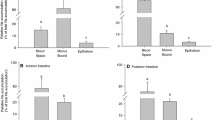
Summary
The influence of adrenal steroids on sodium transport in hen coprodeum was investigated by electrophysiological methods. Laying hens were maintained on low-NaCl diet (LS), or on high-NaCl diet (HS). HS hens were pretreated with aldosterone (128 μg/kg) or dexamethasone (1 mg/kg) before experiment. A group of LS hens received spironolactone (70 or 160 mg/kg, for three days). The effects of these dietary and hormonal manipulations on the amiloride-sensitive part of the short-circuit current were examined. This part is in excellent agreement with the net Na flux, and therefore a direct electrical measurement for Na transport. After depolarizing the basolateral membrane potential with a high K concentration, the apical Na permeability and the intracellular Na activity were investigated by currentvoltage relations for the different experimental conditions.
Plasma aldosterone concentrations (PA) were low in HS hens, dexamethasone-treated HS hens and spironolactonetreated LS hens (<70pm). In contrast LS hens and aldosteronetreated HS hens had a PA concentration of 596±70 and 583±172pm, respectively. LS diet (chronic stimulation) had the largest stimulatory effect on Na transport and apical Na permeability. Hormone-treated animals had three- to fourfold lower values. Spironolactone supply in LS hens decreased Na transport and apical Na permeability about 50%.
The results provide evidence that both mineralo- and glucocorticoids stimulate Na transport in this tissue by increasing the apical Na permeability. Quantitative differences between acute and chronic stimulation reveal a secondary slower adaptation in apical membrane properties.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnason, S.S., Rice, G.E., Chadwick, A., Skadhauge, E. 1986. Plasma levels of arginine vasotocin, prolactin, aldosterone and corticosterone during prolonged dehydration in the domestic fowl: Effect of dietary NaCl.J. Comp. Physiol. B 156:383–397
Bastl, C., Binder, H.J., Hayslett, J.P. 1980. Role of glucocorticoids and aldosterone in maintenance of colonic cation transport.Am. J. Physiol. 238:F181-F186
Binder, H.J. 1978. Effect of dexamethasone on electrolyte transport in the large intestine of the rat.Gastroenterology 75:212–217
Bindslev, N. 1979. Sodium transport in the hen lower intestine. Induction of sodium sites in the brush border by a low sodium diet.J. Physiol. (London) 288:449–466
Bindslev, N., Cuthbert, A.W., Edwardson, J.M., Skadhauge, E. 1982. Kinetics of amiloride action in the hen coprodeum in vitro.Pfluegers Arch. 392:340–347
Charney, A.N., Kinsey, M.D., Myers, L., Gianella, R.A., Gots, R.E. 1975. Na−K-activated adenosine triphosphatase and intestinal electrolyte transport—Effect of adrenal steroids.J. Clin. Invest. 56:653–660
Charney, A.N., Wallach, J., Ceccarelli, S., Donowitz, M., Costenblader, C.L. 1981. Effects of spironolactone and amiloride on corticosteroid-induced changes in colonic function.Am. J. Physiol. 241:G300-G305
Choshniak, J., Munck, B.G., Skadhauge, E. 1977. Sodium chloride transport across the chicken coprodeum. Basic characteristics and dependence on sodium intake.J. Physiol. (London) 271:489–504
Christensen, O., Bindslev, N. 1982. Fluctuation analysis of short-circuit current in a warm-blooded sodium-retaining epithelium: Site current, density, and interaction with triamterene.J. Membrane Biol. 65:19–30
Clauss, W. 1984. Circadian rhythms in Na transport.In: Intestinal Absorption and Secretion. E. Skadhauge and K. Heintze, editors. pp. 273–283. MTP Press, Lancaster
Clauss, W., Arnason, S.S., Munck, B.G., Skadhauge, E. 1984. Aldosterone-induced sodium transport in lower intestine. Effects of varying NaCl intake.Pfluegers Arch. 401:354–360
Clauss, W., Dürr, J., Rechkemmer, G. 1985a. Characterization of conductive pathways in guinea pig distal colon in vitro.Am. J. Physiol. 248:G176-G183
Clauss, W., Dürr, J., Skadhauge, E., Hörnicke, H. 1985b. Effects of aldosterone and dexamethasone on apical membrane properties and Na-transport of rabbit distal colon in vitro.Pfluegers Arch. 403:186–192
