Summary
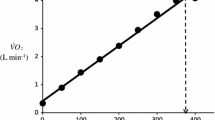
The present paper discusses the factors affecting maximal O2 consumption\(\left( {\dot V_{O_2 } \max } \right)\) in hypoxia (4300 m above sea level) along the following lines: 1) In acute hypoxia, the fractional limitation to\(\dot V_{O_2 } \max \) imposed by circulatory O2 transport (FQ′) is 50%, instead of 70% as in normoxia. This is due to the increase in the blood O2 transport coefficient (βb) as\(P_{O_2 } \) decreases, as a consequence of the sigmoidal shape of the O2 dissociation curve of hemoglobin. The remaining 50% is assumed to be equally partitioned between tissue O2 transfer (Ft′) and mitochondria O2 utilization (Fm′). 2) In chronic hypoxia, FQ′=0.45, Ft′=0.20 and Fm′=0.35, as a consequence of reduced muscle fiber size and muscle mitochondrial density following acclimatization. 3) The relationship between\(\dot V_{O_2 } \max \) and\(PI_{O_2 } \) in both acute and chronic hypoxia reflects the O2 dissociation curve. 4) Acclimatization to chronic hypoxia does not have the function of preserving\(\dot V_{O_2 } \max \).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åstrand, P. O., and Rodahl, K., Textbook of Work Physiology. Mc Graw Hill, New York 1977.
Boyer, S. J., and Blume, F. D., Weight loss and changes in body composition at high altitude. J. appl. Physiol.57 (1984) 1580–1585.
Cerretelli, P., Limiting factors to oxygen transport on Mount Everest. J. appl. Physiol.40 (1976) 658–667.
Cerretelli, P., Gas exchange at altitude, in: Pulmonary Gas Exchange, vol. II: Organism and Environment, pp. 97–147. Ed. J. B. West. Academic Press, New York 1980.
Cymerman, A., Reeves, J. T., Sutton, J. R., Rock, P. B., Groves, B. M., Malconian, M. K., Young, P. M., Wagner, P. D., and Houston, C. S., Operation Everest II: maximal oxygen uptake at extreme altitude. J. appl. Physiol.66 (1989) 2446–2453.
di Prampero, P. E., Metabolic and circulatory limitations to\(\dot V_{O_2 } \max \) at the whole animal level. J. exp. Biol.115 (1985) 319–331.
di Prampero, P. E., and Ferretti, G., Factors limiting maximal oxygen consumption in humans. Respir. Physiol.80 (1990) 113–128.
Ekblom, B., Factors determining maximal aerobic power. Acta physiol. scand. Suppl.556 (1986) 15–19.
Fagraeus, L., Karlsson, J., Linnarson, D., and Saltin, B., Oxygen uptake during maximal work at lowered and raised ambient air pressures. Acta physiol. scand.87 (1973) 411–421.
Ferretti, G., Boutellier, U., Pendergast, D. R., Moia, C., Minetti, A. E., Howald, H., and di Prampero, P. E., Muscular exercise at high altitude. IV. Oxygen transport system before and after exposure to chronic hypoxia. Int. J. Sports Med.11, Suppl. 1 (1990) S15–S20.
Ferretti, G., Hauser, H., and di Prampero, P. E., Muscular exercise at high altitude. VII. Maximal muscular power before and after exposure to chronic hypoxia. Int. J. Sports Med.11, Suppl. 1 (1990) S31–S34.
Fitzgerald, R. S., and Lahiri, S., Reflex responses to chemoreceptor stimulation, in: Handbook of Physiology. The Respiratory System II, pp. 313–362. Eds N. S. Cherniack and J. G. Widdicombe. Am. Physiol. Soc., Bethesda, MD 1986.
Fulco, C. S., Rock, P. B., Trad, L., Forte, V., and Cymerman, A., Maximal cardiorespiratory responses to one- and two-legged cycling during acute and long-term exposure to 4300 meters altitude. Eur. J. appl. Physiol.57 (1988) 761–766.
Hansen, J. E., Vogel, J. A., Stelter, G. P., and Consolazio, C. F., Oxygen uptake in man during exhaustive work at sea level and high altitude. J. appl. Physiol.23 (1967) 511–522.
