Summary
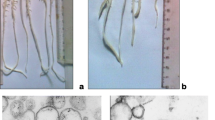
The stress and strain (surface tension and fractional change in area) in the plasma membrane of protoplasts isolated from rye leaves (Secale cereale L. cv Puma) were measured during osmotic expansions from isotonic into a range of more dilute solutions. The membrane surface tension increases rapidly to a maximum and then decreases slowly with some protoplasts lysing in all phases of the expansion. The maximum surface tension is greater for rapid expansions, and protoplasts lyse earlier during rapid expansion. Over the range of expansion rates investigated, the area at which lysis occurs is not strongly dependent on expansion rate. The value of the maximum tension is determined by the expansion rate and the rate at which new material is incorporated into the membrane. During osmotic expansion, protoplasts isolated from cold-acclimated plants incorporate material faster than do those from nonacclimated plants and thus incur lower membrane tensions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dowgert, M.F., Steponkus, P.L. 1984. Behavior of the plasma membrane of isolated protoplasts during a freeze-thaw cycle.Plant Physiol. 75:1139–1151
Evans, E.A., Skalak, R. 1979. Mechanics and thermodynamics of biomembranes. C.R.C. Press, Boca Raton
Gordon-Kamm, W.J., Steponkus, P.L. 1984. The behavior of the plasma membrane following osmotic contraction of isolated protoplasts: Implications in freezing injury.Protoplasma 123:83–94
Mitchison, J.M., Swann, M.M. 1954. The mechanical properties of the cell surface.J. Exp. Biol. 31:443–472
Steponkus, P.L., Dowgert, M.F., Ferguson, J.R., Levin, R.L. 1984. Cryomicroscopy of isolated plant protoplasts.Cryobiology. 21:209–233
Wiest, S.C., Steponkus, P.L. 1978. Freeze-thaw injury to isolated spinach protoplasts and its simulation at above-freezing temperatures.Plant Physiol. 62:599–605
Wolfe, J., Dowgert, M.F., Steponkus, P.L. 1985. Dynamics of membrane exchange of the plasma membrane and the lysis of isolated protoplasts during rapid expansions in area.J. Membrane Biol. 86:127–138
Wolfe, J., Steponkus, P.L. 1981. The stress-strain relation of the plasma membrane of isolated plant protoplasts.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 643:663–668
Wolfe, J., Steponkus, P.L. 1983. Cryobiology of isolated protoplasts: Mechanical properties of the plasma membrane.Plant Physiol. 71:276–285
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolfe, J., Dowgert, M.F. & Steponkus, P.L. Mechanical study of the deformation and rupture of the plasma membranes of protoplasts during osmotic expansions. J. Membrain Biol. 93, 63–74 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871019
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01871019