Abstract
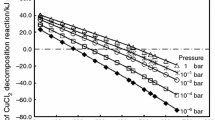
The isothermal decomposition of anhydrous Cu(II) malonate of uniform particle size has been studied at 170, 180 and 190°. Decomposition to cupric oxide takes place via the intermediate formation of 2CuCO3.Cu(OH)2. X-ray diffraction has been employed to identify the decomposition products. The experimental kinetic data for Cu(II) malonate decomposition are best fitted by two stages: (i) a linear process and (ii) a first-order expression. The activation energies for the two kinetic stages have been found to be 45.7 and 57.2 kcal/mole, respectively. A DTA study of Cu(II) malonate decomposition has also been made. Activation energies have been determined via analysis of the DTA curve using the Borchardt and Piloyan equations.
Résumé
On a étudié la décomposition thermique du malonate de cuivre(II) anhydre à 170, 180 et 190°. La décomposition du malonate en CuO se produit avec formation intermédiaire de 2CuCO3.Cu(OH)2. Les produits de décomposition ont été identifiés par diffraction des rayons X. Les données expérimentales correspondent à deux étapes de cinétique différente: (i) un processus linéaire et (ii) une expression du premier ordre. Les énergies d'activation respectives des deux étapes cinétiques s'élèvent à 45.7 et 57.2 kcal.mol/s-1. Le malonate de cuivre(II) a aussi été étudié par ATD. Les énergies d'activation ont été déterminées à partir de la courbe ATD en appliquant les équations de Borchardt et de Piloyan.
Zusammenfassung
Die isotherme Zersetzung von wasserfreiem Cu(II)-malonat einheitlicher Partikelgröße wurde bei Temperaturen von 170°, 180° und 190° untersucht. Die Zersetzung von Cu(II)-malonat zu Kupfer(II)-oxid erfolgt über die intermediäre Bildung von 2CuCO3.Cu(OH)2. Die Röntgendiffraktionstechnik wurde zur Identifizierung der Zersetzungsprodukte eingesetzt. Die Versuchsergebnisse von Cu(II)-malonat können am besten zwei kinetischen Zuständen angepaßt werden: (1) einem linearen Prozeß und (2) einem Ausdruck erster Ordnung. Die entsprechenden Aktivierungsenergien für die zwei kinetischen Zustände waren 45.7 Kcal/Mol bzw. 57.2 Kcal/Mol. Eine DTA-Untersuchung von Cu(II)-malonat wurde ebenfalls durchgeführt. Die Aktivierungsenergien wurden aus der Analyse der DTA-Kurve mittels der Gleichungen von Borchardt und Piloyan bestimmt.
Резюме
Было изучено изотерм ическое разложение частиц одного и того ж е размера малоната меди (II) при те мпературах 170°, 180° и 190°. Разложение малоната меди (II) до окиси меди протека ет через стадию образ ования 2CuCO3. Cu(ОH)2. Для идентификации продуктов разложени я была использована т ехника диффракции рентгено вых лучей. Экспериментальные р езультаты по малонат у меди (II) наилучше соответств уют двум кинетическим стадия м: (1) линейному процесс у и (2) уравнению первого по рядка. Было найдено, что соответс твующие энергии акти вации этих двух кинетических ст адий, соответственно, равны 45,7 ккал/моль 57,2 ккал /моль. Изучено также ДТА малоната ме ди (II). Из кривых ДТА, использ уя уравнения Борхард та и Пилояна, определены э нергии активации.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. S. Bassi and P. C. Kalsi, Ind. J. Chem., (in press)
P. S. Bassi and P. C. Kalsi, J. Chin. Chem. Soc. (communicated)
E. Campi, Ann. Chim., 53 (1963) 96.
L. Dubicki, C. M. Harris, E. Kokot andR. L. Martin, (Univ. New South Wales, Sydney) Inorg. Chem., 5 (1966) 93.
H. T. S.Britlon and E. D.Jarrett, J. Chem. Soc., (1935) 168.
A. I. Vogel, Quantitative Inorganic Analysis, Longmans, Green Co, London, 1962, p. 497.
H. J. Borchardt andF. Daniels, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 79 (1957) 41.
G. O.Piloyan, I. D.Ryabchikov and D. S.Novikova, Nature, Lond. (1966) 1229.
Swanson andTatge, NBS Circular, 539 Vol. I (1953) 49.
Nat. Bur. Standards Circ. 539, 10 (1960) 30.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
One of the authors (P.C.K.) is grateful to the University Grants Comission, New Delhi, for the award of a junior research fellowship. The authors are grateful to Dr. K. N. Goswami of the Physics Department, University of Jammu, for his help in the X-ray studies of the products.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bassi, P.S., Kalsi, P.C. Thermal decomposition of Cu(II) Malonate. Journal of Thermal Analysis 10, 375–381 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01909889
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01909889