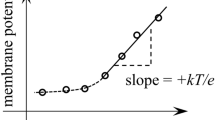
Summary
Equations are developed to examine the effects of secondary active transport processes on the steady-state membrane potential of symmetrical cells. It is shown that, with suitable modifications, equations of the type developed by Goldman, Hodgkin and Katz may be derived to accommodate the contributions to the membrane potential of both electroneutral and electrogenic transporters. Where the membrane potential is function of the dominant medium ions (Na, K, and Cl), other contributions can come only from an electrogenic Na pump and from neutral co- and counter-transporters if, and only if, these involve the dominant ions. Experimental approaches to measure the parameters necessary to solve the equations developed here are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boron, W.F. 1986. Intracellular pH regulation.In: Physiology of Membrane Disorders. (2nd ed.) T.E. Andreoli et al., editors. pp. 423–435. Plenum Medical Book, New York
Cabantchik, Z.I., Kanuf, P.A., Rothstein, A. 1978. The anion transport system of the red blood cell: The role of the membrane protein evaluated by the use of ‘probes’.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 515:239–302
Crane, R.K. 1962. Hypothesis for mechanism of intestinal active transport of sugars.Fed. Proc. 21:891–895
Geck, P., Heinz, E. 1986. The Na−K−2Cl cotransport system.J. Membrane Biol. 91:97–105
Geck, P., Pietrzyk, C., Burckhardt, B.-C., Peiffer, B., Heinz, E. 1980. Electrically silent cotransport of Na+, K+, and Cl− in Ehrlich cells.Biochim. Biohys. Acta 600:432–447
Goldman, D.E. 1943. Potential, impedance and rectification in membranes.J. Gen. Physiol. 27:37–60
Gordon, L.G.M., Macknight, A.D.C. 1991. Application of membrane potential equations to tight epithelia.J. Membrane Biol. 120:155–163
Grinstein, S., Rothstein, A. 1986. Mechanisms of regulation of the Na+/H+ exchanger.J. Membrane Biol. 90:1–12
Hodgkin, A.L., Katz, B. 1949. The effect of sodium ions on the electrical activity of the giant axon of the squid.J. Physiol. 108:37–77
Jacob, R., Piwnica-Worms, D., Horres, C.R., Lieberman, M. 1984. Theoretical effects of transmembrane electroneutral exchange on membrane potential.J. Gen. Physiol. 83:47–56
Jacob, R., Piwnica-Worms, D., Horres, C.R., Lieberman, M. 1985. Electroneutral Na−H exchange may depolarize the resting membrane potential.J. Gen. Physiol. 85:891–895
Jacquez, J.A., Schultz, S.G. 1974. A general relation between membrane potentials, ion activities, and pump fluxes for symmetric cells in a steady state.Math. Biosci. 20:19–25
Kaunitz, J.D., Wright, E.M. 1984. Kinetics of sodiumd-glucose cotransport in bovine intestinal brush border vesicles.J. Membrane Biol. 79:41–51
Knauf, P.A. 1986. Anion transport in erythrocytes.In: Physiology of Membrane Disorders. (2nd ed.) T.E. Andreoli et al., editors. pp. 191–220. Plenum Medical Book, New York
Läuger, P., Jauch, P. 1986. Microscopic description of voltage effects on ion-driven cotransport systems.J. Membrane Biol. 91:275–284
Moreton, R.B. 1969. An investigation of electrogenic sodium pump in snail neurones using the constant field theory.J. Exp. Biol. 51:181–201
Mullins, L.J., Noda, K. 1963. The influence of sodium-free solutions on the membrane potential of frog sartorius muscle.J. Gen. Physiol. 47:117–132
Murer, H., Hopfer, U., Kinne, R. 1976. Sodium/proton antiport in brush border membrane vesicles isolated from the rat small intestine and kidney.Biochem. J. 154:597–604
O'Grady, S.M., Palfrey, H.C., Field, M. 1987. Characteristics and functions of Na−K−Cl cotransport in epithelial tissues.Am. J. Physiol. 253:C177-C192
Restrepo, D., Kimmich, G.A. 1985. Kinetic analysis of the mechanism of intestinal Na+-dependent sugar transport.Am. J. Physiol. 248:C498-C509
Schatzmann, H.J. 1985. Calcium extrusion across the plasma membrane by the calcium pump and the Ca2+−Na+ exchange system.In: Marme, Calcium and Cell Physiology. pp. 18–52. Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Schultz, S.G., Curran, P.F. 1970. Coupled transport of sodium and inorganic solutes.Physiol. Rev. 50:637–718
Scriven, D.R.L., Mundel, T. 1985. Electroneutral Na−H exchange does not depolarize the resting membrane potential.J. Gen. Physiol. 85:933–935
Sjodin, R.A. 1983. Contributions of Na/Ca transport to the resting membrane potential.J. Gen. Physiol. 76:99–108
Teorell, T. 1953. Transport processes and electrical phenomena in ionic membranes.Prog. Biophys. Chem. 3:305–369
Yoshitomi, K., Burckhardt, B.C., Frömter, E. 1985. Rheogenic sodium-bicarbonate cotransport in the peritubular cell membrane of rat renal proximal tubule.Pfluegers Arch. 405:360–366
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gordon, L.G.M., Macknight, A.D.C. Contributions of secondary active transport processes to membrane potentials. J. Membrain Biol. 120, 141–154 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872397
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01872397