Summary
In goldfish intestine chloride was substituted by large inorganic anions (gluconate or glucuronate) either mucosally, serosally or bilaterally. Changes in intracellular activities of chloride (a i Cl−), sodium (a i Na+) and potassium (a i K+), pHi, relative volume, membrane and transepithelial potentials, transepithelial resistance and voltage divider ratio were measured. Control values were:a i Cl−=35 meq/liter, a i Na+=11 meq/liter and a i K+=95 meq/liter. During bilateral substitution the latter two did not change while a i Cl− dropped to virtually zero.
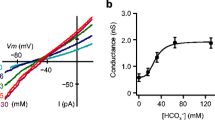
Mucosal membrane potentials (ψms) were: control,-53 mV; serosal substitution,-51 mV; bilateral substitution,-66 mV; while during mucosal substitution a transient depolarization occurred and the final steady state ψms was-66 mV.
During control and bilateral substitution the transepithelial potentials (ψms) did not differ from zero. During unilateral substitutions ψms was small, in the order of magnitude of the errors in the liquid junction potentials near the measuring salt bridges.
During bilateral substitution pH i increased 0.4 pH units. Cellular volume decreased during mucosal substitution to 88% in 40 min; after serosal substitution it transiently increased, but the new steady-state value was not significantly above its control value.
Three minutes after mucosal substitution ana i Cl− of approx. 10 meq/liter was measured.
Chemical concentrations of Na, K and Cl were determined under control conditions and bilateral substitution. Cl concentrations were also measured as a function of time after unilateral substitutions.
The data indicate an electrically silent chloride influx mechanism in the brush border membrane and an electrodiffusional chloride efflux in the basolateral membrane. A substantial bicarbonate permeability is present in the basolateral membrane. The results are in agreement with the observed changes in membrane resistances, volume changes and pH changes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albus, H., Bakker, R., Siegenbeek van Heukelom, J. 1983. Circuit analysis of membrane potentials changes due to electrogenic sodium-dependent sugar transport in goldfish intestinal epithelium.Pfluegers Arch. 398:1–9
Armstrong, W.McD., Bixenman, W.R., Frey, K.F., Garcia-Diaz, J.F., O'Regan, M.G., Owens, J.L. 1979. Energetics of coupled Na+ and Cl− entry into epithelial cells of bullfrog small intestine.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 551:207–219
Armstrong, W.McD., Garcia-Diaz, J.F. 1980. Ion-selective microelectrodes: Theory and technique.Fed. Proc. 39:2851–2859
Baerentsen, H.J., Christensen, O., Thomsen, P.G., Zeuthen, T. 1982. Steady states and the effects of ouabain in theNecturus gallbladder epithelium: A model analysis.J. Membrane Biol. 68:215–225
Baerentsen, H., Giraldez, F., Zeuthen, T. 1983. Influx mechanisms for Na+ and Cl− across the brush border membrane of leaky epithelia: A model and microelectrode study.J. Membrane Biol. 75:205–218
Bakker, R., Dekker, K., Zuidema, T., Groot, J.A. 1982. Transepithelial Cl-transport in goldfishCarassius auratus intestinal mucosa and the effect of theophylline on fluxes and electrophysiology. 4th Conference of the European Society for Comparative Physiology and Biochemistry, Bielefeld (FRG) September 8–11, 1982
Bakker, R., Groot, J.A. 1984. cAMP-mediated effects of ouabain and theophylline on paracellular ion selectivity.Am. J. Physiol. 246:G213-G217
Barry, P.H., Diamond, J.M. 1970. Junction potentials, electrode standard potentials, and other problems in interpreting electrical properties of membranes.J. Membrane Biol. 3:93–122
Burckhardt, B.C., Frömter, E. 1981. Bicarbonate and hydroxylion permeability of the peritubular cell membrane of rat renal proximal tubular cells.Pfluegers Arch. 389:R40
Christoffersen, G.R.J., Skibsted, L.H. 1975. Calcium ion activity in physiological solutions: Influence of anions substituted for chloride.Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 52A:317–322
Cremaschi, D., James, P.S., Meyer, G., Rossetti, C., Smith, M.W. 1984. Developmental changes in intra-enterocyte cation activities in hamster terminal ileum.J. Physiol. (London) 354:363–373
