Summary
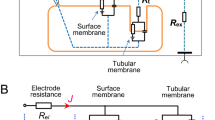
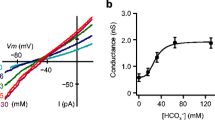
Experiments were performed in intact proximal tubules of the doubly perfused kidney and in fused proximal tubule cells ofRaha esculenta to evaluate the dependence of intracellular pH (pHi) on cell membrane potential applying pH-sensitive and conventional microelectrodes. In proximal tubules an increase of the K− concentration in the peritubular perfusate from 3 to 15 mmol/liter decreased the peritubular cell membrane potential from −55±2 to −38±1 mV paralleled by an increase of pH i , from 7.54±0.02 to 7.66±0.02. The stilbene derivative DIDS hyperpolarized the cell membrane potential from −57 ± 2 to −71 ±4 mV and led to a significant increase of the K−-induced cell membrane depolarization, but prevented the K−-induced intracellular alkalinization. Fused proximal tubule cells were impaled by three microelectrodes simultaneously and cell voltage was clamped stepwise while pH i changes were monitored. Cell membrane hyperpolarization acidified the cell cytoplasm in a linear relationship. This voltage-induced intracellular acidification was reduced to about one-third when HCO3 ions were omitted from the extracellular medium. We conclude that in proximal tubule cells pH i depends on cell voltage due to the rheogenicity of the HCO −3 transport system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpern, R.J. 1985. Mechanism of basolateral membrane H+/OH−/HCO −3 transport in the rat proximal tubule.J. Gen. Physiol. 86:613–636
Ammann, D., Lanter, F., Steiner, R.A., Schultess, P., Shijo, Y., Simon, W. 1981. Neutral carrier based hydrogen ion selective microelectrode for extra and intracellular studies.Anal. Chem. 53:2267–2269
Aronson, P.S., Nee, J., Suhm, M.A. 1982. Modifier role of internal H+ in activating the Na+−H+ exchanger in renal microvillus membrane vesicles.Nature (London) 299:161–163
Biagi, B.A. 1985. Effects of the anion transport inhibitor, SITS, on the proximal straight tubule of the rabbit perfusedin vitro.J. Membrane Biol. 88:25–31
Biagi, B.A., Sohtell, M. 1986. Electrophysiology of basolateral bicarbonate transport in the rabbit proximal tubule.Am. J. Physiol. 250:F267-F272
Boron, W.F., Boulpaep, E.L. 1983. Intracellular pH regulation in the renal proximal tubule of the salamander: Na−H exchange.J. Gen. Physiol. 81:29–52
Boron, W.F., Boulpaep, E.L. 1983. Intracellular pH regulation in the renal proximal tubule of the salamander: Basolateral HCO −3 transport.J. Gen. Physiol. 81:53–94
Brisalla-Diuana, A., Amorena, C., Malnic, G. 1986. Transfer of base across the basolateral membrane of cortical tubules of rat kidney.Pfluegers Arch. 405:209–215
Burckhardt, B.C., Frömter, E. 1987. Evidence for OH−/H+ permeation across the peritubular cell membrane of rat renal proximal tubule in HCO −3 -free solutions.Pfluegers Arch. 409:132–137
Chantrelle, B., Cogan, M.G., Rector, F.C., Jr. 1982. Evidence for coupled sodium/hydrogen exchange in the rat superficial proximal convoluted tubule.Pfluegers Arch. 395:186–189
Dietl, P., Wang, W., Oberleithner, H. 1987. Fused cells of frog proximal tubule: I. Basic membrane properties.J. Membrane Biol. 100:43–51
Frömter, E. 1984. Viewing the kidney through microelectrodes.Am. J. Physiol. 247:F695-F705
Guggino, W.B., London, R., Boulpaep, E.L., Giebisch, G. 1983. Chloride transport across the basolateral cell membrane of theNecturus proximal tubule: Dependence on bicarbonate and sodium.J. Membrane Biol. 71:227–240
Lang, F., Messner, G., Rehwald, W. 1986. Electrophysiology of sodium-coupled transport in proximal renal tubules.Am. J. Physiol. 250:F953-F962
Matsumura, Y., Cohen, B., Guggino, W.B., Giebisch, G. 1984. Electrical effects of potassium and bicarbonate on proximal tubule cells ofNecturus.J. Membrane Biol. 79:145–152
Meech, R.W., Thomas, R.C. 1987. Voltage-dependent intracellular pH inHelix aspersa neurones.J. Physiol. (London) (in press)
Messner, G., Wang, W. Paulmichl, M., Oberleithner, H., Lang, F. 1985. Ouabain decreases apparent potassium-conductance in proximal tubules of the amphibian kidney.Pfluegers Arch. 404:131–137
Oberleithner, H., Gassner, B., Dietl, P. Wang, W. 1988. Amphibian nephron: Isolated kidney and cell fusion.Methods Enzymol. (in press)
Oberleithner, H., Lang, F., Messner, G., Wang, W. 1984. Mechanism of hydrogen ion transport in the diluting segment of frog kidney.Pfluegers Arch. 402:272–280
Oberleithner, H., Weigt, M., Westphale, H.J., Wang, W. 1987. Aldosterone activates Na+/H+ exchange and raises cytoplasmic pH in target cells of the amphibian kidney.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84:1464–1468
Rector, F.C., Jr. 1983. Sodium, bicarbonate, and chloride absorption by the proximal tubule.Am. J. Physiol. 244:F461-F471
Thomas, R.C., Meech, R.W. 1982. Hydrogen ion currents and intracellular pH in depolarized voltage-clamped snail neurons.Nature (London) 299:826–828
Wang, K.W., Deen, W.M. 1980. Chemical, kinetic and diffusional limitations on bicarbonate reabsorption by the proximal tubule.Biophys. J. 31:161–182
Wang, W., Dietl, P., Oberleithner, H. 1987. Evidence for Na+ dependent rheogenic HCO −3 transport in fused cells of frog distal tubules.Pfluegers Arch. 408:291–299
Wang, W., Dietl, P., Oberleithner, H. 1987. Cell membrane potential: A signal to control intracellular pH and transepithelial hydrogen ion secretion in frog kidney.Pfluegers Arch. 409:289–295
Wang, W., Messner, G., Oberleithner, H., Lang, F., Deetjen, P. 1984. The effect of ouabain on intracellular activities of K+, Na+, Cl−, H+ and Ca2+ in proximal tubule of frog kidneys.Pfluegers Arch. 401:6–13
Wang, W., Oberleithner, H., Lang, F. 1983. The effect of cAMP on the cell membrane potential and intracellular ion activities in proximal tubule ofRana esculenta.Pfluegers Arch. 369:192–198
Yoshitomi, K., Burckhardt, B.C., Frömter, E. 1985. Rheogenic sodium-bicarbonate cotransport in the peritubular cell membrane of rat renal proximal tubule.Pfluegers Arch. 405:360–366
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W., Wang, Y., Silbernagl, S. et al. Fused cells of frog proximal tubule: II. Voltage-dependent intracellular pH. J. Membrain Biol. 101, 259–265 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872840
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872840