Summary
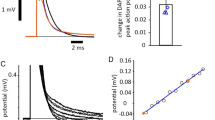
Ultraviolet radiation irreversibly reduces the sodium permeability in nerve membranes and, in addition, induces a change of the potential dependence of the kinetic parameters of sodium inactivation in the node of Ranvier. This second ultraviolet effect shifts the kinetic parameters of sodium inactivationh ∞(V),α h andβ h (V) to more negative potentials (no changes of the slopes of the curves). The amount of the displacement ‡V along the potential axis is equal for the three parameters and depends on the ultraviolet dose. It is about ‡V=−10 mV after an irradiation dose of 0.7 Ws/cm2 at 280 nm. Both ultraviolet-induced effects depend on membrane potential and on the wavelength of the applied radiation. But while the potential shift is enhanced at more negative holding potentials, the ultraviolet blocking is diminished andvice versa. Further, the ultraviolet-induced potential shift is greater at 260 nm than at 280 nm, whereas a maximum sensitivity of ultraviolet blocking is found at 280 nm. Therefore, the two radiation effects are the result of two separate photoreactions. For explanation of the radiation-induced potential shift it is assumed that ultraviolet radiation decreases the density of negative charges at the inner surface of the nodal membrane. From this hypothesis a value for the inner surface potentialψ i was derived. -19 mV≦ψ i ≦-14 mV.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandler, W.K., Hodkin, A.L., Meves, H. 1965. The effect of changing the internal solution on sodium inactivation and related phenomena in giant axons.J. Physiol. (London) 180:821.
Drouin, H., Neumcke, B. 1975. Specific and unspecific charges at the sodium channels of the nerve membrane.Pfluegers Arch. 351:207
Fox, J.M. 1974a. Selective blocking of the nodal sodium channels by ultraviolet radiation. I. Phenomenology of the radiation effect.Pfluegers Arch. 351:287
Fox, J.M. 1974b. Selective blocking of the nodal sodium channels by ultraviolet radiation. II. The interaction of Ca++, H+, and membrane potential.Pfluegers Arch. 351:303
Fox, J.M. 1976a. Ultra-slow inactivation of the ionic currents through the membrane of myelinated nerve.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 426:232
Fox, J.M. 1976b. Investigation of the relation between structure and function in myelinated nerve fibres with aid of ultraviolet radiation.Biophys. Struct. Mechanism 2:1
Fox, J.M., Duppel, W. 1975. The action of thiamine and its di- and triphosphates on the slow exponential decline of the ionic currents in the node of Ranvier.Brain Res. 89:287
Fox, J.M., Stämpfli, R. 1971. Modification of ionic membrane currents of Ranvier nodes by UV-radiation under voltage clamp conditions.Experientia 27:1289
Frankenhaeuser, B. 1960. Quantitative description of sodium currents in myelinated nerve fibres ofXenopus laevis.J. Physiol. (London) 151:491
Frankenhaeuser, B., Huxley, F.A. 1964. The action potential in the myelinated nerve fibres ofXenopus laevis as computed on the basis of voltage clamp data.J. Physiol. (London) 171:302
Gilbert, D. L., Ehrenstein, G. 1969. Effect of divalent cations on potassium conductance of squid axons: Determination of surface charge.Biophys. J. 9:447
Hille, B. 1967. The selective inhibition of delayed potassium currents in nerve by tetraethylammonium ions.J. Gen. Physiol. 50:1287.
Nathan, R.D., Pooler, J.P., DeHaan, R.L. 1976. Ultraviolet-induced alternations of beat rate and electrical properties of embryonic chick heart cell aggregates.J. Gen. Physiol. 67:27.
Neumcke, B., Fox, J.M., Drouin, H., Schwarz, W. 1976. Kinetics of slow variation of peak sodium current in the membrane of myelinated nerve following changes of holding potential or extracellular pH.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 426:245.
Nonner, W. 1969. A new voltage clamp method for Ranvier nodes.Pfluegers Arch. 309:176
Oxford, G.S., Pooler, J.P. 1975. Ultraviolet photoalteration of ion channels in voltageclamped lobster giant axons.J. Membrane Biol. 20:13
Schwarz, W. 1975a. The effect of ultraviolet radiation on the sodium inactivation of myelinated nerve fibres.Pfluegers Arch. 355:R68
Schwarz, W. 1975b. Einfluss ultravioletter Strahlung auf die Inaktivierung des Na-Systems myelinierter Nervenfasern. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Saar, Saarbrücken, Faculty of Science
Stämpfli, R. 1969. Laboratory Techniques in Membrane Biophysics. H. Passow and R. Stämpfli, editors. Springer Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft; Sonderforschungsbereich 38, Membranforschung.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwarz, W., Fox, J.M. Ultraviolet-induced alterations of the sodium inactivation in myelinated nerve fibers. J. Membrain Biol. 36, 297–310 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868156
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01868156