Dagostino, M., Lee, C.O. 1982. Neutral carrier Na+-and Ca2+-selective microelectrodes for intracellular application.Biophys. J. 40:199–207
Duffey, M.E., Turnheim, K., Frizzell, R.A., Schultz, S.G. 1979. Intracellular chloride activities in rabbit gallbladder: Direct evidence for the role of the sodium-gradient in energizing “Uphill” chloride transport.J. Membrane Biol. 42:229–245
Ellory, J.C., Ramos, M., Zeuthen, T. 1979. Cl−-accumulation in the plaice intestinal epithelium.J. Physiol. (London) 287:12P
Field, M., Karnaky, K.J., Smith, P.L., Bolton, J.E., Kinter, W.B. 1978. Ion transport across the isolated intestinal mucosa of the winter flounder,Pseudopleuronectes americanus: I. Functional and structural properties of cellular and paracellular pathways for Na and Cl.J. Membrane Biol. 41:265–293
Fisher, R.S. 1984. Chloride movement across basolateral membrane ofNecturus gallbladder epithelium.Am. J. Physiol. 247:C495-C500
Frizzell, R.A., Field, M., Schultz, S.G. 1979. Sodium-coupled chloride transport by epithelial tissues.Am. J. Physiol. 236:F1-F8
Frömter, E. 1979. Solute transport across epithelia: What can we learn from micropuncture studies on kidney tubules?J. Physiol. (London) 288:1–31
Garcia-Diaz, J.F., O'Doherty, J., Armstrong, W.McD. 1978. Potential profile, K+ and Na+ activities inNecturus small intestine.Physiologist 21:41
Giraldez, F. 1984. Active sodium transport and fluid secretion in the gall-bladder epithelium ofNecturus.J. Physiol. (London) 348:431–455
Groot, J.A. 1981. Cell volume regulation in goldfish intestinal mucosa.Pfluegers Arch. 392:57–66
Groot, J.A. 1982. Aspects of the Physiology of the Intestinal Mucosa of the Goldfish (Carassius auratus L). MultiCopy, Amsterdam
Groot, J.A., Albus, H., Siegenbeek van Heukelom, J. 1979. A mechanistic explanation of the effect of potassium on goldfish intestinal transport.Pfluegers Arch. 379:1–9
Groot, J.A., Dekker, K., Van Riel, J.W., Zuidema, T. 1982. Intracellular ion concentrations and pH of stripped mucosa of goldfish (Carassius auratus) intestine in relation to Cl− transport. 4th conference of the European Society for Comparative Physiology and Biochemistry, Bielefeld (FRG), September 8–11, 1982
Guggino, W.B., Boulpaep, E.L., Giebisch, G. 1982. Electrical properties of chloride transport across theNecturus proximal tubule.J. Membrane Biol. 65:185–196
Halm, D., Krasny, E., Frizzell, R.A. 1982. Apical membrane potassium conductance in flounder intestine: Relation to chloride absorption.Bull. Mount Desert Island Biol. Lab. 21:88–93
Henin, S., Smith, M.W. 1976. Electrical properties of pig colonic mucosa measured during early post-natal development.J. Physiol. (London) 262:169–187
Hudson, R.L., Schultz, S.G. 1984. Sodium-coupled sugar transport: Effects on intracellular sodium activities and sodium-pump activity.Science 224:1237–1239
Jacquez, J.A., Schultz, S.G. 1974. A general relation between membrane potential, ion activities and pump fluxes for symmetric cells in a steady state.Math. Biosci. 20:19–26
Katz, U., Lau, K.R., Ramos, M.M.P., Ellory, J.C. 1982. Thiocyanate transport across fish intestine (Pleuronectes platessa).J. Membrane Biol. 66:9–14
Laprade, R., Cardinal, J. 1983. Liquid junctions and isolated proximal tubule transepithelial potentials.Am. J. Physiol. 244:F304-F319
Lee, C.O., Armstrong, W.McD. 1972. Activities of sodium and potassium ions in epithelial cells of small intestine.Science 175:1261–1264
Liedtke, C.M., Hopfer, U. 1982. Mechanism of Cl− translocation across small intestinal brush-border membrane: II. Demonstration of Cl−−OH− exchange and Cl− conductance.Am. J. Physiol. 242:G272-G280
Meier, P.C., Lanter, F., Ammann, D., Steiner, R.A., Simon, W. 1982. Applicability of available ion-selective liquid membrane microelectrodes to intracellular ion activity measurements.Pfluegers Arch. 393:23–30
Nellans, H.N., Frizzell, R.A., Schultz, S.G. 1973. Coupled sodium-chloride influx across the brushborder of rabbit ileum.Am. J. Physiol. 225:467–475
Okada, Y., Irimajuri, A., Inouye, A. 1976. Intracellular ion concentrations of epithelial cells in rat intestine. Effects of external K and uphill transports of glucose and glycine.Jpn. J. Physiol. 26:427–440
Okada, Y., Sato, T., Inouye, A. 1975. Effects of potassium ions and sodium ions on membrane potential of epithelial cells in rat duodenum.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 413:104–115
