Summary
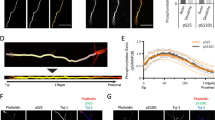
Highly cationic polyethyleneimine was used as an electron microscopic tracer for anionic sites in the axoplasm of rat sciatic and optic nerve fibres. Microtubules showed a markedly increased electron density and aggregated to form large groups, mostly located in the immediate proximity of membranous axoplasmic organelles. Walls of adjacent microtubules were fused; there was also fusion of microtubules with the membranes of smooth axoplasmic reticulum and with axolemma. In contrast, neurofilaments had unaltered electron density and axoplasmic distribution. Staining and clustering of microtubules were interpreted as electrostatic binding of cationic polyethyleneimine to acidic tubulin. These findings may be relevant to the role of microtubules in fast axonal transport.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behnke, O. (1975) An outer component of microtubules.Nature 257, 709–10.
Burton, P. R. (1981) Polymorphic assemblies of tubulin. InCell and Muscle Motility, Vol. 1 (edited byDowben, R. M. &Shay, J. W.), pp. 289–333. New York, London: Plenum Press.
Ishikawa, H., Tsukita, S. &Tsukita, S. (1982) Association of the cytoskeleton with cell membranes — a concept of plasmalemmal undercoat. InBiological Functions of Microtubules and Related Structures (edited bySakai, H., Mohri, H. &Borisy, G. G.), pp. 377–89. Tokyo, New York: Academic Press.
Jacobs, M., Bennett, P. M. &Dickens, M. J. (1975) Duplex microtubule is a new form of tubulin assembly induced by polycations.Nature 257, 707–9.
Jordan, M. A., Margolis, R. L., Himes, R. H. &Wilson, L. (1986) Identification of a distinct class of vinblastine binding sites on microtubules.Journal of Molecular Biology 187, 61–73.
Kim, H., Binder, L. I. &Rosenbaum, J. L. (1979) The periodic association of MAP2 with brain microtubules in vitro.Journal of Cell Biology 80, 266–76.
Olmsted, J. B., Marcum, J. M., Johnson, K. A., Allen, C. &Borisy, G. G. (1974) Microtubule assembly: some possible regulatory mechanisms.Journal of Supramolecular Structure 2, 429–50.
Pachter, J. S., Liem, R. K. H. &Shelanski, M. L. (1984) The neuronal cytoskeleton.Advances in Cellular Neurobiology 5, 113–42.
Reale, E., Luciano, L. &Kühn, K.-W. (1983) Ultrastructural architecture of proteoglycans in the glomerular basement membrane.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 31, 662–8.
Schlaepfer, W. W. (1971) Vincristine-induced axonal alterations in rat peripheral nerve.Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 30, 488–505.
Schnapp, B. J. &Reese, T. S. (1982) Cytoplasmic structure in rapid-frozen axons.Journal of Cell Biology 94, 667–9.
Schurer, J. W., Hoedemaeker, P. J. &Molenaar, I. (1977) Polyethyleneimine as tracer particle for (immuno) electron microscopy.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 25, 384–7.
Schurer, J. W., Kalicharan, D., Hoedemaeker, P. J. &Molenaar, I. (1978) The use of polyethyleneimine for demonstration of anionic sites in basement membranes and collagen fibrils.Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 26, 688–9.
Sloboda, R. D. &Rosenbaum, J. L. (1979) Decoration and stabilization of intact, smooth-walled microtubules with microtubule associated proteins.Biochemistry 18, 48–55.
Suzuki, Y., Maesawa, A., Matsui, K., Oite, T., Koda, Y. &Arakawa, M. (1983) Alteration of glomerular anionic sites by the development of subepithelial deposits in experimental glomerulonephritis in the rat.Virchows Archiv, B. Cell Pathology 44, 209–22.
Suzuki, Y., Maruyama, Y., Arakawa, M. &Oite, T. (1984) Preservation of fixed anionic sites in the GBM in the acute proteinuric phase of cationic antigen mediated in-situ immune complex glomerulonephritis in the rat.Histochemistry 81, 243–6.
Wilson, L., Bryan, J., Ruby, A. &Mazia, D. (1970) Precipitation of proteins by vinblastine and calcium ions.Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences USA 66, 807–14.
Wilson, L., Morse, A., Jordan, M. A. &Margolis, R. L. (1982) Interaction of vinblastine with steady-state microtubules in vitro: mechanism of inhibition of net tubulin addition to assembly ends. InBiological Functions of Microtubules and Related Structures (edited bySakai, H., Mohri, H. &Borisy, G. G.), pp. 61–72. Tokyo, New York: Academic Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scheidt, P., Friede, R.L. Axonal microtubules are stained and cross-linked by highly cationic polyethyleneimine. J Neurocytol 16, 215–220 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01795305
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01795305