Abstract
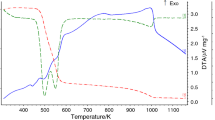
8-hydroxyquinoline (oxine) and uranyl acetate react in the solid state in 1∶3 stoichiometry to give UO2(C9H6NO)2·C9H6NOH. This reaction is diffusion controlled with an activation energy of 44.4 kJ mol−1. The reaction occurs by the surface migration of 8-hydroxyquinoline, which penetrates the product lattice to react with uranyl acetate. The isothermal decomposition of the solution phase product UO2Q2·HQ (Q=C9H6NO) obeys the Prout-Tompkins equation with an energy of activation of 53.3 kJ mol−1.
Zusammenfassung
Die Festkörperreaktion von 8-Hydroxychinolin und Uranylazetat im Verhältnis 1∶3 liefert UO2(G9H6NO)2·C9H6NOH. Die Reaktion ist diffusionsbestimmt und besitzt eine Aktivierungsenergie von 44.4 kJmol−1. Die Reaktion verläuft durch die Oberflächenmigration von 8-Hydroxychinolin, welches zur Reaktion mit Uranylazetat in das Gitter des Produktes eindringt. Die thermische Zersetzung der Mischphase UO2Q2·HQ mitQ=C9H6NO unterliegt der Prout-Tompkins-Gleichung mit einer Aktivierungsenergie von 53,3 kJ·mol−1.
Резюме
8-оксихинолин и уранил ацетат реагируют в твердом состоянии в с техиометрическом соотношении 1∶3, образу я соединение UO2(C9H6NO)2·C9H6NOH. Реакция определяетс я диффузионным механи змом с энергией актив ации 44,4 кдж·моль−1. Реакция п ротекает путем поверхностной магра ции 8-оксихинолина, кот орый проникает в решетку у ранилацетата и реагирует с ним. Изоте рмическое разложени е жидкой фазы UO2 Q 2 · HQ (Q=C9H6NO) подчиняется уравнен ию Праута-Томпкинса с энергией активации 53,3 кдж·моль−1.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. I. Vogel, A Textbook of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, Fourth edition, p. 422, ELBS and Longman, London (1982).
A. Burger, Medicinal Chemistry, Third edition, p. 635, Wiley-Interscience, London (1970).
U. Casellato and P. A. Vigato, Coord. Chem. Rev., 26 (1978) 85.
L. Abate, A. Chisari, R. Maggiore and G. Siracura, J. Thermal Anal., 27 (1983) 139.
Ibid, 28 (1983) 277.
N. A. Lange and G. M. Forker, Handbook of Chemistry, p. 341, McGraw-Hill, USA (1952)
F. Frere, J. Amer. Chem. Soc., 55 (1933) 4363.
R. P. Rastogi, P. S. Bassi and S. L. Chadha, J. Phys. Chem., 67 (1963) 2569.
G. Giergio, B. Mentzen, M. Breyssi and B. Claudel, J. Inorg. Nucl. Chem., 32 (1970) 1517.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bassi, P.S., Chopra, G.S. & Kaur, K. Solid state reactivity of organic compounds with inorganic compounds. IV synthesis and thermal decomposition of uranium oxinate in the solid state. Journal of Thermal Analysis 35, 1213–1221 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01913040
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01913040