Abstract
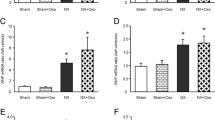
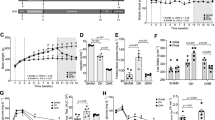
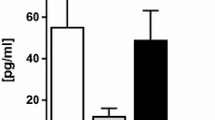
The renal effects of an unsaturated fat (UNSAT) diet in mild to moderate two-kidney, one-clip (2K1C) renovascular hypertension were evaluated. An UNSAT diet (37% by energy) prevented the development of hypertension compared to 2K1C rats fed a high saturated fat (SAT) (37% by energy) and a normal fat (CONTROL) (11% by energy) diet. Urinary sodium and fractional sodium excretion increased in 2K1C rats as compared to SHAM operated controls, regardless of the diet received. In the early weeks of the experiment (weeks 2–4 post-surgery to induce hypertension), an enhanced natriuresis occurred in the 2K1C UNSAT as compared to the 2K1C CONTROL and SAT diet groups. This resulted from an increase in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR in mls·min−1) as measured using the single-injection [51Cr] EDTA method (2K1C UNSAT; 1.99±0.18 versus 2K1C SAT; 1.27±0.09, p<0.02; and versus SHAM CONTROL; 1.45×0.01; p<0.02). The increased GFR was not associated with alterations in effective renal plasma flow (ERPF) as measured using the single-injection [125I] Na hippurate method. No differences in sodium excretion; GFR; ERPF or renal blood flow (microsphere technique) were noted between the 2K1C UNSAT and SAT diet groups at weeks 6–8 post-surgery, despite a continued antihypertensive effect of the UNSAT diet. Hence, the antihypertensive effect of an unsaturated fat diet in 2K1C renovascular hypertension in rats is associated with transient glomerular changes leading to an enhanced natriuresis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Pietinen, P., and Huttunen, J. K., Eur. Heart. J.8 (Suppl B) (1987) 9.
Hoffmann, P., Prost. Leuk. and Med.21 (1986) 113.
Walczyk, M. H., and McCarron, D. A., Am. J. Cardiol.60 (1987) 59G.
Norton, G. R., Katzeff, I. E., Mendelsohn, D., and Rosendorff, C., J. Hypertension5 (Suppl 5) (1987) S232.
Norton, G. R., Katzeff, I. E., Woodiwiss, A. J., and Rosendorff, G., Cardiovasc. Res.26 (1992) 973.
Adam, O., and Wolfram, G., Am. J. clin. Nutr.40 (1984) 220.
Rosenthal, J., Simone, P. G., and Silbergleit, A., Prostaglandins5 (1974) 435.
Leenen, F. H., and de Jong, W., J. appl. Physiol.31 (1971) 142.
Bunag, R. D., J. appl. Physiol.34 (1973) 279.
Trifunovic, B., Woodiwiss, A., and Norton, G. R., Experientia51 (1995) 5.
Puska, P., Iacano, J. M., and Nissinen, A., Lanceti (1983) 1.
Hall, J. E., Guyton, A. C., and Farr, B. M., Am. J. Physiol.232(1 (1977) F72.
Bryan, C. W., Jarchow, R. C., and Maher, J. F., J. Lab. clin. Med.8(6 (1972) 845.
Malik, A. B., Kaplan, J. E., and Saba, T. M., J. appl. Physiol.40(3 (1976) 472.
Swales, J. D., Thurston, H., Queiroz, F. P., and Medina, A., J. Lab. clin. Med.80(4 (1972) 539.
de la Riva, I. J., Morera, S., Kurnjek, M. L., Basso, N., Dominguez Mon, M., and Taquini, A. C., Archs. int. Physiol. Biochim.89 (1981) 115.
Nijkamp, F. P., and de Jong, W., Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. Thér.265 (1983) 103.
Soma, M., Manku, M. S., and Horrobin, D. F., Can. J. Physiol. Pharmac.63 (1985) 325.
Mills, D. E., Ward, R. P., Mah, M., and De Vette, L., Lipids24(1 (1989) 17.
Swales, J. D., Lancetii (1977) 702.
Norman, R. A., Enobakhare, J. A., De Clue, J. W., Douglas, B. H., and Guyton, A. C., Am. J. Physiol.234 (1978) R98.
Miksche, L. W., Miksche, V., and Gross, F., Circ. Res.27 (1970) 973.
Provoost, A. P., de Keijzer, M. H., Wolff, E. D., Molenaar, J. C., Renal Physiol.6 (1983) 1.
Codde, J. P., Beilin, L. J., and Croft, K. D., J. Hypertens.2 (1984) 65.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Norton, G.R., Woodiwiss, A.J. & Trifunovic, B. Renal effects of a high unsaturated fat diet in renal artery stenosis in rats. Experientia 52, 34–41 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01922413
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01922413