Summary
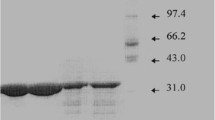
Acid phosphatase ofEimeria tenella oocysts (Peak II) was purified 77-fold with a recovery of 26% using protamine sulfate precipitation, DEAE-cellulose chromatography and Sephadex G-200 gel filtration. This enzyme occurs in multiple forms as indicated by two peaks which can be separated by DEAE-cellulose chromatography and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The partially purified enzyme has optimal activity at pH 4.5. With p-nitrophenyl phosphate the Km and Vmax values for (Peak II) were 25 mM and 1.57 μmol/min/mg protein, respectively. The enzyme (Peak II) ist strongly inhibited by Hg++, Cu++, iodoacetamide, fluoride and molybdate. Tartrate and other divalent metal ions have no effect on enzyme activity. The partially purified Peak II phosphatase is not a glycoprotein as it is not absorbed on concanavalin-A Sepharose and its treatment with bacterial neuraminidase does not alter its elution profile through DEAE cellulose.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Roche, J., Phosphatases, in: Enzymes, vol. 1, pp. 473–510. Eds J. B. Sumner and K. Myrback. Academic Press, New York 1950.
Hollander, V. P., Acid phosphatases, in: Enzymes, vol. 4, pp. 449–497. Ed. P. Boyer. Academic Press, New York 1971.
Gill, B. S., and Ray, H. N., Phosphatases and their significance inEimeria tenella. Ind. J. Vet. Sci. Ani. Husb.24 (1954) 239–244.
Ray, H. N., and Gill, B. S., Preliminary observations on alkaline phosphatase in experimentalEimeria tenella infections in chicks. Ann. trop. Med. Parasitol48 (1954) 8–10.
Frandsen, J. C.,Eimeria stiedae: cytochemical identification of acid and alkaline phosphatases, carboxylic ester hydrolases and succinate, lactate and glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenases in endogenous stages or rabbit tissues. Exp. Parasitol.23 (1968) 398–411.
Shirley, M. W., Enzyme variation inEimeria species of chicken. Parasitology71 (1975) 369–376.
Rollinson, D., Electrophoretic variation of enzymes in chicken coccidia. Tran. R. Soc. trop. Med. Hyg.69 (1975) 436–437.
Farooqui, A. A., Lujan, R., and Hanson, W. L., Acid hydrolases of the coccidian,Eimeria tenella. Experientia39 (1983) 1368–1370.
Vetterling, J. M., Continuous-flow differential density flotation of coccidial oocysts and a comparison with other methods. J. Parasitol.55 (1969) 412–417.
Roberson, E. L., Hanson, W. L., and Chapman Jr, W. L.,Trypanosoma cruzi. Effect of antithymocyte serum in mice and neonatal thymectomy in rats. Exp. Parasitol.34 (1973) 168–180.
Helwig, J. J., Farooqui, A. A., Bollack, C., and Mandel, P., Distribution of lysosomal hydrolases in glomerular and tubular fractions of rabbit kidney cortex. Int. J. Biochem.8 (1977) 323–327.
Fiske, C. H., and Subba Row, Y., The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J. biol. Chem.66 (1925) 375–400.
Bradford, M. M., A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of proteindye binding. Analyt. Biochem.72 (1976) 248–254.
Brewer, J. M., and Ashworth, R. B., Disc electrophoresis. J. chem. Educ.46 (1969) 41–45.
Farooqui, A. A., Purification and properties of arysulfatase A from human placenta. Archs int. Physiol. Biochem.84 (1976) 479–492.
Andrews, P., The gel filtration behaviour of proteins related to their molecular weights over a wide range. Biochem. J.96 (1965) 595–606.
Ryley, J. F., Bentley, M., Manners, D. J., and Stark, J. R., Amylopectin, the storage polysaccharide of the coccidiaEimeria brunetti andE. tenella. J. Parasitol.55 (1969) 839–845.
Helwig, J. J., Farooqui, A. A., Bollack, C., and Mandel, P., Purification and some properties of tartrate-sensitive acid phosphatase from rabbit kidney cortex. Biochem. J.175 (1978) 321–329.
Farooqui, A. A. and Hanson, W. L., Comparison of arylsulphatases fromEimeria tenella (parasite) and chicken caecum (host). Biochem. J.242 (1987) 97–102.
Patel, A., and Koenig, H., Brain lysosomal hydrolases I. Solubilization and electrophoretic behavior of acid hydrolases in nerve-ending and mitochondrial-lysosomal fractions from rat brain. Effect of autolysis, neuraminidase and storage. Neurochem. Res.1 (1976) 275–298.
Farooqui, A. A., Adam, D. D., Hanson, W. L., and Prestwood, A. K., Studies on the enzymes ofSarcocystis suicanis: Purification and characterization of an acid phosphatase. J. Parasitol.73 (1987) 681–688.
Lam, K., Lai, L., Burkart, P. T., and Yam, L. T., Kinetic properties of tartrate resistant acid phosphatase isolated from human spleen with leukemic reticuloendotheliosis. J. biol. Chem.252 (1977) 3371–3373.
Krebs, E. G., and Beavo, J. A., Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation of enzymes. A. Rev. Biochem.48 (1979) 923–959.
Cohen, P., The role of protein phosphorylation in neural and hormonal control of cellular activity. Nature296 (1982) 613–620.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farooqui, A.A., Hanson, W.L. Partial purification and characterization of acid phosphatase from sporulated oocysts ofEimeria tenella. Experientia 44, 437–440 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01940540
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01940540