Conn, J.W., Hinerman, D.L. 1977. Spironolactone-induced inhibition of aldosterone biosynthesis in primary aldosteronism: Morphological and functional studies.Metabolism 26:1293–1307
Cuthbert, A.W., Edwardson, J.M., Bindslev, N., Skadhauge, E. 1982. Identification of potential components of the transport mechanism for Na in the hen colon and coprodeum.Pfluegers Arch. 392:347–351
DeLong, J., Civan, M.M. 1984. Apical sodium entry in split frog skin: Current-voltage relationship.J. Membrane Biol. 82:25–40
Dürr, J.E., Clauss, W. 1984. Effects of aldosterone and dexamethasone on Na-permeability in rabbit descending colon.Pfluegers Arch. 400:R28
Eldrup, E., Mollgard, K., Bindslev, N. 1980. Possible epithelial sodium channels visualized by freeze fracture.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 596:152–157
Frizzell, R.A., Schultz, S.G. 1978. Effect of aldosterone on ion transport by rabbit colon in vitro.J. Membrane Biol. 39:1–26
Frizzell, R.A., Turnheim, K. 1978. Ion transport by rabbit colon: II. Unidirectional sodium influx and the effects of amphotericin B and amiloride.J. Membrane Biol. 40:193–211
Frömter, E., Higgins, J.T., Gebler, B. 1981. Electrical properties of amphibian urinary bladder epithelia. IV. The current-voltage relationship of the sodium channels in the apical cell membrane.In: Ion Transport by Epithelia. S.G. Schultz, editor. pp. 31–45. Raven, New York
Fuchs, W., Hviid Larsen, E., Lindemann, B. 1977. Currentvoltage curve of sodium channels and concentration dependence of sodium permeability in frog skin.J. Physiol. (London) 267:137–166
Funder, J.W., Feldmann, D., Edelman, I.S. 1973. Glucocorticoid receptors in rat kidney: The binding of tritiated-dexamethasone.Endocrinology 92:1005–1013
Garcia-Diaz, J.F., Essig, A. 1985. Capacitive transients in voltage-clamped epithelia.Biophys. J. 48:519–523
Geering, K., Giradet, M., Bron, C., Kraehenbuhl, J.P., Rossier, B.C. 1982. Hormonal regulation of (Na+K+)-ATPase biosynthesis in the toad bladder. Effects of aldosterone and 3,5,3-triiodo-l-thyronine.J. Biol. Chem. 257:10338–10343
Goldmann, G.E. 1943. Potential, impedance and rectification in membranes.J. Gen. Physiol. 27:37–60
Helman, S.I., O'Neil, R.G., Fisher, R.S. 1975. Determination of theE Na of frog skin from studies of its current-voltage relationship.Am. J. Physiol. 229:947–951
Klemperer, G., Garcia-Diaz, J.F., Nagel, W., Essig, A. 1986. Basolateral membrane potential and conductance in frog skin exposed to high serosal potassium.J. Membrane Biol. 90:89–96
Lewis, S.A., Wills, N.K., Eaton, D.C. 1978. Basolateral membrane potential of a tight epithelium: Ionic diffusion and electrogenic pumps.J. Membrane Biol. 41:117–148
Li, J.H.Y., Palmer, L.G., Edelman, I.S., Lindemann, B. 1982. The role of sodium-channel density in the natriferic response of the toad urinary bladder to an antidiuretic hormone.J. Membrane Biol. 64:77–89
Marver, D. 1984. Assessment of mineralocorticoid activity in the rabbit colon.Am. J. Physiol. 246:F437-F446
Palmer, L.G. 1984. Use of potassium depolarization to study apical transport properties in epithelia.In: Current Topics in Membranes and Transport. J.B. Wade and S.A. Lewis, editors. pp. 105–121. Academic, New York
Palmer, L.G., Edelman, I.S., Lindemann, B. 1980. Current-voltage analysis of apical sodium transport in toad urinary bladder. Effects of inhibitors of transport and metabolism.J. Membrane Biol. 57:59–71
Palmer, L.G., Li, J.H.Y., Lindemann, B., Edelman, I.S. 1982. Aldosterone control of the density of sodium channels in the toad urinary bladder.J. Membrane Biol. 64:91–102
Rice, G.E., Skadhauge, E. 1982. Colonic and coprodeal transepithelial transport parameters in NaCl-loaded domestic fowl.J. Comp. Physiol. B 147:65–69
Sakauye, C., Feldman, D. 1976. Agonist and antimineralocorticoid activities of spirolactones.Am. J. Physiol. 231:93–97
Sandor, T., Skadhauge, E., DiBattista, J.A., Mehdi, A.Z. 1986. Interrelations of the intestinal glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptor systems with salt homeostasis.In: Progress in Avian Osmoregulation. M.R. Hughes and A.C. Chadwick, editors. Leeds Philosophical and Literary Soc., Leeds (in press)
