Summary
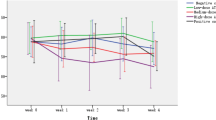
The acute toxicity of cyclophosphamide, studied orally in chinese hamsters and intravenously in Tif: MAGf (SPF) mice, showed seasonal variation in Chinese hamsters but not in mice.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.M. Boyd, Can. med. Ass. J.98, 278 (1968).
J.F. von Ledebur and K. Wachholder, Pflügers Arch.231, 114 (1932).
H. von Mayersbach, Drug Res.28, 1824 (1978).
A. Goulden, in: Methods of Statistical Analysis, p. 404. John Wiley, New York/London 1960.
SAS User's Guide, in: Statistical Analysis system. Raleigh, North Carolina 1979.
R. Bloch and B. Camguilhelm, C.r. Soc. Biol.160, 1500 (1966).
P. Berthold, in: Endogene Jahresperiodik. Universitätsverlag GmbH, Konstanz 1974.
K. Hoffmann, Drug Res.28, 1836 (1978).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Acknowledgement. I thank Mr R. Gebus for skilful technical and Mr A.P. Grieve for statistical assistance.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pericin, C. Effect of seasonal variation on the acute toxicity of cyclophosphamide in the Chinese hamster (Cricetulus griseus) and the mouse under laboratory conditions. Experientia 37, 401–402 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01959886
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01959886