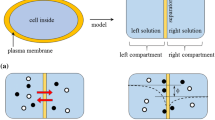
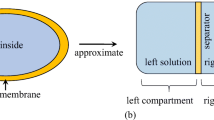
Abstract
Membrane theory makes it possible to compute the membrane potential of living cells accurately. The principle is that the plasma membrane is selectively permeable to ions and that its permeability to mobile ions determines the characteristics of the membrane potential. However, an artificial experimental cell system with an impermeable membrane can exhibit a nonzero membrane potential, and its characteristics are consistent with the prediction of the Goldman–Hodgkin–Katz eq., which is a noteworthy concept of membrane theory, despite the membrane’s impermeability to mobile ions. We noticed this troublesome facet of the membrane theory. We measured the potentials through permeable and impermeable membranes where we used the broad varieties of membranes. Then we concluded that the membrane potential must be primarily, although not wholly, governed by the ion adsorption-desorption process rather than by the passage of ions across the cell membrane. A theory based on the Association-Induction Hypothesis seems to be a more plausible mechanism for the generation of the membrane potential and to explain this unexpected physiological fact. The Association-Induction Hypothesis states that selective ion permeability of the membrane is not a condition for the generation of the membrane potential in living cells, which contradicts the prediction of the membrane theory. Therefore, the Association-Induction Hypothesis is the actual cause of membrane potential. We continued the theoretical analysis by taking into account the Association-Induction Hypothesis and saw that its universality as a cause of potential generation mechanism. We then concluded that the interfacial charge distribution is one of the fundamental causes of the membrane potential.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Bagatolli LA, Stock RP (2021) Lipids, membranes, colloids and cells: a long view. BBA Biomembranes. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2021.183684
Bagatolli LA, Mangiarotti A, Stock RP (2021) Cellular metabolism and colloids: realistically linking physiology and biological physical chemistry. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 162:79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2020.06.002
Barrow GM (1979) Physical chemistry. McGraw-Hill Inc., New York
Berg J (2021) An ion-selective electrode for detection of ammonium in wastewater treatment plants. Degree Project in Chemical Science and Engineering, Second Cycle, 30 Credits Stockholm, Sweden
Chang D (1983) Dependence of cellular potential on ionic concentrations. Data supporting a modification of the constant field equation. Biophys J 43(2):149–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(83)84335-5
Cheng KL (1998) Explanation of misleading Nernst slope by Boltzmann equation. Microchem J 59:457–461. https://doi.org/10.1006/mchj.1998.1624
Cheng KL (2002) Recent development of non-faradaic potentiometry. Microchem J 72(3):269–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0026-265X(02)00092-9
Covington A (1981) Ion-selective electrodes. The Royal Society of Chemistry, London
Criscuolo F, Hanitra MIN, Taurino I, Carrara S, Micheli GD (2021) All-solid-state ion-selective electrodes: a tutorial for correct practice. IEEE Sens J 21(20):22143–22154. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSEN.2021.3099209
Cronin J (1987) Mathematical aspects of Hodgkin-Huxley neural theory. Cambridge University Press, New York
Diamond JM, Harrison SC (1966) The effect of membrane fixed charges on diffusion potentials and streaming potentials. J Physiol 183:37–57. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007850
Durst RA (Ed) (1969) Ion-selective electrodes. Institute for Materials Research National Bureau of Standards, Washington D.C
Ermentrout GB, Terman TH (2010) Mathematical foundations of neuroscience, vol 35. Interdisciplinary applied mathematics book. Springer, New York
Fischer RB (1974) Ion-selective electrodes. Proc California Assoc Chem Teach 51(6):387–390. https://doi.org/10.1021/ed051p387
Galassi VV, Wilke N (2021) On the coupling between mechanical properties and electrostatics in biological membranes. Membranes. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes11070478
Hodgkin AL, Howrowicz P (1959) The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potential of single muscle fibers. J Physiol 148(1):127–160. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006278
Hwang SG, Hong JK, Sharma A, Pollack GH, Bahng GW (2018) Exclusion zone and heterogeneous water structure at ambient temperature. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0195057
Jaeken L (2017) The neglected functions of intrinsically disordered proteins and the origin of life. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 126:31–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2017.03.002
Jaeken L (2021) The greatest error in biological sciences, started in 1930 and continuing up to now, generating numerous profound misunderstandings. Curr Adv Chem Biochem 5:156–164. https://doi.org/10.9734/bpi/cacb/v5/1969F
Katchalsky A (1971) Polyelectrolytes. Pure Appl Chem 26(3–4):327–374. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac197126030327
Katoh T, Inda Y, Nakajima K, Ye R, Baba M (2010) Lithium/air batteries using Li-Ion conducting glass ceramics. ITE-IBA Lett Batter New Technol Med 3(4):327–374
Keener J, Sneyd J (2008) Mathematical physiology: I: cellular physiology. Interdisciplinary applied mathematics. Springer, New York
Kowacz M, Pollack GH (2020) Cells in new light: ion concentration, voltage, and pressure gradients across a hydrogel membrane. AOS Omega 5(33):21024–21031. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c02595
Lewis GN, Randall M (1961) Thermodynamics. McGraw-Hill series in advanced chemistry, New York
Ling GN (1992) A revolution in the physiology of the living cell. Krieger Pub Co, Malabar
Ling GN (1997) Debunking the alleged resurrection of the sodium pump hypothesis. Physiol Chem Phys 29:123–198
Ling GN (2001) Life at the cell and below-cell level: the hidden history of a fundamental revolution in biology. Pacific Press, New York
Ling GN (2007) Nano-protoplasm: the Ultimate Unit of Life. Physiol Chem Phys & Med NMR 39:111–234
Manoj KM, Soman V, Jacob VD, Parashar A, Gideon DA, Kumar M, Manekkathodi A, Ramasamy S, Pakshirajan K, Bazhin NM (2019) Chemiosmotic and murburn explanations for aerobic respiration: predictive capabilities, structure-function correlations and chemico-physical logic. Arch Biochem Biophys. 676:108128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2019.108128
Manoj KM, Jacob VD (2020) The murburn precepts for photoreception. Biomed Rev 31:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpap.2020.100015
Manoj KM, Manekkathodi A (2021) Light’s interaction with pigments in chloroplasts: the murburn perspective. J Photochem Photobiol. 5:100015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpap.2020.100015
Matveev V (2017) Comparison of fundamental physical properties of the model cells (protocells) and the living cells reveals the need in protophysiology. Int J Astrobiol 16(1):97–104. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1473550415000476
Matveev V (2019) Cell theory, intrinsically disordered proteins, and the physics of the origin of life. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 149:114–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2019.04.001
Moreton RB (1968) An application of the constant-feld theory to the behaviour of giant neurons of the snail. Helix aspersa. J Exp Biol 48(3):611–662. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.48.3.611
Naik VA (2016) Principle and applications of ion selective electrodes-an overview. Int J Appl Res Sci Eng 2:2456–124X.