Schoen, H.F., Erlij, D. 1985. Current-voltage relations of the apical and basolateral membranes of the frog skin.J. Gen. Physiol. 86:257–287
Schultz, S.G. 1979. Application of equivalent electrical circuit models to study of sodium transport across epithelial tissues.Fed. Proc. 38:2024–2029
Schultz, S.G. 1981. Homocellular regulatory mechanisms in sodium-transporting epithelia: Avoidance of extinction by “flush-through”.Am. J. Physiol. 241:F579-F590
Schultz, S.G. 1984. A cellular model for active sodium absorption by mammalian colon.Annu. Rev. Physiol. 46:435–451
Schultz, S.G., Thompson, S.M., Suzuki, Y. 1981. Equivalent electrical circuit models and the study of Na transport across epithelia: I. Nonsteady-state current-voltage relations.Fed. Proc. 40:2443–2449
Sellin, J.H., DeSoignie, R.C. 1985. Steroids alter ion transport and absorptive capacity in proximal and distal colon.Am. J. Physiol. 249:G113-G119
Skadhauge, E. 1983. Temporal adaptation and hormonal regulation of sodium transport in the avian intestine.In Intestinal Transport. M. Gilles-Baillien and R. Gilles, editors. pp. 284–294. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg
Skadhauge, E. 1984. Introduction of an epithelium with huge variation in sodium transport and novel aldosterone effects.In: Intestinal Absorption and Secretion. E. Skadhauge and K. Heintze, editors. pp. 201–208. MTP Press, Lancaster
Skadhauge, E., Clauss, W., Arnason, S.S., Thomas, D.H. 1985. Mineralocorticoid regulation of lower intestinal ion transport.In: Transport Processes, Iono- and Osmoregulation. R. Gilles and M. Gilles-Baillien, editors. pp. 118–133. Springer, Berlin
Skadhauge, E., Thomas, D.H., Chadwick, A., Jallageas, M. 1983: Time course of adaptation to low and high NaCl diets in the domestic fowl. Effects on electrolyte excretion and on plasma hormone levels (aldosterone, corticosterone and prolactin).Pfluegers Arch. 396:301–307
Tang, J., Abramcheck, F.J., Van Driessche, W., Helman, S.I. 1985. Electrophysiology and noise analysis of K-depolarized epithelia of frog skin.Am. J. Physiol. 249:C421-C429
Thomas, D.H., Jallageas, M., Munck, B.G., Skadhauge, E. 1980. Aldosterone effects on electrolyte transport of the lower intestine (coprodeum and colon) of the fowl(Gallus domesticus) in vitro.Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 40:44–51
Thomas, D.H., Skadhauge, E. 1979. Chronic aldosterone therapy and the control of transepithelial transport of ions and water by the colon and coprodeum of the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus) in vivo.J. Endocrinol. 83:239–250
Thomas, D.H., Skadhauge, E. 1982. Time course of adaption to low and high NaCl diets in the domestic fowl. Effects on electrical behaviour of isolated epithelia from the lower intestine.Pfluegers Arch. 395:165–170
Thompson, S.M., Sellin, J.H. 1986. Relationships among sodium current, permeability, and Na activities in control and glucocorticoid-stimulated rabbit descending colon.J. Membrane Biol. 92:121–134
Thompson, S.M., Suzuki, Y., Schultz, S.G. 1982. The electrophysiology of rabbit descending colon: I. Instantaneous transepithelial current-voltage relations and the current-voltage relations of the Na-entry mechanism.J. Membrane Biol. 66:41–54
Turnheim, K., Thompson, S.M., Schultz, S.G. 1983. Relation between intracellular sodium and active sodium transport in rabbit colon: Current-voltage relations of the apical sodium entry mechanisms in the presence of varying luminal sodium concentrations.J. Membrane Biol. 76:299–309
Will, P.C., DeLisle, R.C., Cortright, R.N., Hopfer, U. 1981. Induction of amiloride-sensitive sodium transport in the intestines by adrenal steroids.Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 372:64–78
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clauss, W., Dürr, J.E., Guth, D. et al. Effects of adrenal steroids on Na transport in the lower intestine (Coprodeum) of the hen. J. Membrain Biol. 96, 141–152 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869240
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869240