Abstract
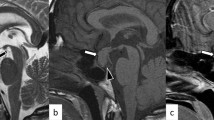
Pineal gland glucose utilization (GU) and capillary permeability (CP) were measured in unanesthetized rats, using complementary quantitative autoradiographic techniques. GU values within the pineal tissue were homogeneously distributed around 70 μmol of glucose/100 g each min, i.e., they were approximately 30% lower than in the cortical gray structures. The blood-to-brain transfer constant of [14C]-α-aminoisobutyric acid, as an index of CP, was up to ten orders of magnitude higher than that for the rest of the brain. These measurements were carried out at that point in the circadian rhythm that corresponds to the minimum level of neurosecretory activity of the pineal gland.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blasberg RG, Fenstermacher JD, Patlak CS (1983) Transport of α-aminoisobutyric acid across brain capillary and cellular membranes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 3:8–32
d'Avella D, Cicciarello R, La Torre F, Princi P, Greenberg RP, d'Aquino S, Caputi AP (1984) The effect of the calcium-antagonist nimodipine upon local cerebral glucose utilization in the rat brain. Life Sci 34:2583–2588
Goochee C, Rasband W, Sokoloff L (1980) Computerized densitometry and color coding of [14C] deoxyglucose autoradiographs. Ann Neurol 7:359–370
Ito M, Kadekaro M, Sokoloff L (1988) Local glucose utilization of the brain and pineal gland during stimulation of the cervical sympathetic trunk. J Pineal Res 5:51–62
Ohno K, Pettigrew KD, Rapoport SI (1978) Lower limits of cerebrovascular permeability to nonelectrolytes in the conscious rat. Am J Physiol 235:H299-H307
Sokoloff L, Reivich M, Kennedy C, Des Rosiers MH, Patlak CS, Pettigrew KD, Sakurada O, Shinohara M (1977) The [14C]-deoxyglucose method for the measurement of local cerebral glucose utilization: theory, procedure, and normal values in the conscious and anesthetized albino rat. J Neurochem 28:897–916
Tyson GW, Teasdale GM, Graham DI, McCulloch J (1982) Cerebrovascular permeability following MCA occlusion in the rat. The effect of halothane-induced hypotension. J Neurosurg 57:186–196
Vollrath L (1981) The pineal organ. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cicciarello, R., d'Avella, D., De Blasi, F. et al. Autoradiographic assessment of pineal gland glucose utilization and capillary permeability in the unanesthetized rat. Child's Nerv Syst 6, 222–224 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01850978
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01850978