Summary
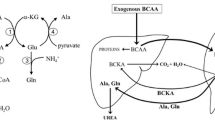
Studies in anorectic tumor-bearing rats indicate that anorexia is correlated to imbalances of neutral amino acids in blood and CNS. Consequently plasma amino acids of patients with neoplastic and non-neoplastic internal diseases were studied during phases of anorexia; special regard was given to the precursors of dopamine and serotonin. Anorectic patients were compared to non-anorectic patients with neoplasia. During anorexia, plasma levels of valine and leucine and hence the ratio of the molar concentrations of Val+Leu+Ile/Phe+Tyr were significantly decreased in each anorectic patient as compared to non-anorectic patients whose ratios were always within the normal ranges. As aromatic and branched-chain amino acids compete for penetration of the blood brain barrier, the decrease of the amino acid ratio may induce a raised flux of phenylalanine and tyrosine into the CNS which results in an increased activation of dopaminergic neurons — known to cause anorexia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AS:
-
Aminosäuren
- CML:
-
Chronisch-myeloische Leukämie
- Ile:
-
Isoleucin
- Leu:
-
Leucin
- m:
-
männlich
- M:
-
Median
- Phe:
-
Phenylalanin
- Tyr:
-
Tyrosin
- Val:
-
Valin
- VZK:
-
Verzweigtkettige Aminosäuren
- w:
-
weiblich
Literatur
Barry VC, Klawans HL (1976) On the role of dopamine in the pathophysiology of anorexia nervosa. J Neur Transm 38:107–122
Carruba MO, Ricciardi S, Müller EE, Mantegazza P (1980) Anorectic effect of lisuride and other ergot derivates in the rat. Eur J Pharmac 64:133–141
Fernstrom JD, Wurtman RJ (1972) Brain serotonin content: physiological regulation by plasma neutral amino acids. Science 178:414–416
Fernstrom JD, Faller DV (1978) Neutral amino acids in the brain: changes in response to food ingestion. J Neurochem 30:1531–1538
Fernstrom JD, Wurtman RJ, Hammarstrom-Wiklund B, Rand WM, Munro HN, Davidson CS (1979) Diurnal variations in plasma concentrations of tryptophan, tyrosine and other neutral amino acids: effect of dietary protein intake. Am J Clin Nutr 32:1912–1922
Fischer JE, Funovics JM, Aguirre A, James JH, Keane JM, Wesdorp RIC, Yoshimura N, Westman T (1975) The role of plasma amino acids in hepatic encephalopathy. Surgery 78:276–290
Fürst P, Bergström J, Hellström B, Vinnars E, Herfarth Ch, Klippel C, Merkel N, Schultis K, Elwyn D, Hardy M, Kinney J (1981) Amino acid metabolism in cancer. In: Kluthe R, Löhr GW (Hrsg) Nutrition and metabolism in cancer. International Workshop, Freiburg 1979. Thieme, Stuttgart New York, S 75–88
Grünert A, Engels J, Seewald U, Dölp R, Ahnefeld FW (1984) Untersuchungen zur parenteralen Applikation von Aminosäuren. Referenzbereich-Untersuchungstechnik-Interpretation der Untersuchungsergebnisse-Aminosäurenmuster als Kriterium der Regulation der Homöostase. Infusionstherapie 11:12–25
Gudelsky GA, Moore KE (1976) Differential drug effects on dopamine concentrations and rates of turnover in the median eminence, olfactory tubercle and corpus striatum. J Neural Transm 38:95–105
Iyer GYN (1959) Free amino acids in leukocytes from normal and leukemic subjects. J Lab Clin Med 54:229–231
Kelley JJ, Waisman HA (1957) Quantitative plasma amino acid values in leukemic blood. Blood 12:635–643
Krause R, James JH, Ziparo V, Fischer JE (1979) Brain tryptophan and the neoplastic anorexia-cachexia syndrome. Cancer 44:1003–1008
Kruk ZL (1973) Dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine inhibit feeding in rates. Nature NB 246:52–53
von Meyenfeldt M, Chance WT, Fischer JE (1982) Correlation of changes in brain indoleamine metabolism with onset of anorexia in rats. Am J Surg 143:133–138
Ollenschläger G (1982) Zur Pathogenese und Therapie der Malnutrition in der Onkologie. Z Ernährungswiss 21:124–145
Pardridge WM (1977) Kinetics of competitive inhibition of neutral amino acid transport across the blood brain barrier. J Neurochem 28:103–108
Riederer P (1980) The distribution and metabolism of 1-tryptophan in healthy probands under dietary conditions. Intern J Clin Pharmac Ther Tox 18:31–36
Riederer P, Kienzl E, Jellinger K, Kleinberger G (1983) Branched chain amino acids in hepatic failure: effects on brain function. In: Kleinberger G, Deutsch E (Eds) New Aspects of Clinical Nutrition. S. Karger, Basel München, pp 505–515
Rössle M, Herz R, Luft M, Gerok W (1981) Therapie des Coma hepaticum: Einfluß einer adaptierten Aminosäurenlösung auf die Serum- und Liquorkonzentrationen von Aminosäuren und Ammoniak. Z Gastroenterologie 29:494–495
Sachs L (1974) Angewandte Statistik. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Sanghvi IS, Singer G, Friedman E, Gershon S (1975) Anorexigenic effects of d-amphetamine and l-dopa in the rat. Pharmac Biochem Beh 3:81–86
Scally MC, Ulus I, Wurtman RJ (1977) Brain tyrosine level controls striatal dopamine synthesis in haloperidol-treated rats. J Neural Transm 41:1–6
Wurtman RJ, Larin F, Mostafapour S, Fernstrom JD (1974) Brain catechol synthesis: Control by brain tyrosine concentration. Science 185:183–184
Zakaria M, Brown PR, Farnes MP, Barker BE (1982) HPLC analysis of aromatic amino acids, nucleosides and bases in plasma of acute lymphocytic leukemics on chemotherapy. Clin Chim Acta 126:69–80
Ollenschläger G, Lang R, Schindler J (1984) Zur Pathogenese von Übelkeit und Erbrechen bei zytostatischer Therapie. Infusionstherapie 11:73–74
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Herrn Prof. Dr. W. Kaufmann zur Vollendung des 60. Lebensjahres gewidmet
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ollenschläger, G., Lang, R., Fekl, W. et al. Imbalanzen neutraler Plasma-Aminosäuren als pathogenetischer Faktor der Anorexie. Klin Wochenschr 62, 1102–1107 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01782466
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01782466