Os, C.H. van, Wiedner, G., Wright, E.M. 1979. Volume flows across gallbladder epithelium induced by small hydrostatic and osmotic gradients.J. Membrane Biol. 49:1–20
Reuss, L. 1979. Electrical properties of cellular transepithelial pathway inNecturus gallbladder: III. Ionic permeability of the basolateral cell membrane.J. Membrane Biol. 47:239–259
Reuss, L. 1983. Basolateral co-transport in NaCl-absorbing epithelium.Nature (London) 305:723–726
Reuss, L., Cheung, L.Y., Grady, T.P. 1982. Mechanisms of cation permeation across apical cell membrane ofNecturus gallbladder: Effects of luminal pH and divalent cations on K+ and Na+ permeability.J. Membrane Biol. 59:211–224
Reuss, L., Weinman, S.A. 1979. Intracellular ionic activities and transmembrane electrochemical potential differences in gallbladder epithelium.J. Membrane Biol. 49:345–362
Rose, R.C., Schultz, S.G. 1971. Studies on the electrical potential profile across rabbit ileum: Effects of sugars and amino acids on transmural and transmucosal electrical potential differences.J. Gen. Physiol 57:639–663
Sackin, H., Boulpaep, E.L. 1981. Isolated perfused salamander proximal tubule: II. Monovalent ion replacement and rheogenic transport.Am. J. Physiol. 241:F540-F555
Schultz, S.G. 1980. Basic principles of membrane transport.In: IUPAB Biophysics Series 1, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge-London-New York-New Rochelle-Melbourne-Sydney
Shindo, T., Spring, K.R. 1981. Chloride movement across the basolateral membrane of proximal tubule cells.J. Membrane Biol. 58:35–42
Siegenbeek van Heukelom, J. 1978. The electrical characteristics of the absorptive goldfish intestinal epithelium.Gastroent. Clin. Biol. 2:329
Siegenbeek van Heukelom, J., Van den Ham, M.D., Albus, H., Groot, J.A. 1981. Microscopical determination of the filtration permeability of the mucosal surface of the goldfish intestinal epithelium.J. Membrane Biol. 63:31–39
Smith, P.L., Welsh, M.J., Stewart, C.P., Frizzell, R.A., Orellana, S.A., Field, M. 1981. Chloride absorption by the intestine of the winter flounderPseudopleuronectes americanus: Mechanism of inhibition by reduced pH.Bull. Mount Desert Island Biol. Lab. 20:96–101
Spring, K.R., Giebisch, G. 1977. Tracer Na fluxes inNecturus proximal tubule.Am. J. Physiol. 232:F461-F470
Spring, K.R., Kimura, G. 1978. Chloride reabsorption by renal proximal tubules ofNecturus.J. Membrane Biol. 38:233–254
Turnberg, L.A., Bieberdorf, F.A., Morowski, S.G., Fordtran, J.S. 1970. Interrelationship of chloride, bicarbonate, sodium and hydrogen transport in human ileum.J. Clin. Invest. 49:557–567
Waddell, W.J., Butler, T.C. 1959. Calculation of the intracellular pH from the distribution of 5,5-dimethyl-2,4-oxazolidinedione (DMO). Application to skeletal muscle of the dog.J. Clin. Invest. 38:720–729
White, J.F. 1976. Intracellular potassium activities inAmphiuma small intestine.Am. J. Physiol. 231:1214–1219
White, J.F. 1977. Activity of chloride in absorptive cells ofAmphiuma small intestine.Am. J. Physiol. 232:E553-E559
White, J.F. 1980. Bicarbonate-dependent chloride absorption in small intestine: Ion fluxes and intracellular chloride activities.J. Membrane Biol. 53:95–107
Zeuthen, T. 1981. On the effects of amphotericin B and ouabain on the electrical potentials ofNecturus gallbladder.J. Membrane Biol. 60:167–169
Zeuthen, T., Monge, C. 1976. Electrical potentials and ion activities in the epithelial cell layer of the rabbit ileum in vivo.In: Ion and Enzyme Electrodes in Biology and Medicine. M. Kessler et al., editors. p. 345. Urban and Schwar zenberg, Munich
Zeuthen, T., Ramos, M., Ellory, J.C. 1978. Inhibition of active chloride transport by piretanide.Nature (London) 273:678–680
Zuidema, T., Dekker, K., Siegenbeek van Heukelom, J. 1985. The influence of organic counterions on junction potentials and measured membrane potentials.Bioelectrochem. Bioenerg. (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuidema, T., van Riel, J.W. & van Heukelom, J.S. Cellular and transepithelial responses of goldfish intestinal epithelium to chloride substitutions. J. Membrain Biol. 88, 293–304 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871093
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871093