Hartley, L. H., Vogel, J. A., and Landowne, M., Central, femoral, and brachial circulation during exercise in hypoxia. J. appl. Physiol.34 (1973) 87–90.
Hoppeler, H., Kleinert, K., Schlegel, C., Claassen, H., Howald, H., and Cerretelli, P., Muscular exercise at high altitude. II. Morphological adaptations of human skeletal muscle to chronic hypoxia. Int. J. Sports Med.11, Suppl. 1 (1990) S3–S9.
Kontos, H. A., Levasseur, J. E., Richardson, D. W., Mauck, H. P. Jr, and Patterson, J. L. Jr, Comparative circulatory responses to systemic hypoxia in man and in unaesthetized dog. J. appl. Physiol.23 (1967) 381–386.
Lahiri, S., Role of arterial O2 flow in peripheral chemoreceptor excitation. Fedn Proc.39 (1980) 2648–2652.
Pugh, L. G. C. E., Cardiac output in maximal exercise at 5800 m (19,000 ft). J. appl. Physiol.19 (1964) 441–447.
Pugh, L. G. C. E., Gill, M. B., Lahiri, S., Milledge, J. S., Ward, M. P., and West, J. B., Muscular exercise at great altitudes. J. appl. Physiol.19 (1964) 431–440.
Rahn, H., and Otis, A. B., Man's respiratory response during and after acclimatization to high altitude. Am. J. Physiol.157 (1949) 445–449.
Reeves, J. T., Groves, B. M., Sutton, J. R., Wagner, P. D., Cymerman, A., Malconian, M. K., Rock, P. B., Young, P. M., and Houston, C. S., Operation Everest II: preservation of cardiac function at extreme altitude. J. appl. Physiol.63 (1987) 531–539.
Rowell, L. B., Human cardiovascular adjustments to heat and thermal stress. Physiol. Rev.54 (1974) 75–159.
Saltin, B., Physiological adaptation to physical conditioning. Old problems rivisited. Acta med. scand. Suppl.711 (1986) 11–24.
Saltin, B., Grover, R. F., Blomqvist, C. G., Hartley, L. H., and Johnson, R. L. Jr, Maximal oxygen uptake and cardiac output after 2 weeks at 4300 m. J. appl. Physiol.25 (1968) 400–409.
Shephard, R. J., A non-linear solution of the oxygen conductance equation: applications to performances at sea level and at an altitude of 7350 ft. Int. Z. angew. Physiol.27 (1969) 212–225.
Shephard, R. J., The oxygen conductance equation, in: Frontiers of Fitness, pp. 129–154. Ed. J. R. Shephard. Charles C. Thomas, Springfield, IL 1971.
Stenberg, J., Ekblom, B., and Messin, R., Hemodynamic response to work at simulated altitude, 4000 m. J. appl. Physiol.21 (1966) 1589–1594.
Taylor, C. R., and Weibel, E. R., Design of the mammalian respiratory system. I. Problem and strategy. Respir. Physiol.44 (1981) 1–10.
Vogel, J. A., Hansen, J. E., and Harris, C. W., Cardiovascular responses in man during exhaustive work at sea level and high altitude. J. appl. Physiol.23 (1967) 531–539.
Ward, M. P., Milledge, J. S., and West, J. B., High Altitude Medicine and Physiology. University of Pennsylvania Press, Philadelphia, PA 1989.
Weibel, E. R., The pathway for oxygen. Structure and function in the mammalian respiratory system. Harvard University Press, Cambridge, MA 1984.
West, J. B., Respiratory and circulatory control at high altitude. J. exp. Biol.100 (1982) 147–157.
West, J. B., Rate of ventilatory acclimatization to extreme altitude. Respir. Physiol.74 (1988) 323–333.
West, J. B., Boyer, S. J., Graber, D. J., Hackett, P. H., Maret, K. H., Milledge, J. S., Peters, R. M., Pizzo, C. J., Samaja, M., Sarnquist, F. H., Schoene, R. B., and Winslow, R. M., Maximal exercise at extreme altitude on Mount Everest. J. appl. Physiol.55 (1983) 688–698.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferretti, G. On maximal oxygen consumption in hypoxic humans. Experientia 46, 1188–1194 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01936934
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01936934