Olschewski A, Olschewski H, Bräu ME, Hempelmann G, Vogel W, Safronov BV (2001) Basic electrical properties of in situ endothelial cells of small pulmonary arteries during postnatal development. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 25:285–290. https://doi.org/10.1165/ajrcmb.25.3.4373
Pollack GH (2013) The fourth phase of water: beyond solid, liquid, and vapor. Edgescience 16:14
Pollack GH (2014) The fourth phase of water: beyond solid, liquid, and vapor. Ebner & Sons, Seattle
Radu A, Radu T, McGRAW C, Dillingham P, Anastasova-Ivanova S, Diamond D (2013) Ion selective electrodes in environmental analysis. J Serb Chem Soc 78(11):1729–1761. https://doi.org/10.2298/JSC130829098R
Rechnitz GA (1973) Mechanistic aspects of ion-selective membrane electrodes. A subjective view. Int Union Pure Appl Chem 5:457–471
Schneider MF (2021) Living systems approached from physical principles. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 162:2–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2020.10.001
Shinagawa Y (1976) Physical basis of membrane potential (written in Japanese). Membrane (Japanese written journal) 1:176–183
Shklyar TF, Safronov AP, Klyuzhin IS, Pollack GH, Blyakhman FA (2008) A correlation between mechanical and electrical properties of the synthetic hydrogel chosen as an experimental model of Cytoskeleton. Biophysics 53(6):544–549. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn1018768
Tamagawa H, Ikeda K (2018) Another interpretation of Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation based on the Ling’s adsorption theory. Eur Biophys J 47:869–879. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-018-1332-0
Tamagawa H (2018) Mathematical expression of membrane potential based on Ling’s adsorption theory is approximately the same as the Goldman-Hodgkin-Katz equation. J Biol Phys 45(1):13–30. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10867-018-9512-9
Tamagawa H, Mulembo T, Delalande B (2021a) The need of the reconsideration of generation mechanism of membrane potential by mean of the Ling’s adsorption theory. Eur Biophys J 50(6):793–803. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-021-01526-4
Tamagawa H, Mulembo T, Delalande B (2021b) What can S-shaped potential profiles tell us about the mechanism of membrane potential generation? Euro Biophys J 50(6):805–818. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00249-021-01531-7
Temsamani KR, Cheng KL (2001) Studies of chloride adsorption on the Ag/AgCl electrode. Sens Actuators B 76(1–3):551–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0925-4005(01)00624-4
Uteshev VV (2010) Evaluation of Ca2+ permeability of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in hypothalamic histaminergic neurons. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin 42(1):8–20. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmp101
Wang A, Pollack GH (2021) Effect of infrared radiation on interfacial water at hydrophilic surfaces. Colloid Interface Sci Commun 42:100397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colcom.2021.100397
Wnek GE (2015) Perspective: do macromolecules play a role in the mechanisms of nerve stimulation and nervous transmission? J Polym Sci Part B Polym Phys 54(1):7–14. https://doi.org/10.1002/polb.23898
Wright EM, Diamond JM (1968) Efects of pH and polyvalent cations on the selective permeability of gall-bladder epithelium to monovalent ions. Biochim Biophys Acta 163(1):57–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/0005-2736(68)90033-3
Zhang X, Wakamatsu H (2002) A new equivalent circuit different from the Hodgkin-Huxley model, and an equation for the resting membrane potential of a cell. Artif Life Robot 6(3):140–148. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02481329
Zheng J, Pollack GH (2006) Solute exclusion and potential distribution near hydrophilic surfaces. In: Pollack GH, Cameron IL, Wheatley DN (eds) Water and the Cell. Springer, Dordrecht
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
H.T. conceived and designed the study. H.T. also performed experiments and data analysis. H.T. and B.D. wrote the draft, checked its logic, and then performed its revision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Tamagawa, H., Delalande, B. The membrane potential arising from the adsorption of ions at the biological interface. BIOLOGIA FUTURA 73, 455–471 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42977-022-00139-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42977-022-00139-y