modification of neutrophils with amino group blocking reagents of different chemical specificities showed that dansyl chloride caused inhibition of chemotaxis without suppression of random movement. Dansylated neutrophils, like control cells, ingested bacteria. Neither the stimulated cyanide-insensitive respiration, nor lactate production during phagocytosis, was affected significantly by dansylation as compared with the inhibition of directed movement.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Boyden, J. exp. Med.115, 453 (1962).
P.A. Ward, Am. J. Path.64, 521 (1971).
T. Yamashita, N. Imaizumi and S. Yuasa, Cryobiology16, 112 (1979).
T. Yamashita, Y. Tanaka, T. Horigome and E. Fujikawa, Experientia35, 1054 (1979).
S.H. Zigmond and J.G. Hirsch, Exp. Cell Res.73, 383 (1972).
S. Udenfriend, S. Stein, P. Böhlen, W. Dairman, W. Leimgruber and M. Weigele, Science178, 871 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamashita, T., Takamori, K. & Tanaka, Y. A possible preferential inhibition of chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear neutrophils by a chemical modification. Experientia 35, 1345–1347 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01963999
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01963999