Summary
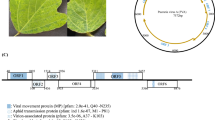
Complementary DNA representing 2 108 nucleotides at the 3′ end of the genomic RNA of the whitefly-transmitted sweetpotato mild mottle virus (SPMMV) was cloned after PCR. Sequence analysis revealed an open reading frame of 1 797 nucleotides which codes for a protein of 599 amino acids, followed by a 3′ non-coding region of 311 nucleotides. Alignment of the deduced amino acid sequence with corresponding sequences of other members of thePotyviridae demonstrated that part of the presumptive RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and the coat protein coding regions of SPMMV are found at the 3′ end of its genome, in that order. Alignment of the amino acid sequence of the core of SPMMV coat protein with those of selected members of thePotyviridae showed limited identity, thus demonstrating — with phylogenetic analysis — that SPMMV belongs to a distinct genus of the familyPotyviridae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison RF, Johnston RE, Dougherty WG (1986) The nucleotide sequence of the coding region of tobacco etch virus genomic RNA: evidence for the synthesis of a single polyprotein. Virology 154: 9–20
Brunt AA (1992) The general properties of potyviruses. In: Barnett OW (ed) Potyvirus taxonomy. Springer, Wien New York, pp 3–16 (Arch Virol [Suppl] 5)
Chirgwin J, Przybila A, MacDonald R, Rutter W (1979) Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry 18: 5294–5299
Colinet D, Kummert J (1993) Identification of a sweetpotato feathery mottle virus isolate from China (SPFMV-CH) by the polymerase chain reaction with degenerate primers. J Virol Methods 45: 149–159
Colinet D, Kummert J, Lepoivre P, Semal J (1994) Identification of distinct potyviruses in mixedly-infected sweetpotato by the polymerase chain reaction with degenerate primers. Phytopathology 84: 65–69
Domier LL, Franklin KM, Shahabuddin M, Hellman GM, Overmeyer JH, Hiremath ST, Siaw MEE, Lomonossoff GP, Shaw JG, Rhoads E (1986) The nucleotide sequence of tobacco vein mottling virus. Nucleic Acids Res 14: 5417–5430
Domier LL, Shaw JG, Rhoads RE (1987) Potyviral proteins share amino acid sequence homology with picorna-, como-, and caulimoviral proteins. Virology 158: 20–27
Frohman MA (1990) RACE: Rapid amplification of cDNA ends. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: A guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 28–38
Gough KH, Shukla DD (1993) The nucleotide sequence of Johnsongrass mosaic virus genomic RNA. Intervirology 136: 181–192
Higgins D, Sharp P (1989) Fast and sensitive multiple sequence alignments on a microcomputer. CABIOS 5: 151–153
Higgins D, Bleasly A, Fuchs R (1991) Clustal V: improved software for multiple sequence alignment. CABIOS 8: 189–191
Hollings M, Stone OM, Bock KR (1976) Purification and properties of sweetpotato mild mottle, a whitefly-borne virus from sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas) in East Africa. Ann Appl Biol 82: 511–528
Jayaram C, Hill JH, Miller WA (1992) Complete nucleotide sequences of two soybean mosaic virus strains differentiated by response of soybean containing the Rsv resistance gene. J Gen Virol 73: 2067–2077
Johansen E, Rasmussen OF, Heide M, Borkhardt B (1991) The complete nucleotide sequence of pea seed-borne mosaic virus RNA. J Gen Virol 72: 2625–2632
Kashiwazaki S, Minobe Y, Minobe T, Hibino H (1990) Nucleotide sequence of barley yellow mosaic virus RNA 1: a close evolutionary relationship with potyviruses. J Gen Virol 71: 2781–2790
Koonin EV (1991) The phylogeny of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases of positive-strand RNA viruses. J Gen Virol 72: 2197–2206
Langeveld SA, Dore JM, Memelink J, Derks AFLM, Vandervlugt CIM, Asjes CJ, Bol JF (1991) Identification of potyviruses using the polymerases chain reaction with degenerate primers. J Gen Virol 72: 1531–1541
Lain S, Riechmann JL, Garcia JA (1989) The complete nucleotide sequence of plum pox potyvirus RNA. Virus Res 13: 157–172
Moyer JW, Salazar LF (1989) Virus and virus-like diseases of sweetpotato. Plant Dis 73: 451–455
Niblett CL, Zagula KR, Calvert LA, Kendall TL, Stark DM, Smith CE, Beachy RN, Lommel SA (1991) cDNA cloning and nucleotide sequence of the wheat streak mosaic virus capsid protein gene. J Gen Virol 72: 499–504
Nicolas O, LaLiberté JF (1991) The use of PCR for cloning of large cDNA fragments of turnip mosaic potyvirus. J Virol Methods 32: 57–66
Nicolas O, LaLiberté JF (1992) The complete nucleotide sequence of turnip mosaic potyvirus RNA. J Gen Virol 73: 2785–2793
Pappu SS, Brand R, Pappu HR, Rybicki EP, Gough KH, Frenkel MJ, Niblett CL (1993) A polymerase chain reaction method adapted for selective amplification and cloning of 3′ sequences of potyviral genomes: application to desheen mosaic virus. J Virol Methods 41: 9–20
Poch O, Sauvaget I, Delarue M, Tordo N (1989) Identification of four conserved motifs among the RNA-dependent polymerase encoding elements. EMBO J 8: 3867–3874
Riechmann JS, Lain S, Garcia JA (1992) Highlights and prospects of potyvirus molecular biology. J Gen Virol 73: 1–16
Robaglia C, Durand-Tardif M, Tronchet M, Boudazin G, Astier-Manifacier S, Casse-Delbart F (1989) Nucleotide sequence of potato virus Y (N strain) genomic RNA. J Gen Virol 70: 935–947
Rybicki E, Shukla DD (1992) Coat protein phylogeny and systematics of potyviruses. In: Barnett OW (ed) Potyvirus taxomomy. Springer, Wien New York, pp 139–170 (Arch Virol [Suppl] 5)
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York
Shukla DD, Ward CW (1989a) Possible members of the potyvirus group transmitted by mites or whiteflies share epitopes with aphid-transmitted definitive members of the group. Arch Virol 105: 143–151
Shukla DD, Ward CW (1989b) Identification and classification of potyviruses on the basis of coat protein sequence data and serology. Arch Virol 106: 171–200
Shukla DD, Ward CW, Brunt AA (1994) The Potyviridae. CAB International, Wallingford
Ward CW, Shukla DD (1991) Taxonomy of potyviruses: current problems and some solutions. Intervirology 32: 269–296
Ward CW, McKern NM, Frenkel MJ, Shukla DD (1992) Sequence data as the major criterion for potyvirus classification. In: Barnett OW (ed) Potyvirus taxonomy. Springer, Wien New York, pp 283–297 (Arch Virol [Suppl] 5)
Yeh SD, Jan FJ, Chian CH, Doong TJ, Chen MC, Chung PH, Bau HJ (1992) Complete nucleotide sequence and genetic organisation of papaya ringspot virus RNA. J Gen Virol 73: 2531–2541
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colinet, D., Kummert, J. & Lepoivre, P. Molecular evidence that the whitefly-transmitted sweetpotato mild mottle virus belongs to a distinct genus of thePotyviridae . Archives of Virology 141, 125–135 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01718593
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01718593